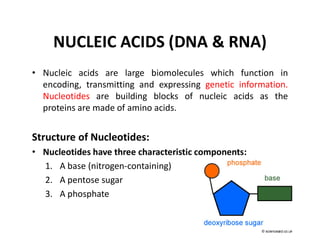
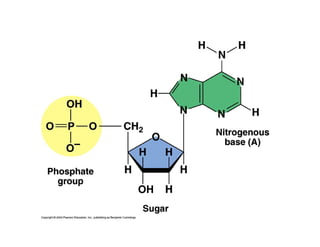
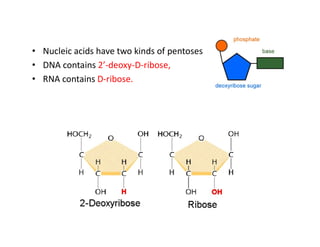
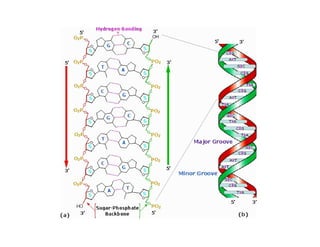
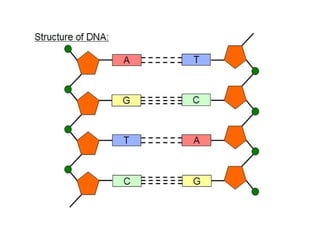
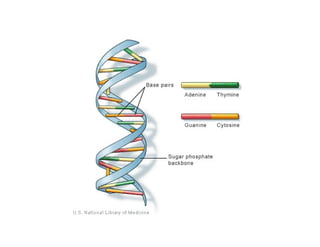
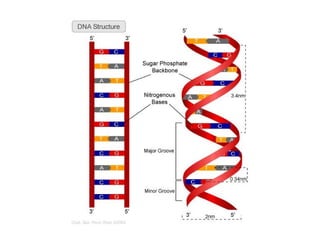
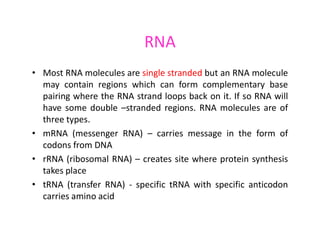
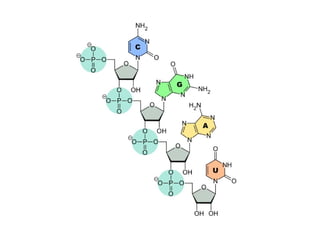
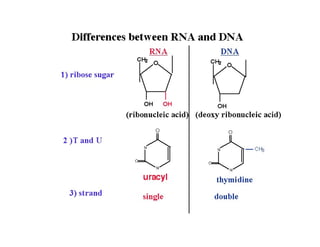
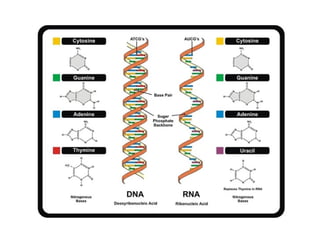
Nucleic acids, including DNA and RNA, are large biomolecules essential for encoding, transmitting, and expressing genetic information, composed of nucleotides that contain a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group. DNA consists of two helical chains of nucleotides forming a double helix with complementary base pairing, while RNA typically exists as a single strand but can have double-stranded regions. Both types of nucleic acids involve specific purines and pyrimidines, with RNA types including mRNA, rRNA, and tRNA, each playing distinct roles in genetic function.