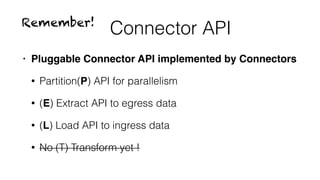
Sqoop on Spark provides a way to run Sqoop jobs using Apache Spark for parallel data ingestion. It allows Sqoop jobs to leverage Spark's speed and growing community. The key aspects covered are:
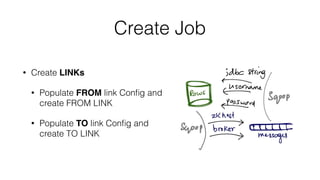
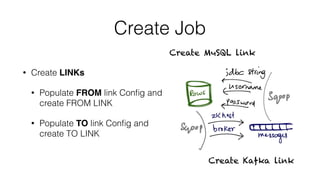
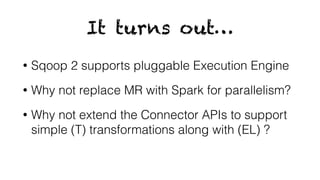
- Sqoop jobs can be created and executed on Spark by initializing a Spark context and wrapping Sqoop and Spark initialization.
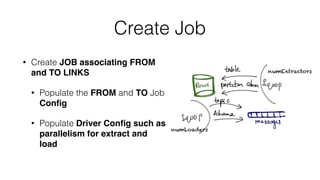
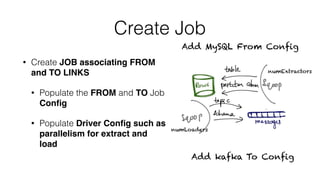
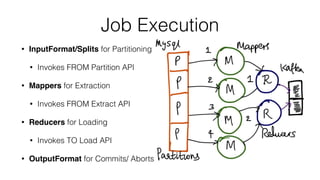
- Data is partitioned and extracted in parallel using Spark RDDs and map transformations calling Sqoop connector APIs.
- Loading also uses Spark RDDs and map transformations to parallelly load data calling connector load APIs.
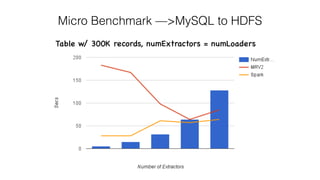
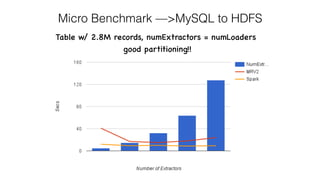
- Microbenchmarks show Spark-based ingestion can be significantly faster than traditional MapReduce-based Sqoop for large datasets









![Create Job API
public static void createJob(String[] jobconfigs) {
CommandLine cArgs = parseArgs(createOptions(), jobconfigs);
MLink fromLink = createFromLink(‘jdbc-connector’, jobconfigs);
MLink toLink = createToLink(‘kafka-connector’, jobconfigs);
MJob sqoopJob = createJob(fromLink, toLink, jobconfigs);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/june9235pmuberbasavarajchandarv3-150701222803-lva1-app6892/85/Sqoop-on-Spark-for-Data-Ingestion-20-320.jpg)







![public class SqoopJDBCHDFSJobDriver {
public static void main(String[] args){
final SqoopSparkJob sparkJob = new SqoopSparkJob();
CommandLine cArgs = SqoopSparkJob.parseArgs(createOptions(), args);
SparkConf conf = sparkJob.init(cArgs);
JavaSparkContext context = new JavaSparkContext(conf);
MLink fromLink = getJDBCLink();
MLink toLink = getHDFSLink();
MJob sqoopJob = createJob(fromLink, toLink);
sparkJob.setJob(sqoopJob);
sparkJob.execute(conf, context);
}
Create Sqoop Spark Job
1
2
3
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/june9235pmuberbasavarajchandarv3-150701222803-lva1-app6892/85/Sqoop-on-Spark-for-Data-Ingestion-31-320.jpg)