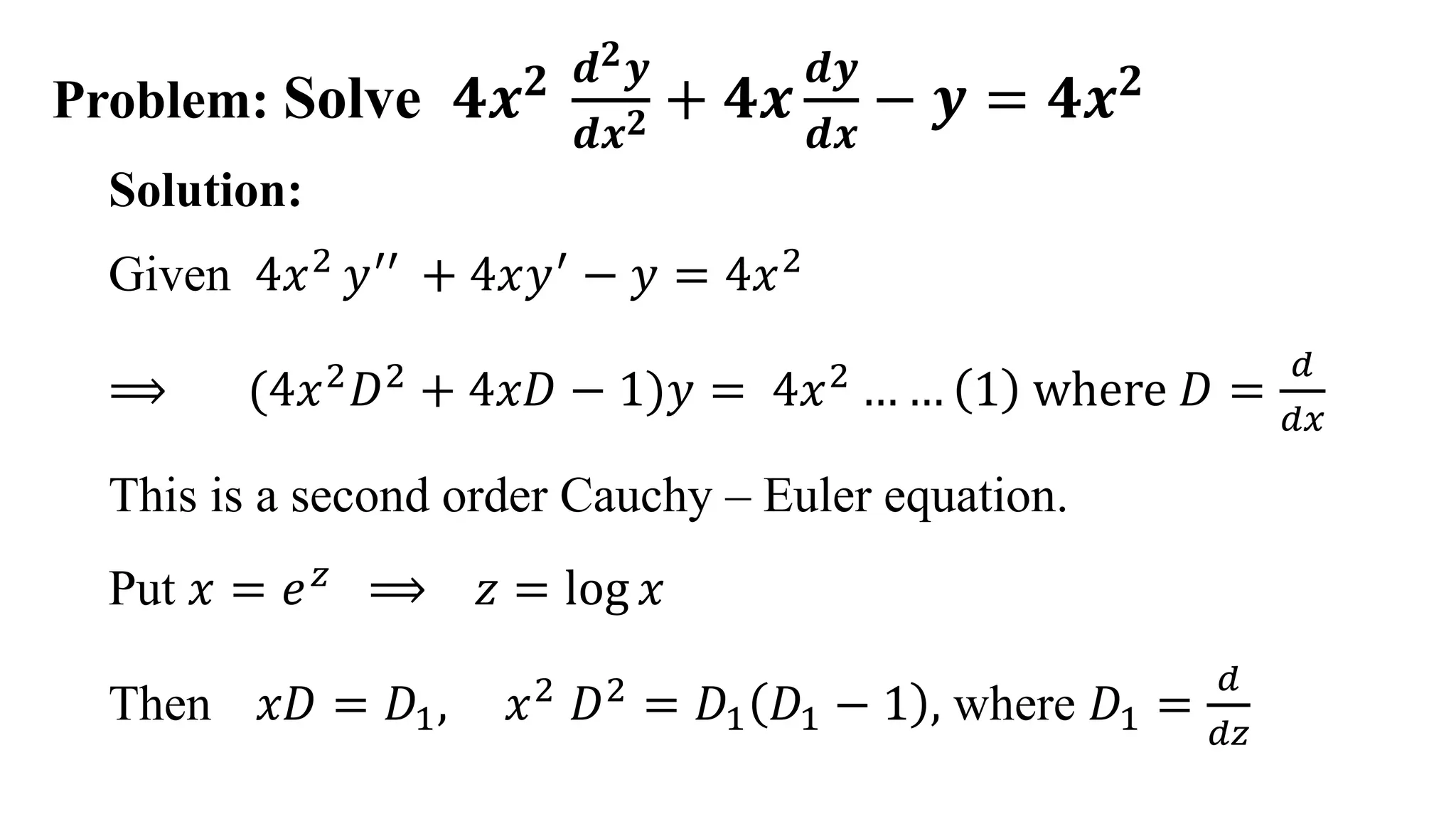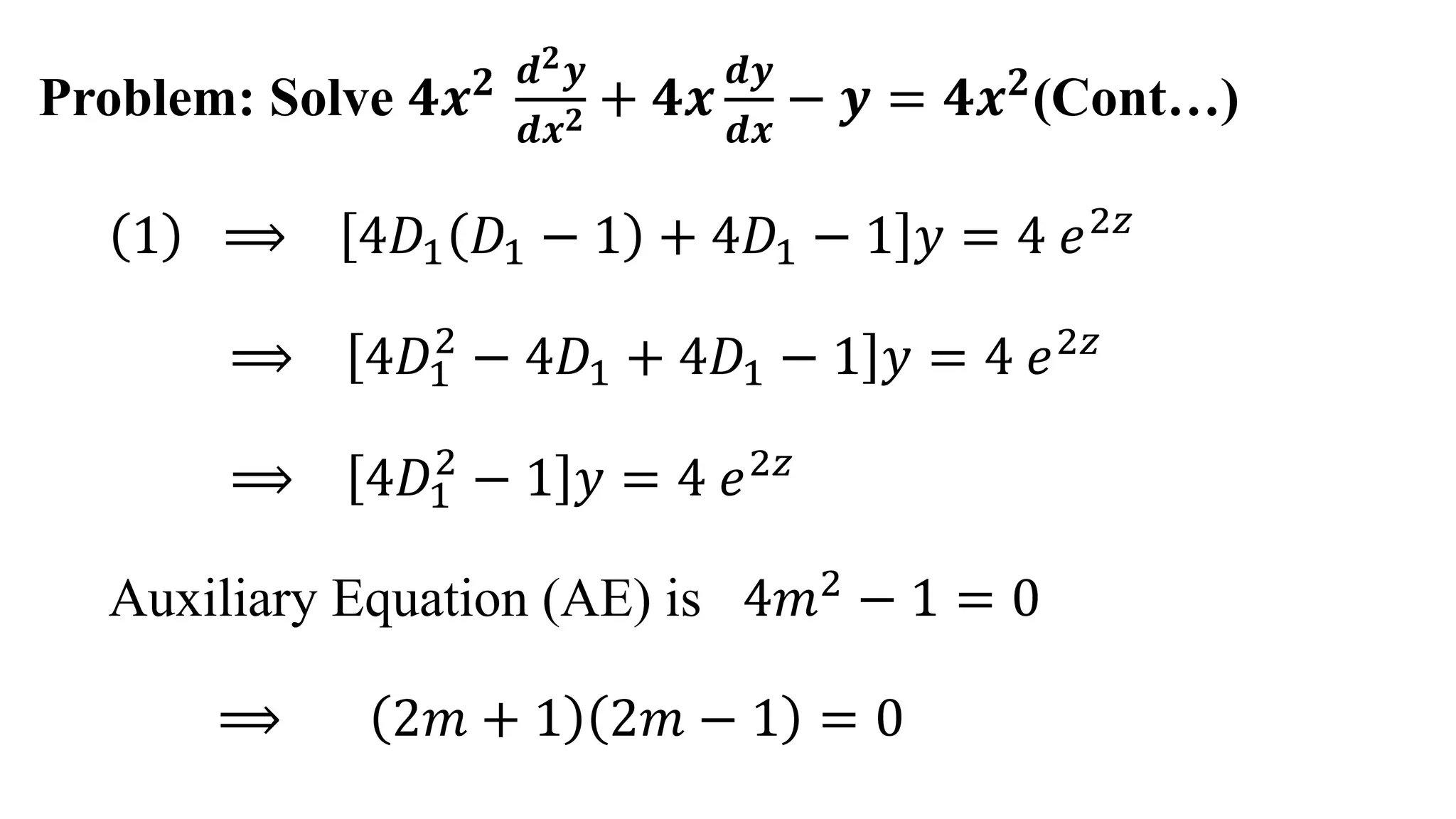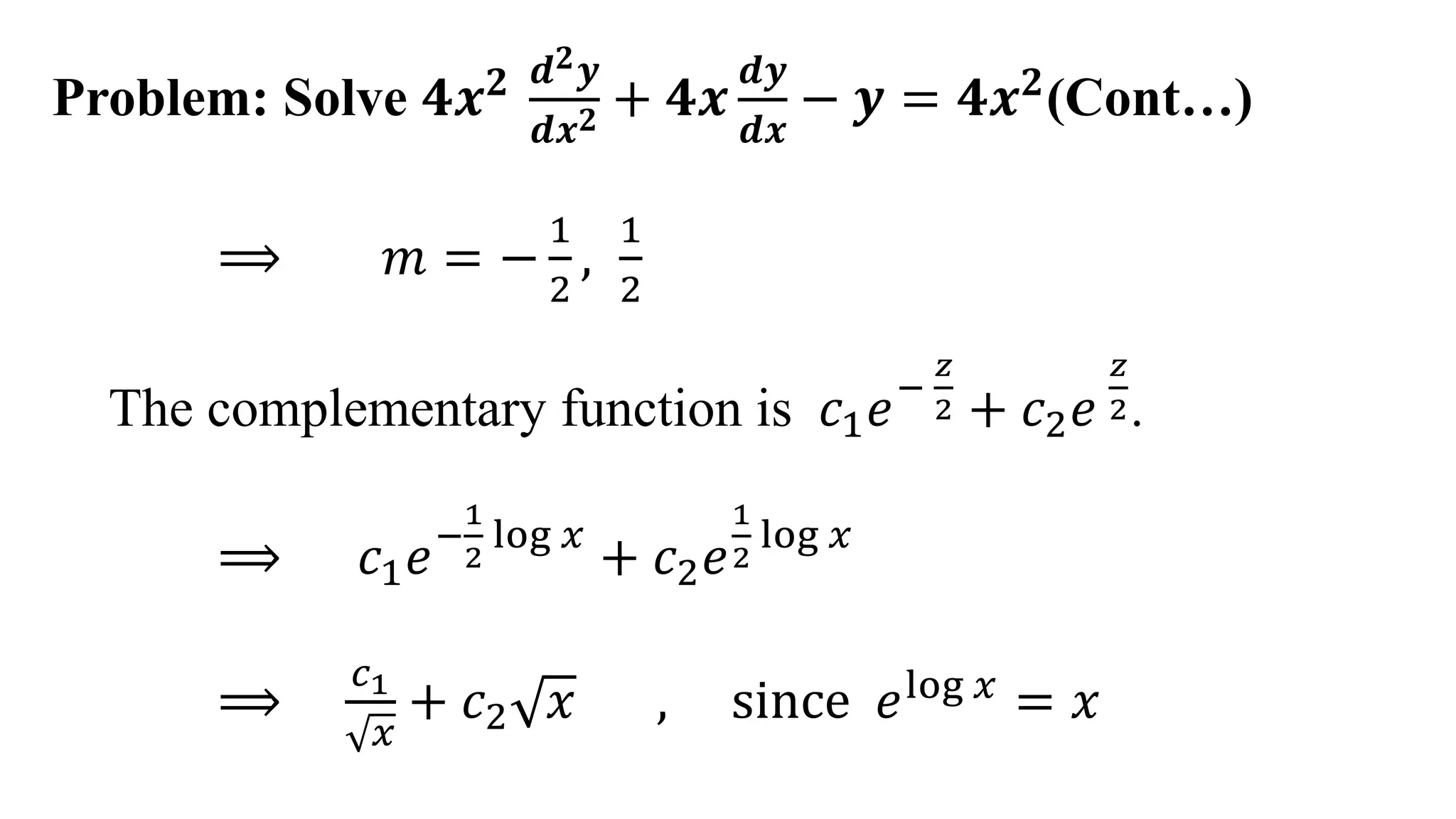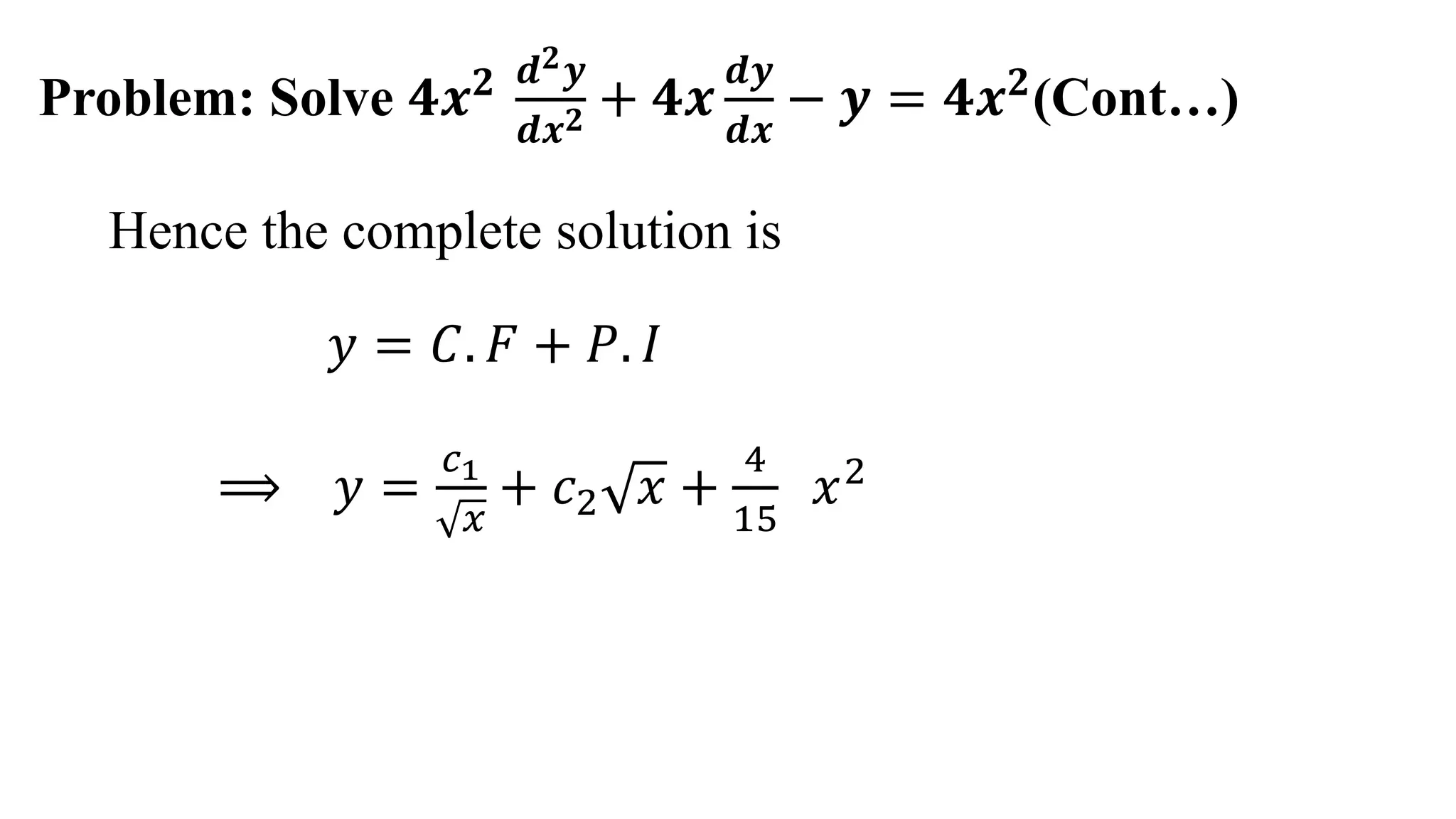This document provides an example of solving a Cauchy-Euler homogeneous differential equation. It begins by defining Cauchy-Euler equations as linear differential equations involving powers of x and derivatives of y. An example 2nd order equation is given and transformed using a change of variable x=e^z. The auxiliary equation is obtained and the complementary function found to be c1/x + c2x. The particular integral is calculated to be 4/15x^2. The complete solution is the sum of the complementary function and particular integral.