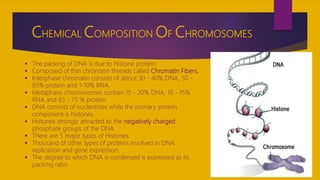
This document provides information on the structure of chromosomes. It begins by defining a chromosome as a threadlike structure found in the nucleus of cells that carries genetic information in the form of genes. Chromosomes are made up of 50% protein and 50% DNA, and contain many genes. The document then discusses the specific structures of chromosomes, including chromatids, centromeres, and chromosome arms. It also describes the chemical composition of chromosomes, noting they are made up of DNA, histone proteins, and other non-histone proteins involved in DNA replication and expression. The document concludes by discussing how DNA is packaged into nucleosomes and higher order structures to achieve its packing ratio within the chromosome.