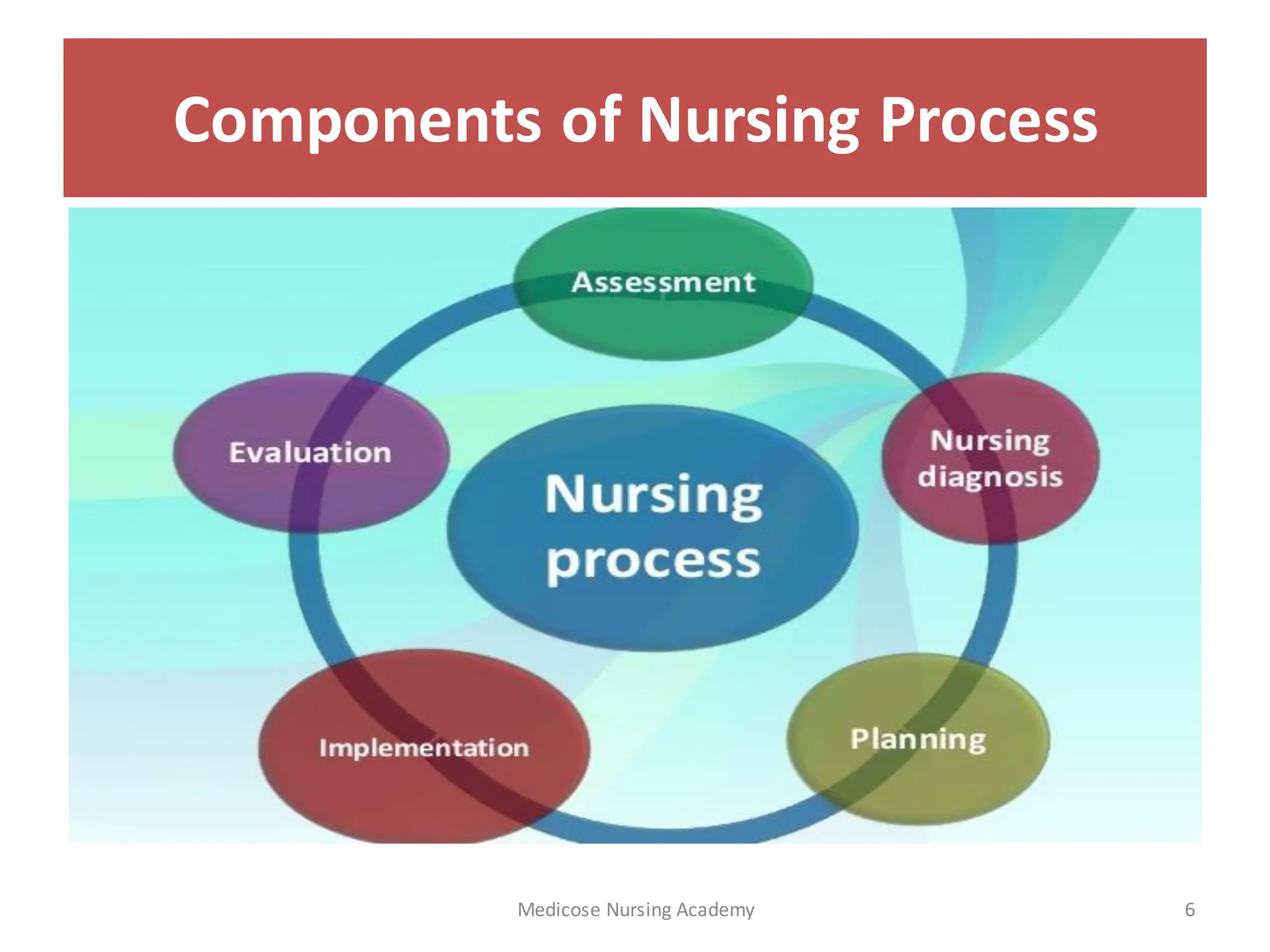
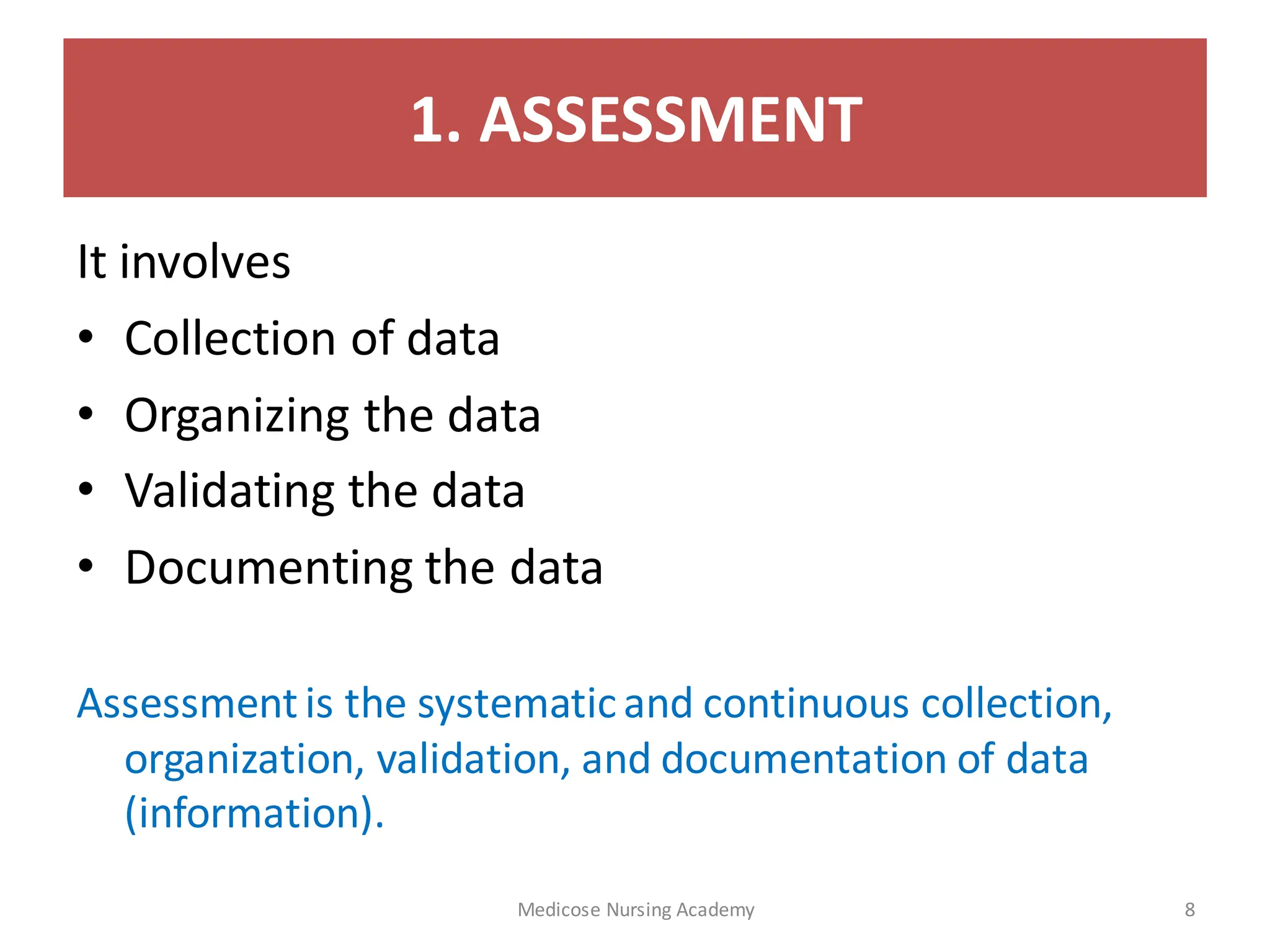
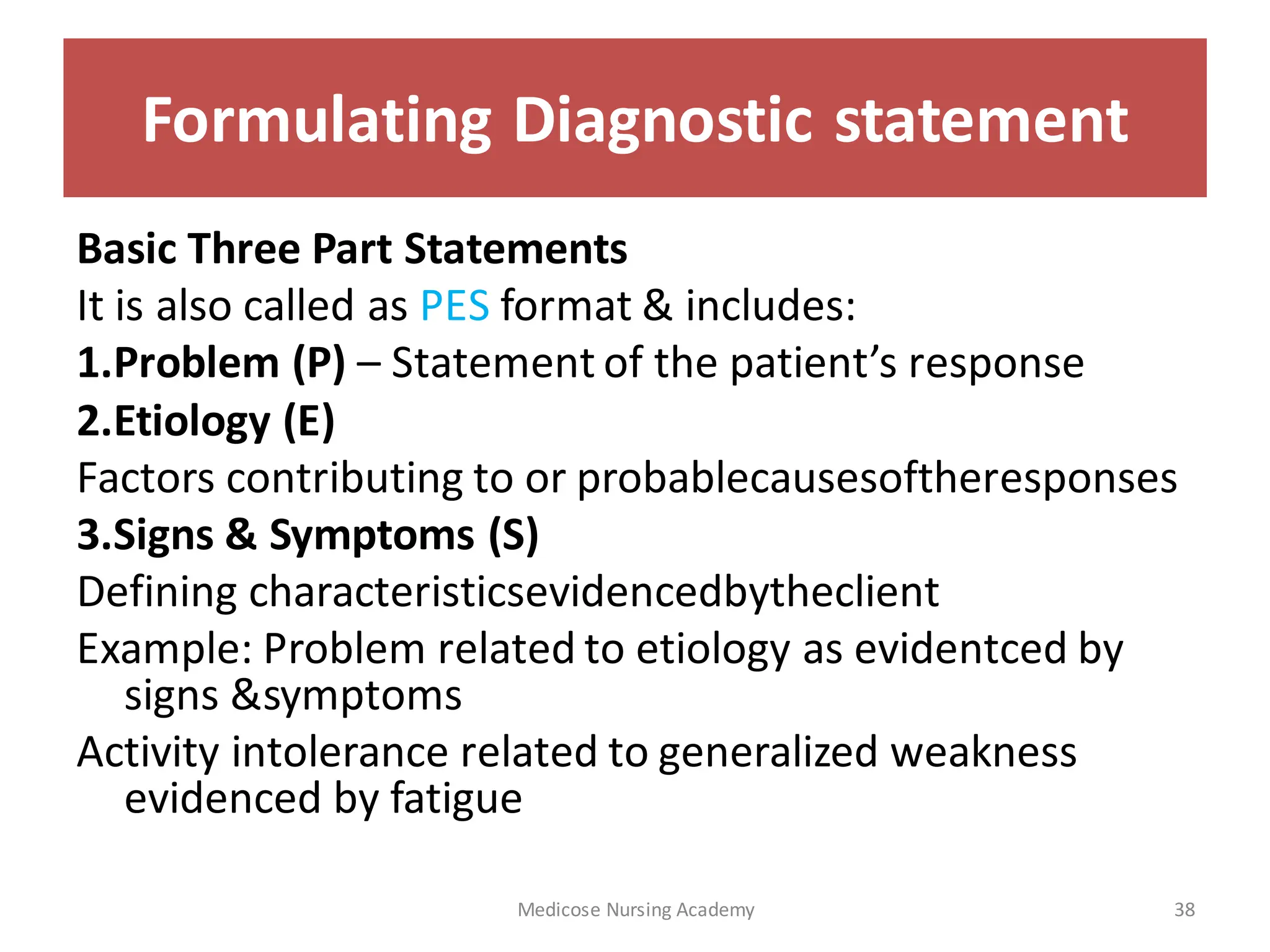
The document outlines the nursing process, a scientific method used to assess client needs and develop a care plan, composed of assessment, diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation. Key components include identifying health statuses, creating targeted interventions, and utilizing critical thinking. Furthermore, it emphasizes the importance of ongoing assessment and documentation to provide effective patient care.