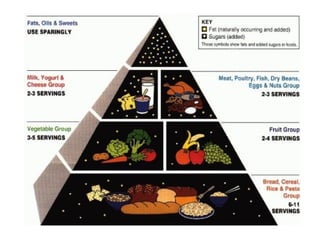
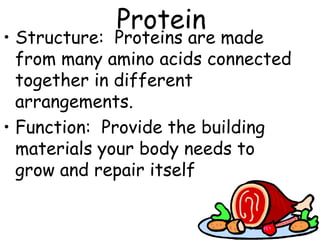
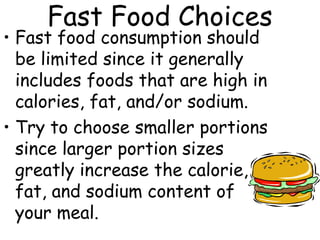
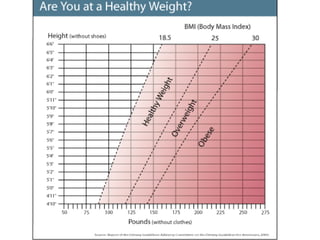
Here are some healthier options for fast food:
- Quarter Pounder with Cheese (hold mayo) and small fries instead of large. Water instead of soda.
- Subway 6-inch turkey sub on wheat bread with lettuce, tomato, onion. Water or unsweetened iced tea.
- Wendy's Jr. Bacon Cheeseburger (hold mayo), side salad with light dressing instead of fries. Water.
- Taco Bell Fresco menu items like tacos or burrito, minus sour cream. Water or unsweetened iced tea.
The key is choosing smaller portions of leaner meats when available and filling half your plate with fruits and vegetables. Avoid