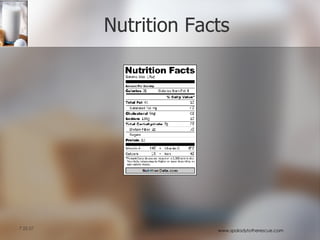
The document discusses the importance of nutrition and how food choices impact health, including the distinction between hunger and appetite. It highlights factors that influence eating behavior, obesity statistics, and dietary guidelines for healthy eating. The presentation emphasizes the significance of understanding serving sizes, nutrient quality, and the need for moderation in diet.




































![Thank you for your time. I have enjoyed meeting with you today. Charlotte R. Williams, MAEd, CHES [email_address] “ Providing timely solutions for Community Health needs” Nutrition 101 Are your food choices making the grade?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nutrition-101-120019803738304-5/85/Nutrition-101-39-320.jpg)