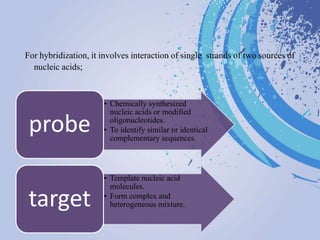
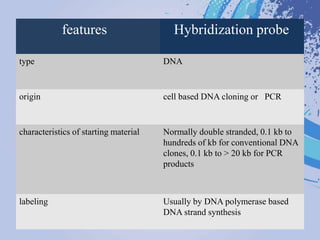
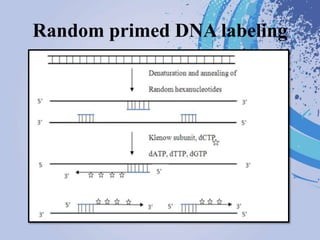
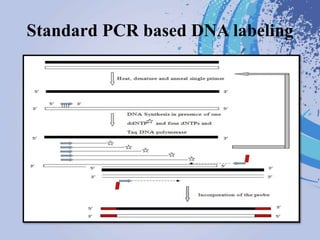
DNA probes are short segments of DNA or RNA that are labeled to allow for detection when bound to complementary nucleic acid sequences. Probes can be labeled through various methods, including fluorescent dyes, isotopic labeling using radioactive atoms, or non-isotopic labeling using molecules like biotin. Labeled probes are used in techniques like Southern blotting, PCR, and in situ hybridization to detect specific DNA or RNA sequences and analyze genetic material.