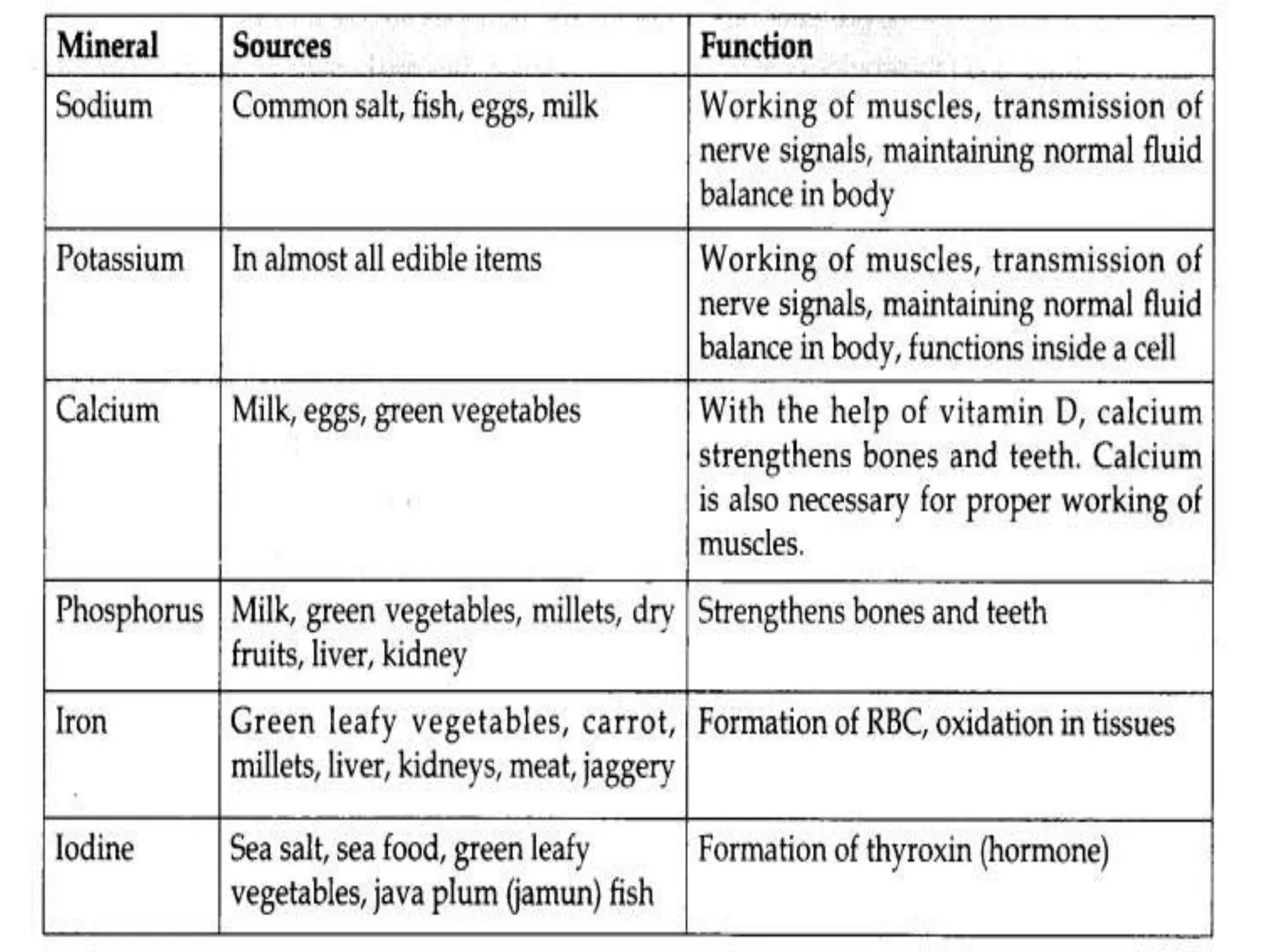
This document discusses the components of food, including nutrients like carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, dietary fibers, and water. It describes the functions of each nutrient and provides tests to identify their presence in foods. A balanced diet containing adequate amounts of all nutrients is important for good health and preventing deficiency diseases and malnutrition, which can result from a lack of certain nutrients. Common deficiency diseases include scurvy, goitre, and anemia. Protein-energy malnutrition can manifest as kwashiorkor or marasmus in severe cases.