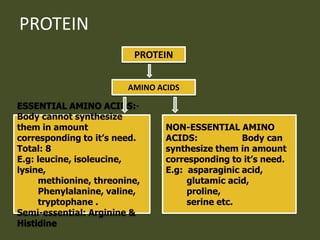
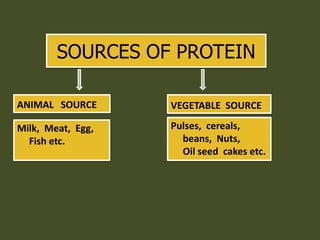
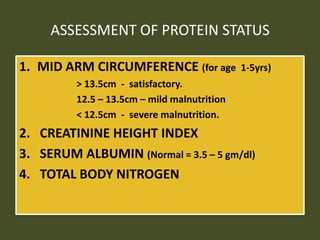
This document discusses nutrition, dietetics, and protein. It defines nutrition as the science of food and its relationship to health. Dietetics is defined as the practical application of nutritional principles, including meal planning for healthy and sick individuals. The document then classifies foods by origin (animal or vegetable), chemical composition (proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals), and predominant function (body building, energy giving, protective). Several pages are devoted to discussing protein in detail, including essential and non-essential amino acids, sources of protein, and assessing the nutritive value of proteins. The protein requirement for different groups is also outlined.