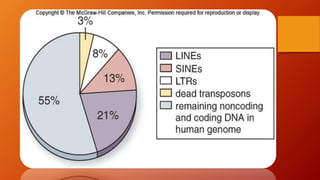
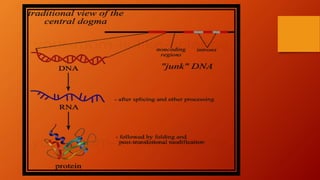
1. Non-coding DNA makes up the majority of DNA in eukaryotic organisms but does not encode for proteins. It was once referred to as "junk DNA" but is now known to have important functions.
2. There are several types of non-coding DNA, including regulatory elements, introns, pseudogenes, repeats, transposons, telomeres, and various non-coding RNAs.
3. While the amount of non-coding DNA varies between species, it plays roles in chromosome structure, gene expression regulation, and protecting the genome from degradation.