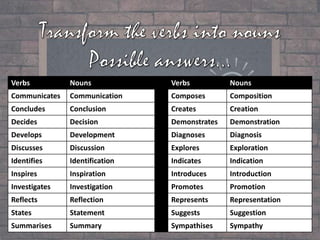
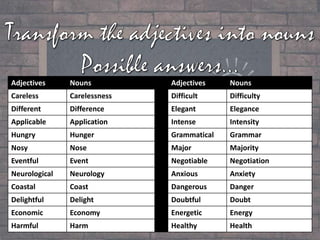
This document discusses nominalization, which is the process of turning verbs and adjectives into nouns. It provides examples of parts of speech like verbs, adjectives, and nouns. Verbs show actions or states of being, adjectives describe nouns, and there are common nouns, proper nouns, and pronouns. The document then lists verbs and their nominalized noun forms, adjectives and their nominalized noun forms, and defines nominalization as the creation of nouns from other parts of speech.