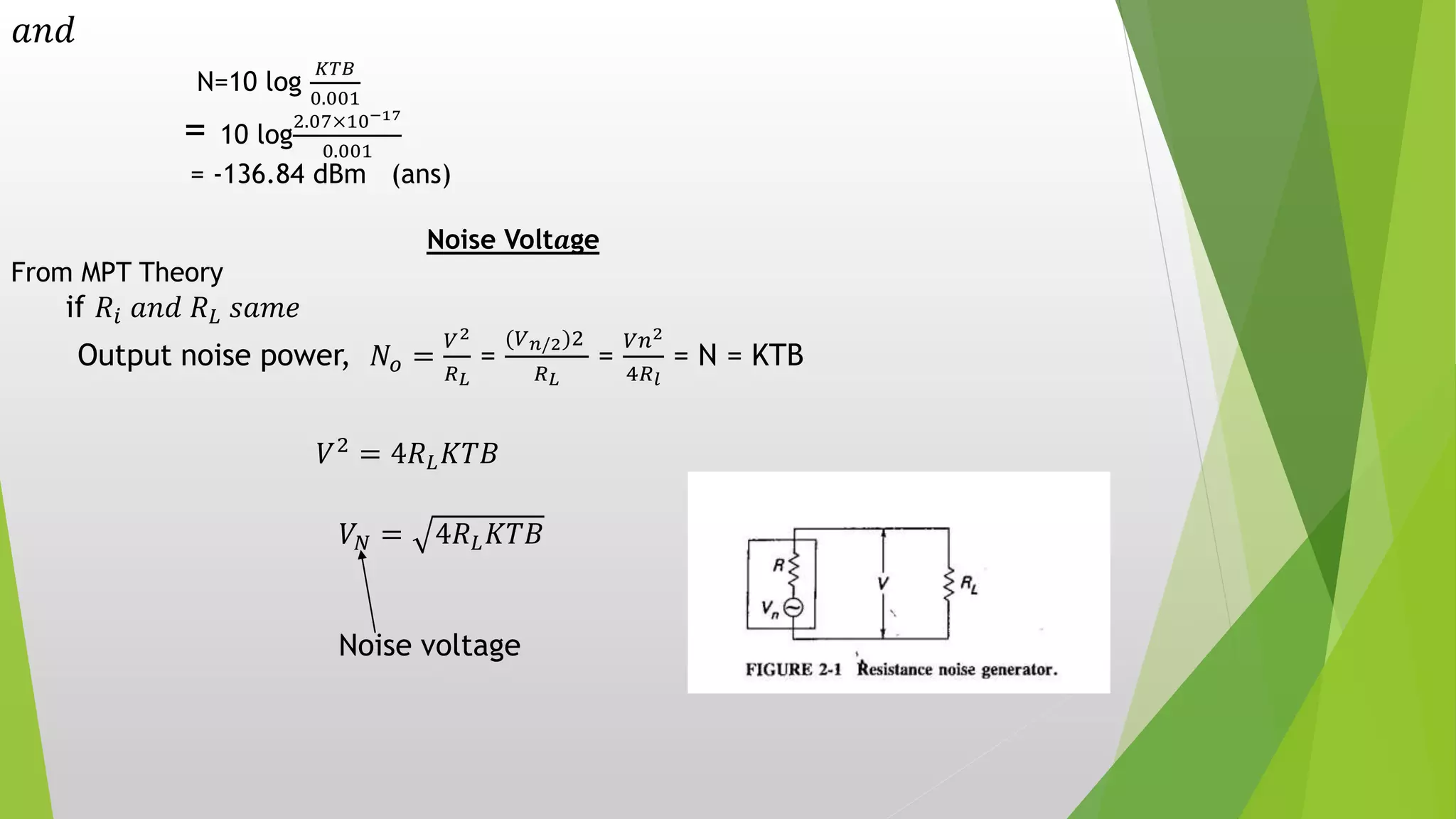
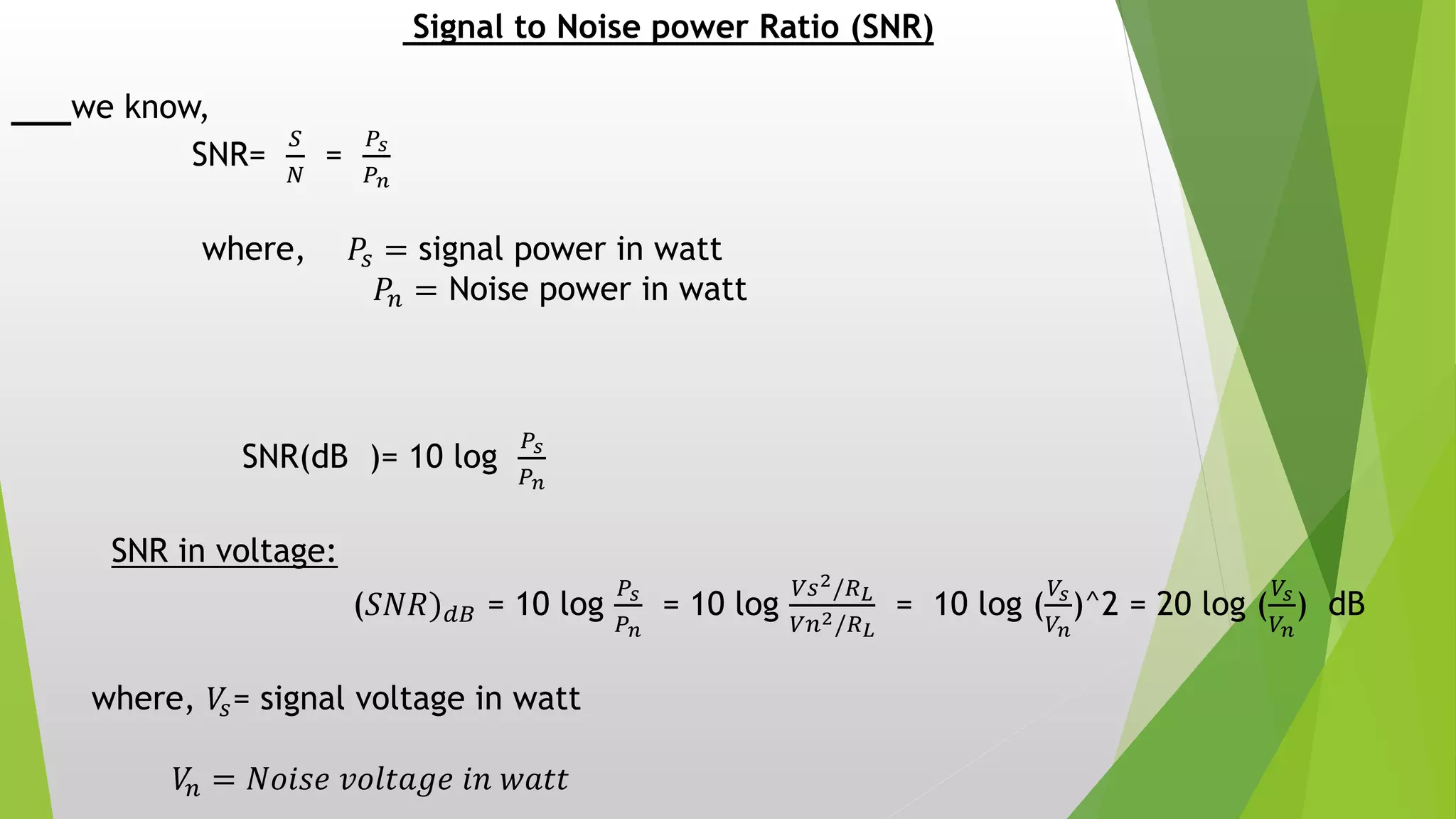
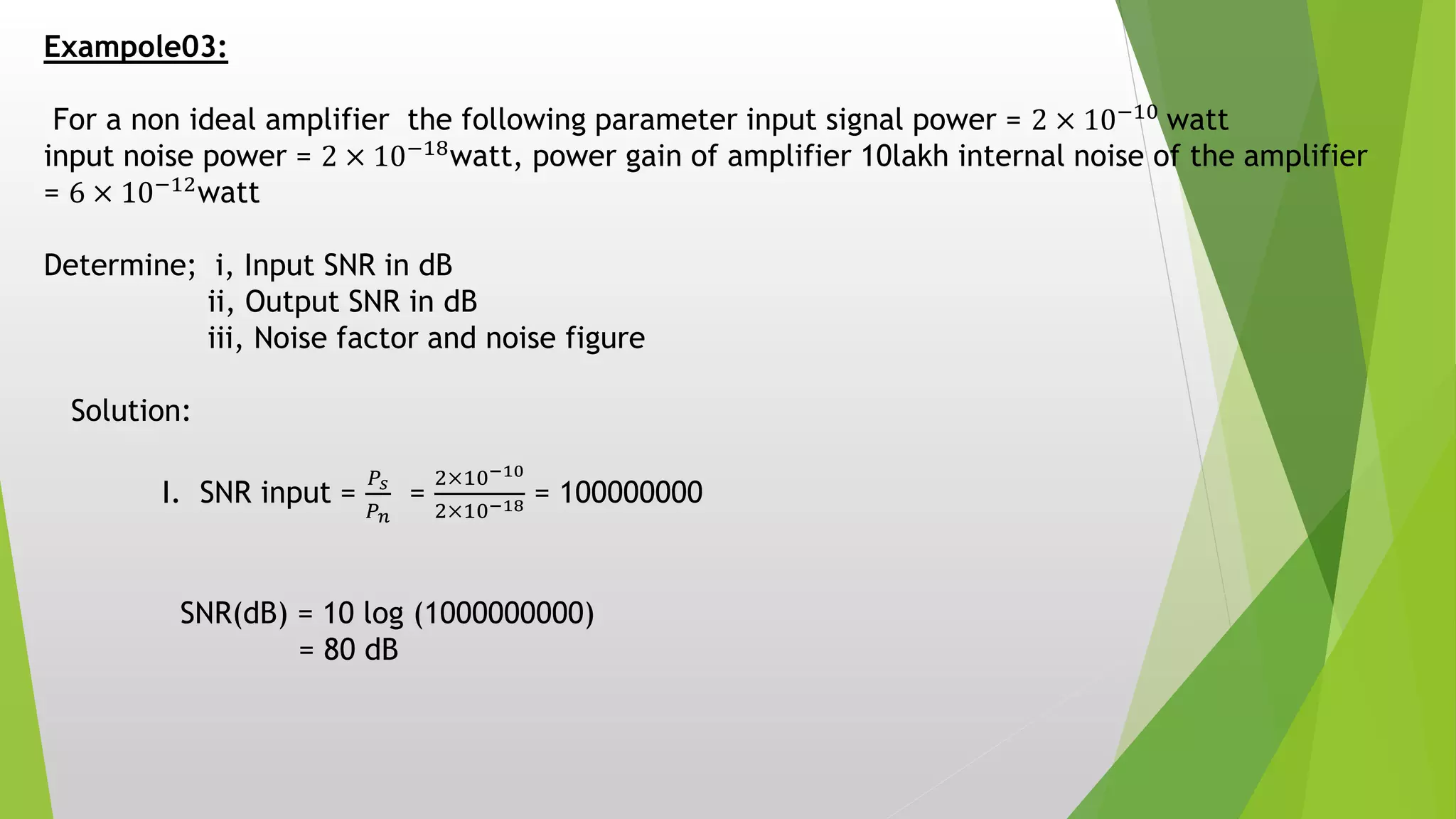
Electrical noise is any unwanted electrical energy, generally unwanted audio signals between 0-15 KHz are considered noise. Thermal noise is created by the random motion of free electrons in a conductor causing thermal agitation. The noise power in watts (N) can be calculated using N=KTB, where K is Boltzmann's constant, T is the absolute temperature in Kelvin, and B is the bandwidth. White noise is where the noise power is the same across all frequencies. Signal to noise power ratio (SNR) is the ratio of signal power to noise power, measured in decibels. Noise factor is the ratio of input SNR to output SNR, and noise figure is 10 times the log of the noise