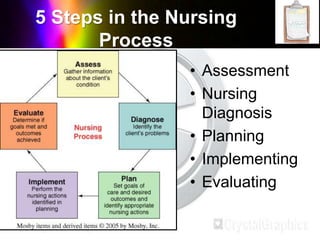
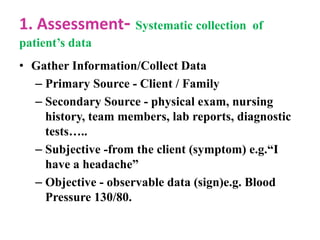
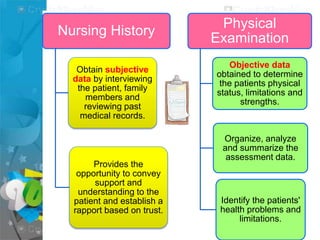
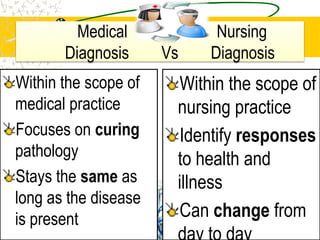
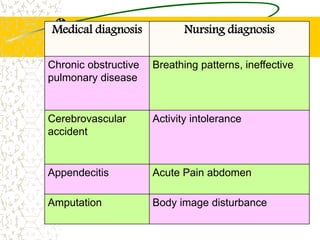
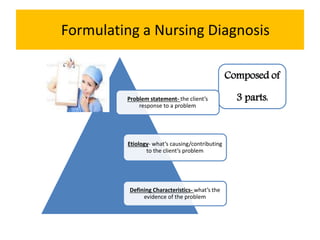
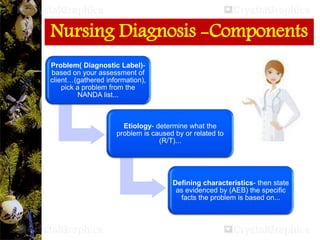
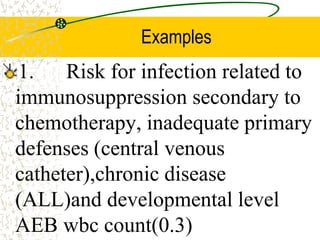
The document outlines the importance of nursing diagnosis and care plans in clinical practice, emphasizing the nursing process as a framework for effective patient care. It details the steps involved in creating individualized nursing care plans based on patient assessments, the components of nursing diagnosis, and the types of nursing diagnoses recognized by the North American Nursing Diagnosis Association (NANDA). Additionally, it discusses challenges faced in implementing nursing care plans in Nigeria and concludes that effective nursing care relies on accurate diagnoses and the development of coherent care plans.