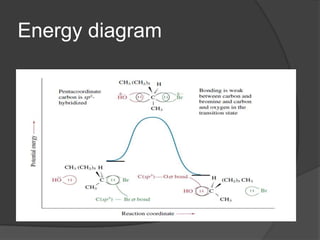
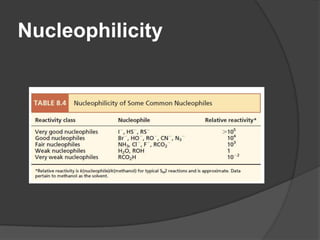
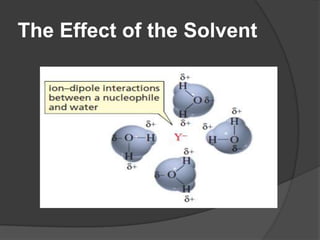
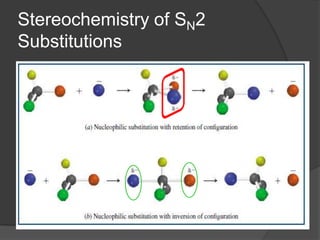
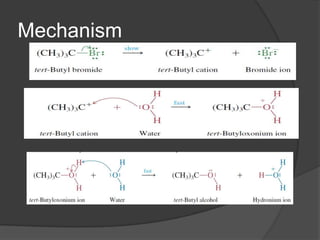
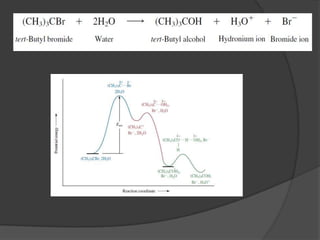
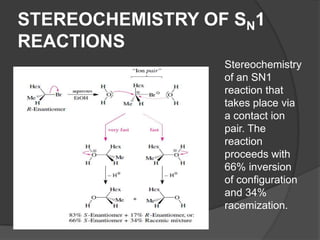
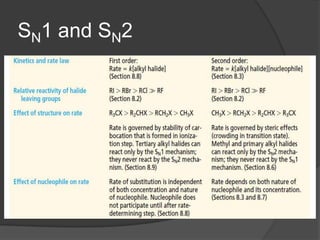
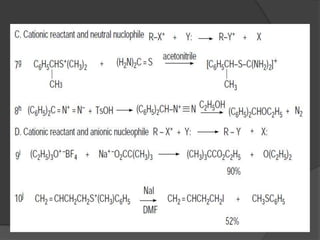
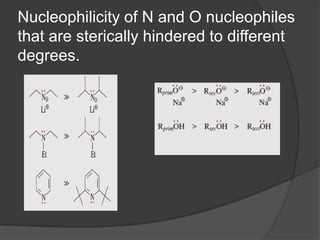
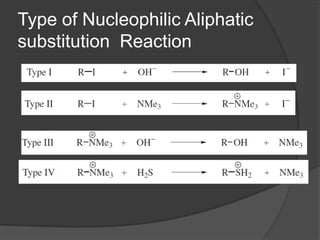
This document discusses nucleophilic substitution reactions, specifically SN1 and SN2 reactions. It defines nucleophiles and explains that they are usually anions or neutral species that can donate an electron pair. The document then covers several factors that affect the rates and mechanisms of SN1 and SN2 reactions, including the leaving group, the nucleophile, the solvent, and steric effects. It describes the single-step SN2 mechanism and stepwise SN1 mechanism involving a carbocation intermediate. Several examples of nucleophilic substitution reactions are also provided.







![The SN2 Mechanism
a single step process
Involves no intermediates
Involves only one transition state, which is of
low polarity
Follows second order (bimolecular) kinetics.
That is, rate=k[substrate][nucleophile]
backside attack](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/substitution-130422091310-phpapp02/85/Substitution-Reaction-10-320.jpg)