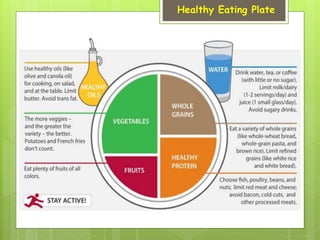
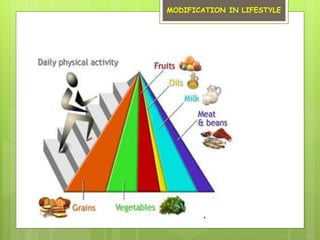
This document provides information on nutrition and maintaining a balanced diet. It discusses the importance of eating a variety of nutrients including carbohydrates, proteins, vitamins, minerals, and fats. Examples of foods in each category are given. The document also outlines tips for making healthy cooking choices, such as using oils low in saturated fat and cooking methods that do not involve deep frying. Overall, the key message is that a balanced diet from all food groups is important for providing the body with the nutrients it needs for good health, energy, and disease prevention.