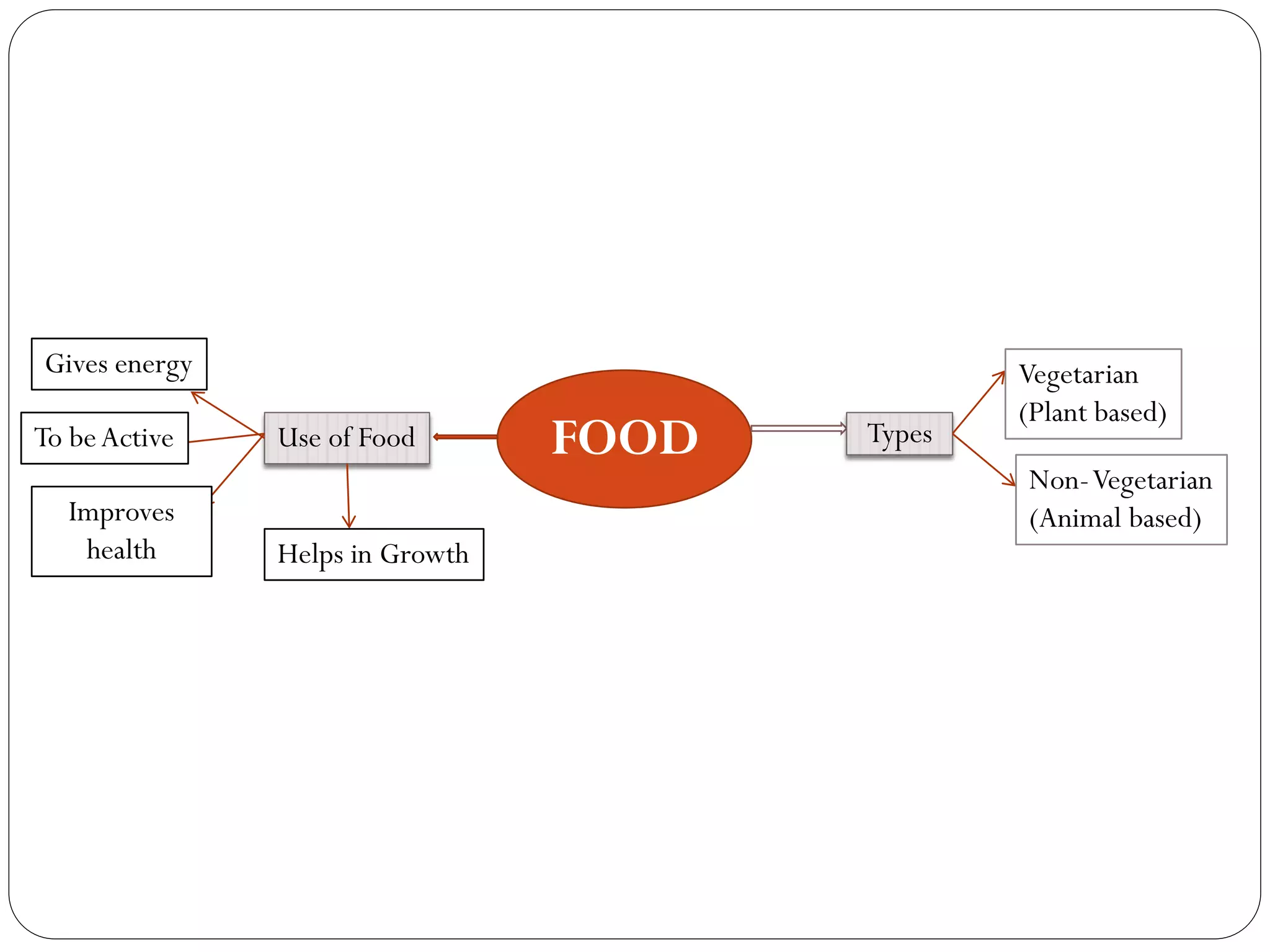
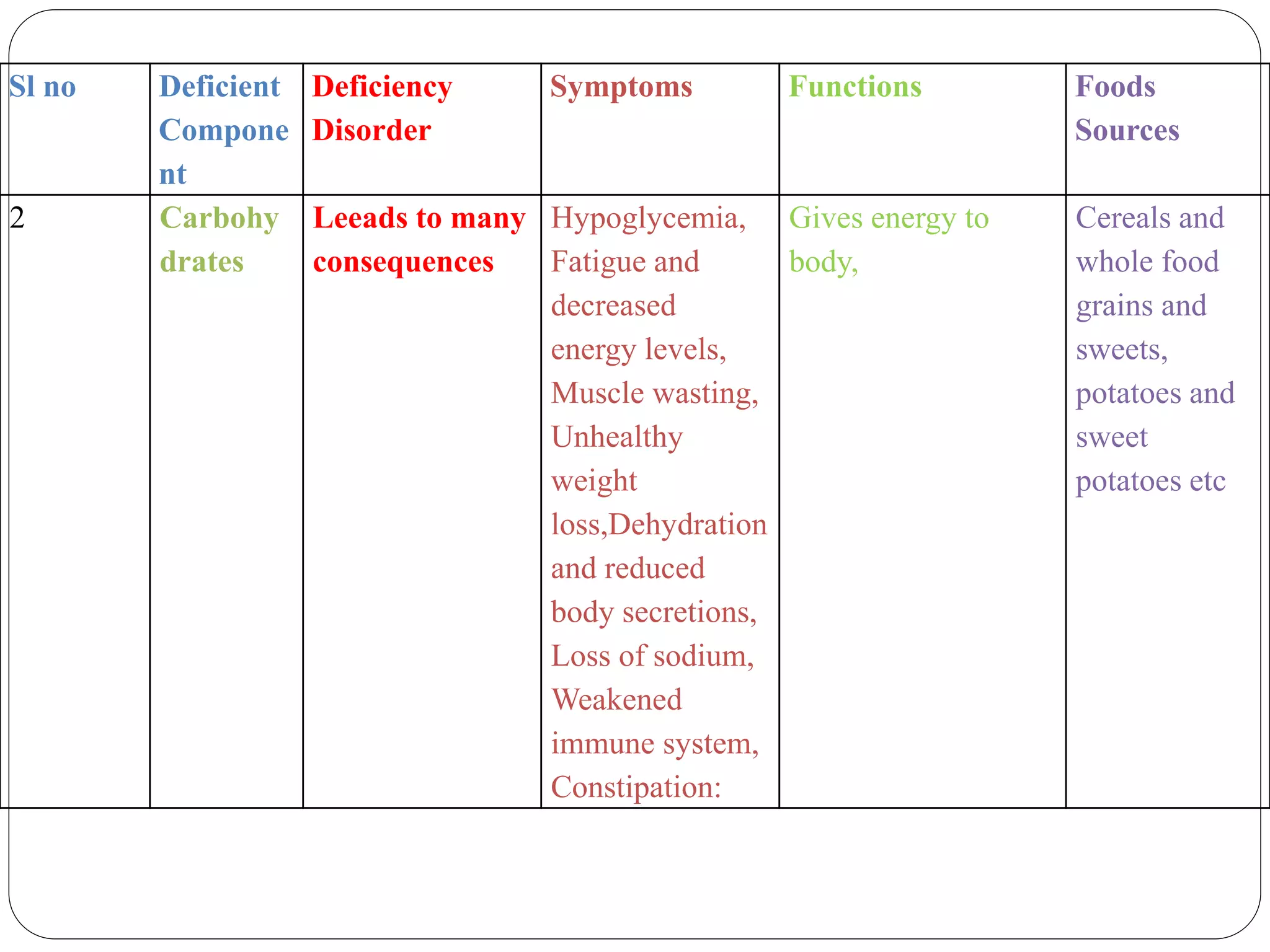
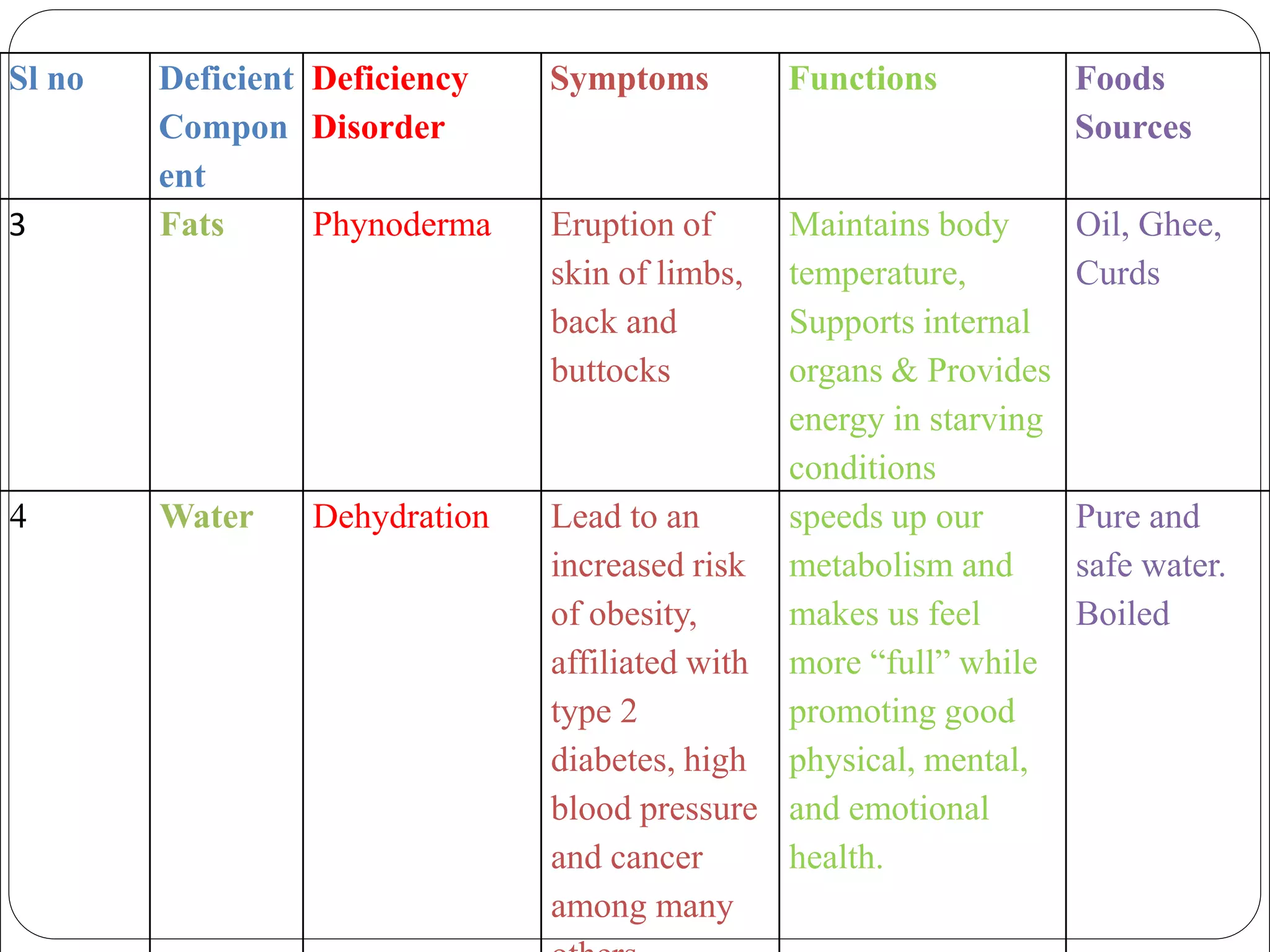
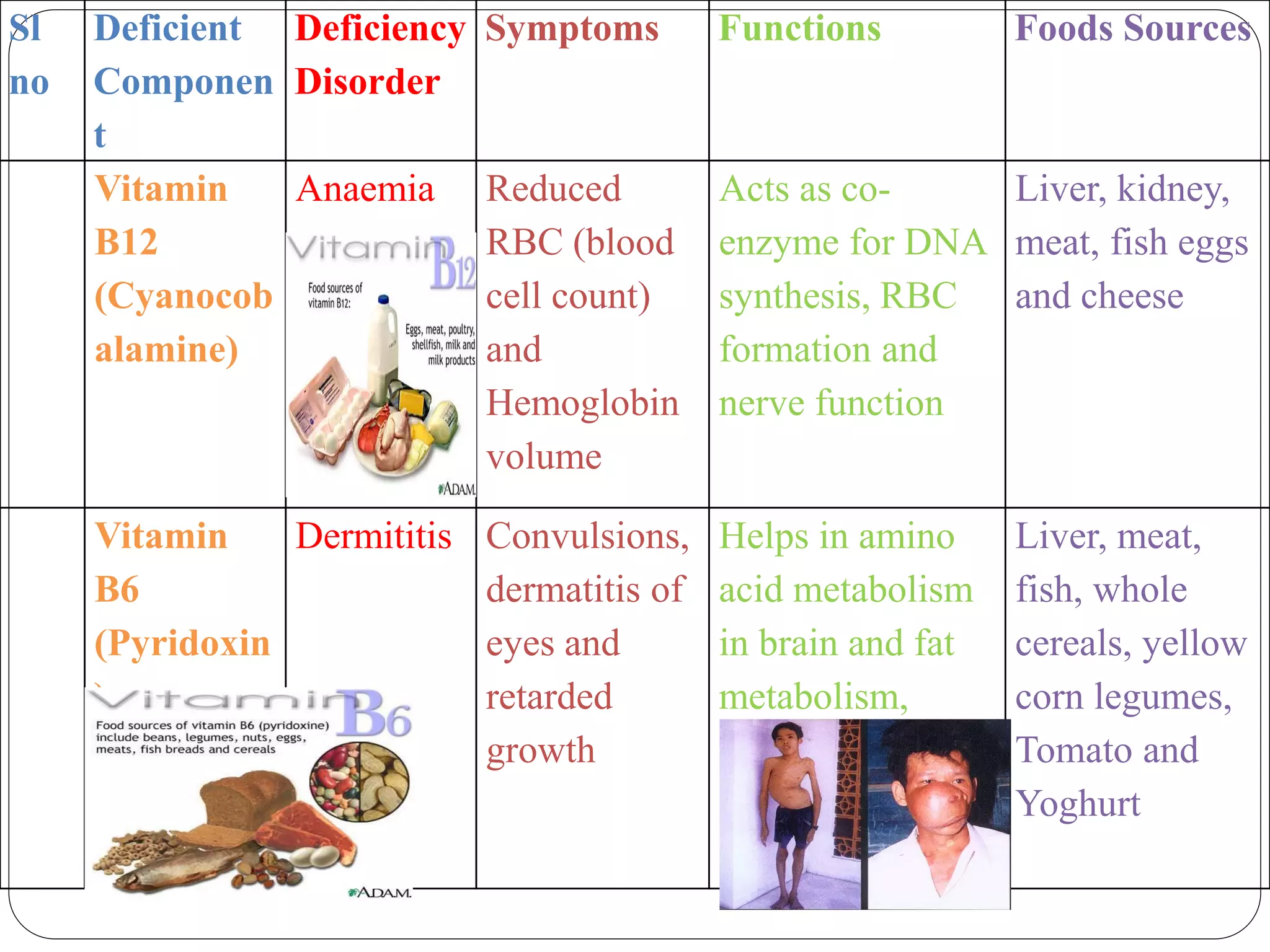
