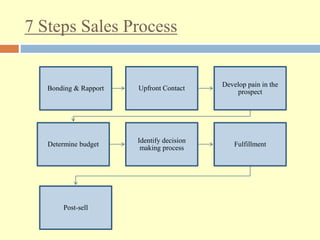
The document outlines a consultative selling approach that emphasizes understanding customer needs and building rapport through a structured seven-step sales process. Key steps include establishing trust, identifying customer pain points, discussing budget and decision-making processes, and ensuring effective communication post-sale. Ultimately, the goal is to provide tailored solutions that address specific customer challenges for mutual benefit.