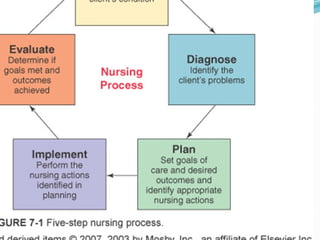
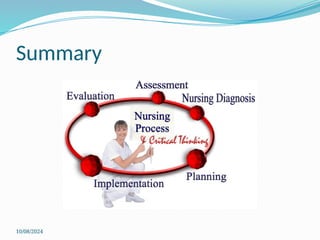
The nursing process is a systematic method for delivering individualized nursing care, comprising five distinct steps: assessment, diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation (ADPIE). It focuses on identifying and addressing patients' unique health responses while considering their personal values and needs, ultimately leading to improved outcomes. Key components include thorough data collection and documentation to guide interventions and measure the effectiveness of care plans.