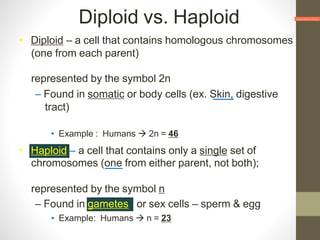
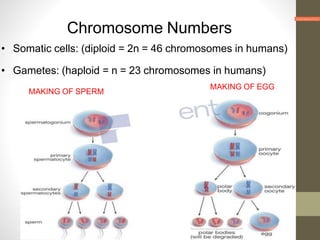
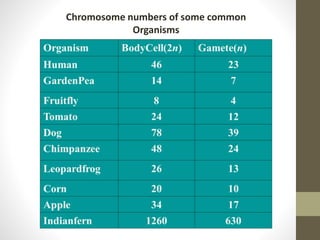
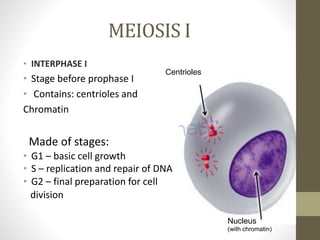
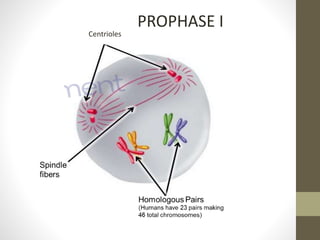
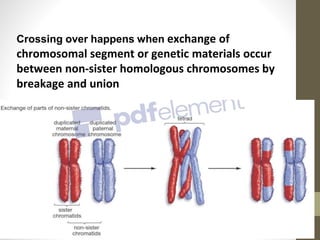
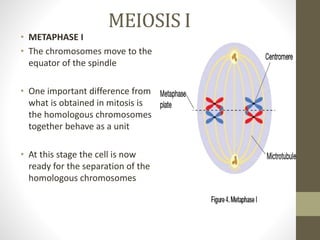
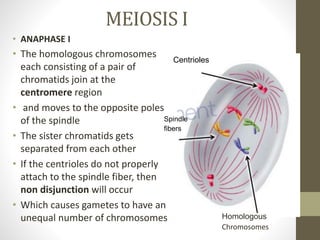
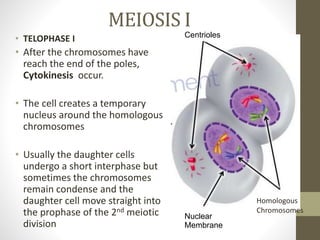
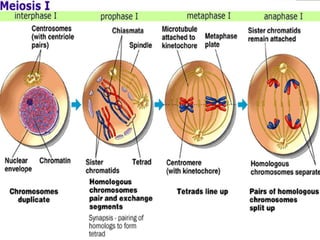
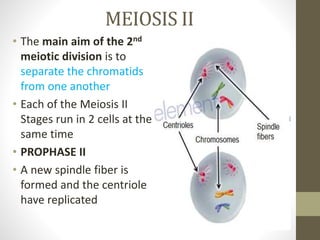
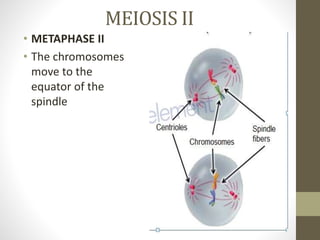
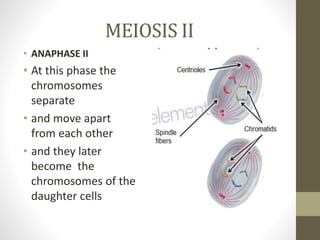
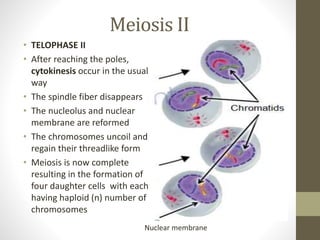
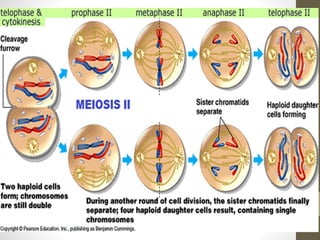
Cell division occurs through mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis produces somatic cells with identical chromosomes to the parent cell, while meiosis produces gametes with half the number of chromosomes. Meiosis has two divisions: meiosis I separates homologous chromosomes and reduces the number to haploid, and meiosis II separates sister chromatids to produce four haploid daughter cells each with a single set of chromosomes. This ensures genetic variation and maintains chromosome number from generation to generation.