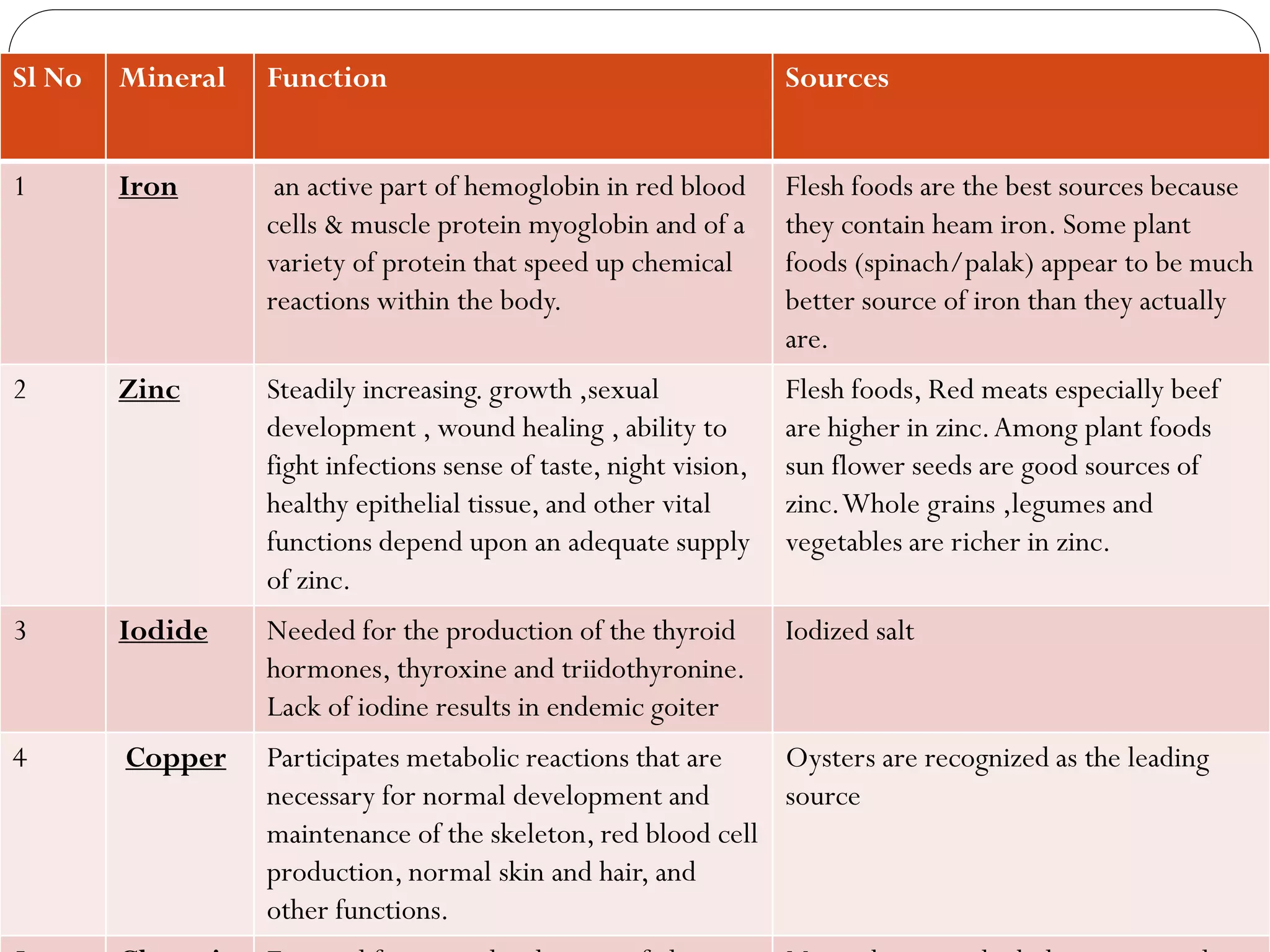
This document discusses food and nutrition. It defines food and explains that food provides energy, supports growth and repair of tissues, and provides nutrients like carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, vitamins, minerals, water and roughage. It lists common food sources for each nutrient constituent. The document also discusses nutritional disorders that can result from deficiencies of specific nutrients, such as protein deficiency disorders like kwashiorkor and marasmus, and vitamin and mineral deficiency disorders and their associated symptoms.