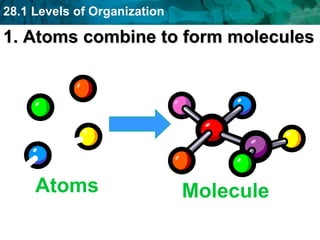
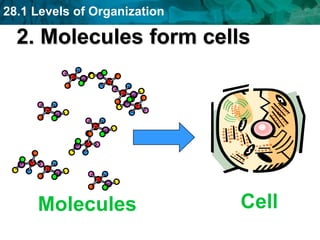
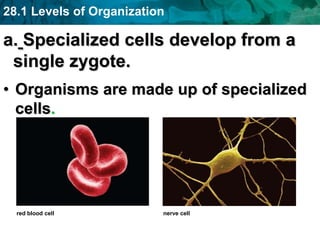
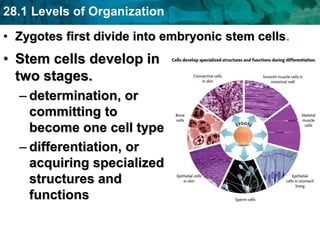
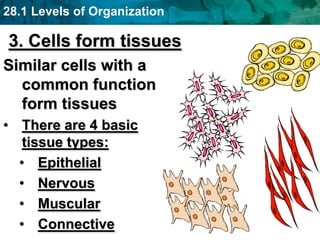
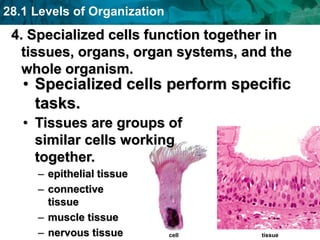
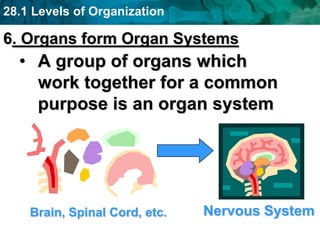
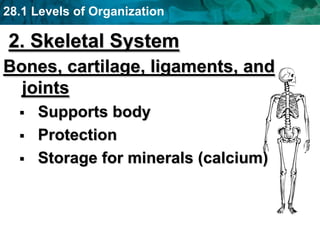
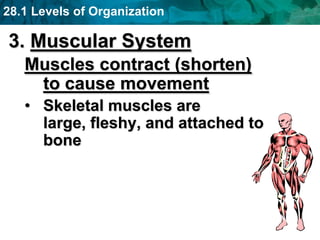
The human body and other organisms have five levels of organization: atoms, molecules, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organism. Atoms combine to form molecules, molecules form cells, similar cells form tissues, tissues combine to form organs, organs that work together form organ systems, and all the organ systems combine to form the whole organism. The document then provides examples of the 10 major organ systems that make up the human body.