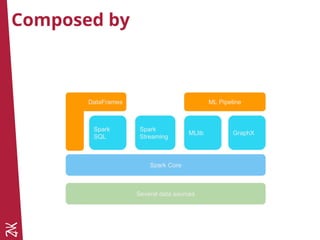
The document introduces Apache Spark, a cluster computing framework that enables scalable data processing, and Apache Zeppelin, a web-based notebook for interactive data analytics. It covers Spark's history, core concepts like RDDs and DataFrames, and its capabilities for machine learning through Spark MLlib. Zeppelin facilitates data visualization and collaboration, supporting multiple programming languages for data ingestion and analysis.

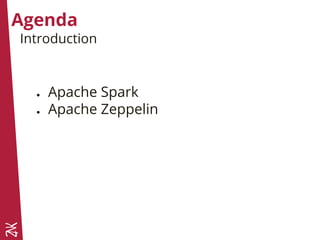















![Run locally
val master = "local"
val master = "local[*]"
val master = "local[4]"
val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("sample")
.setMaster(master)
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nigthclazzspark-160316143110/85/NigthClazz-Spark-Machine-Learning-Introduction-a-Spark-et-Zeppelin-19-320.jpg)








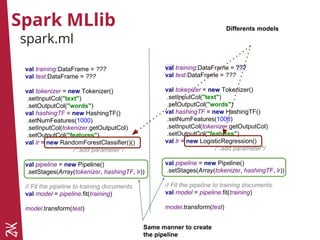
![Spark MLlib
spark.mllib
val sc = //init sparkContext
val (trainingData, checkData) = sc.textFile
("train.csv")
/*transform*/
.randomSplit(Array(0.98, 0.02))
val model = RandomForest.trainClassifier(
trainingData,
10,
Map[Int, Int](),
30,
"auto",
"gini",
7,
100,
0)
val prediction = model.predict(...)
//init sparkContext
val (trainingData, checkData) = sc.textFile("train.
csv")
/*transform*/
.randomSplit(Array(0.98, 0.02))
val model = new
LogisticRegressionWithLBFGS()
.setNumClasses(10)
.run(train)
val prediction = model.predict(...)
Each model exposes its own
interface](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nigthclazzspark-160316143110/85/NigthClazz-Spark-Machine-Learning-Introduction-a-Spark-et-Zeppelin-36-320.jpg)