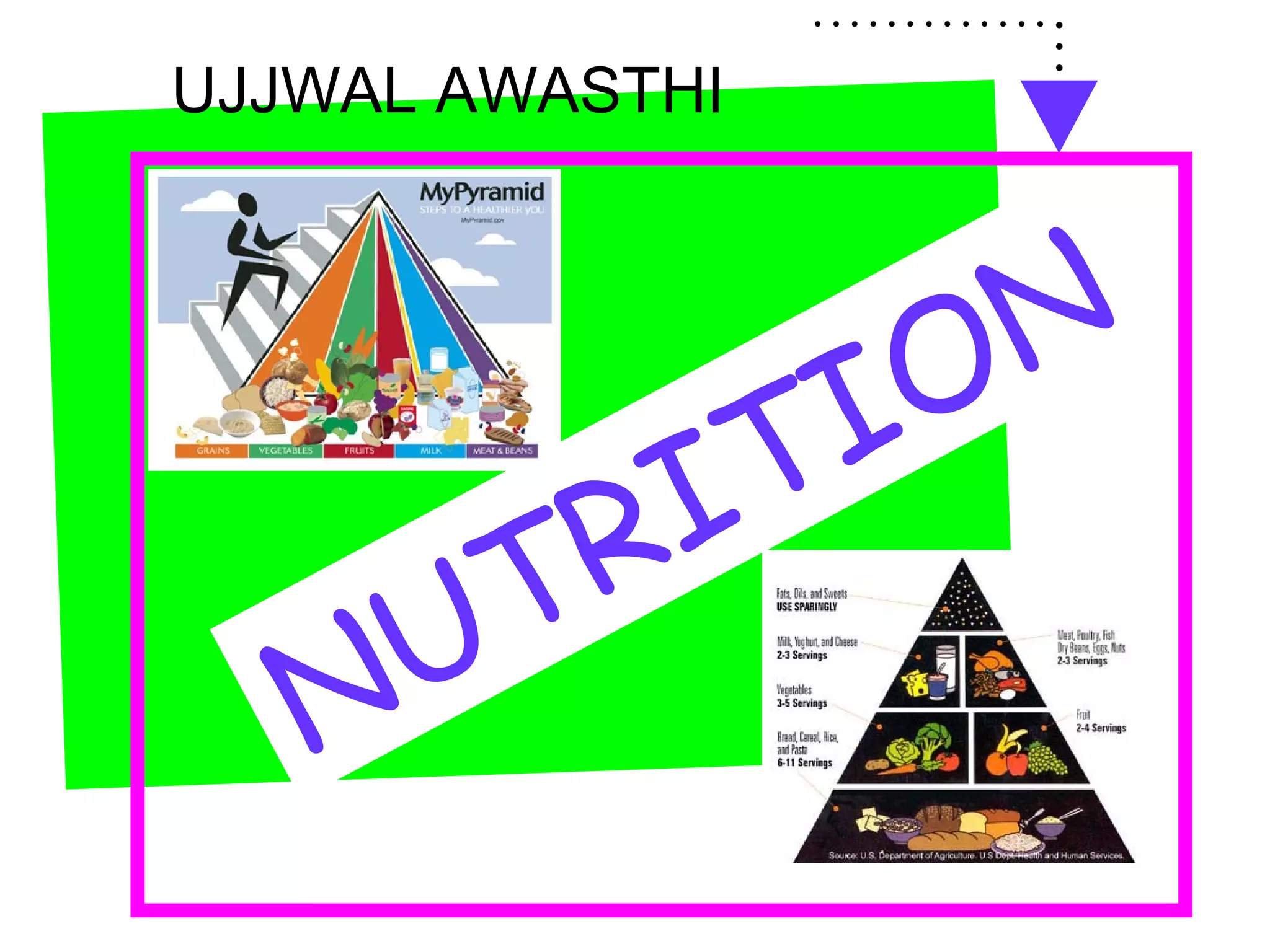
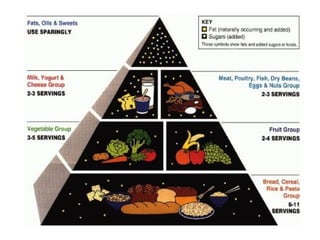
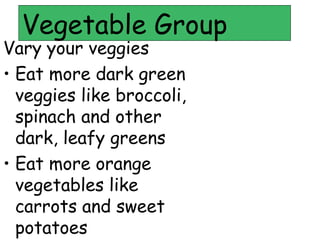
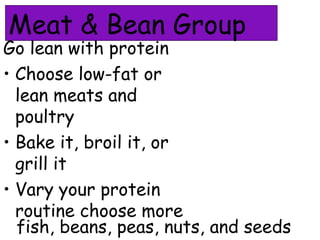
This document provides information on nutrition and healthy eating. It discusses the major food groups and recommends eating a variety of whole grains, vegetables, fruits, dairy, protein foods, and healthy fats. It also covers nutrients like carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins and minerals. Physical activity is recommended as part of a healthy lifestyle. Potential health issues like obesity, eating disorders, and "fad diets" are also addressed.