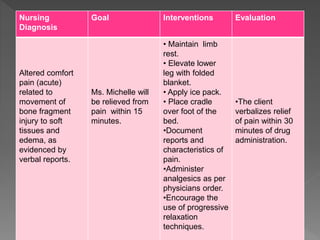
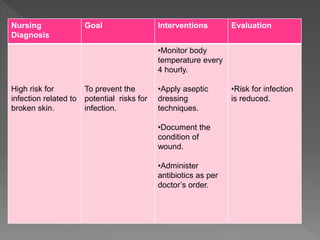
The document discusses evaluation as the final step of the nursing process. Evaluation is defined as judging the effectiveness of nursing care in meeting client goals based on behavioral responses. It is an ongoing, continuous process used to determine how well the care plan is working and ensure quality care. There are different types of evaluation, including process, outcome, ongoing, intermittent, and terminal evaluations. Evaluation involves collecting objective and subjective data to assess if client goals were met and nursing interventions were appropriate. It provides a basis for revising the nursing care plan as needed.