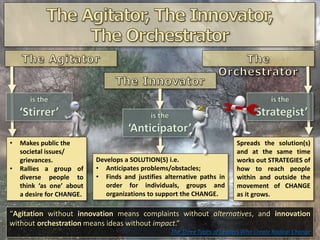
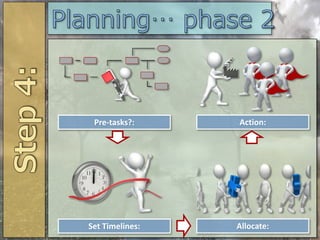
The document discusses the process of social change, emphasizing the importance of collective action and leadership in addressing societal grievances. It highlights influential figures such as Mahatma Gandhi, Nelson Mandela, and Eddie Mabo, who have pioneered significant changes through innovative and peaceful means. Furthermore, it explores the distinctions between social and cultural change, the necessity for governmental priorities in these areas, and the theoretical perspectives on societal structures and inequalities.