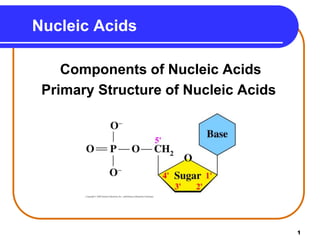
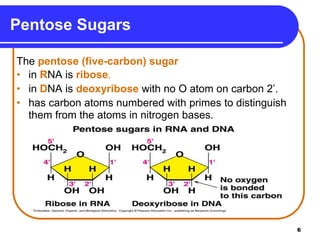
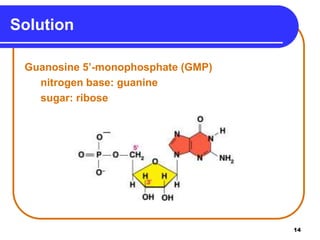
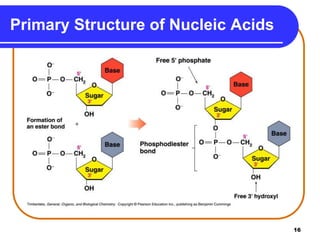
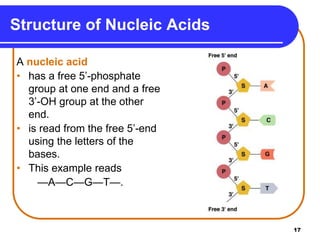
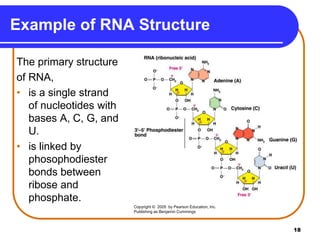
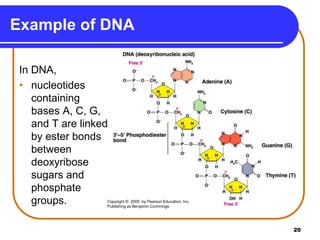
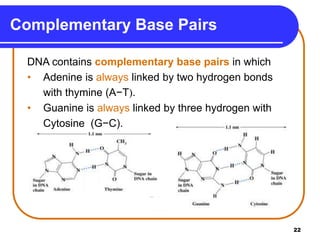
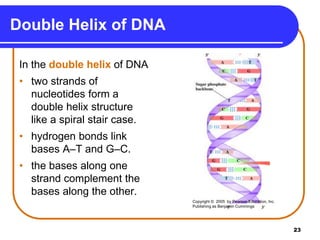
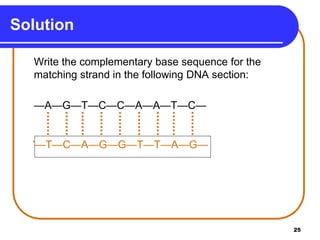
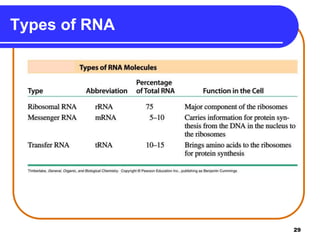
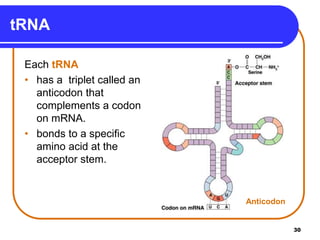
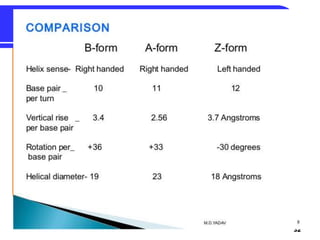
The document summarizes key components and structures of nucleic acids. It describes that nucleic acids are made up of nucleotides, which consist of a nitrogen-containing base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group. The two types of nucleic acids are DNA and RNA. DNA contains the bases adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine, while RNA contains adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil instead of thymine. Nucleotides are linked by phosphodiester bonds to form single-stranded nucleic acids. In DNA, the strands wind together to form the double helix structure, with bases on one strand hydrogen bonding to complementary bases on the other strand.