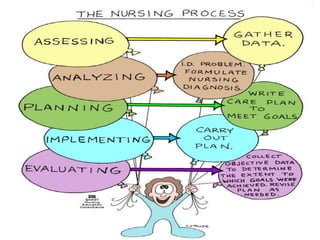
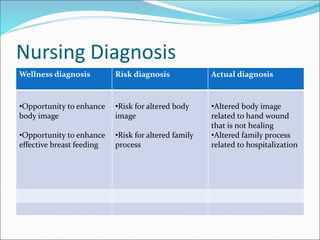
The document discusses the nursing process and its five components: assessment, diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation. It focuses on the assessment and diagnosis components. Assessment involves collecting, validating, organizing, interpreting, and documenting client data from various sources. Diagnosis involves analyzing the assessment data to identify client problems or risks, form nursing diagnoses, and determine appropriate nursing interventions. Nursing diagnoses are clinical judgments that describe a client's response to actual or potential health problems and include a label and related factors.