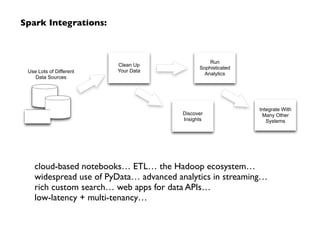
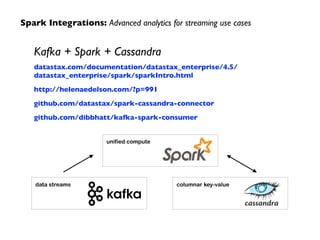
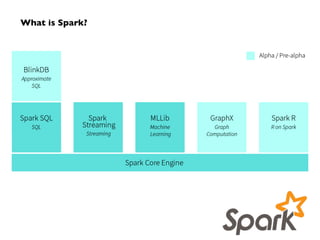
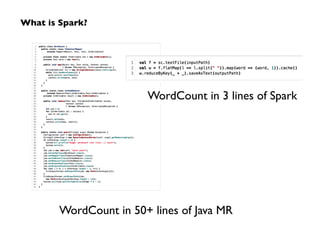
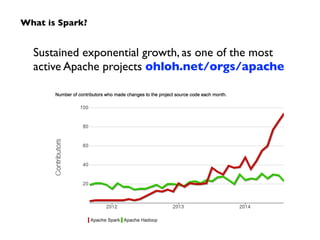
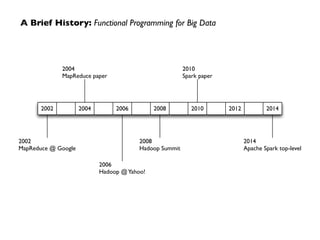
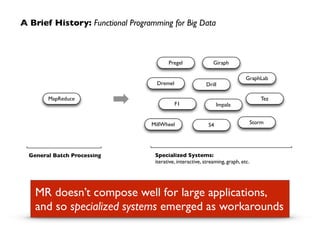
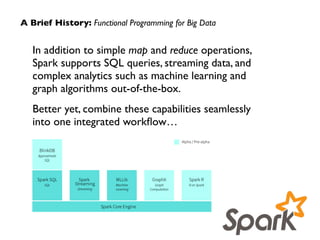
Apache Spark, developed at UC Berkeley in 2009 and open-sourced in 2010, has emerged as a leading open-source community for big data, providing in-memory computing and supporting a wide range of analytics tasks on Hadoop clusters. It integrates seamlessly with various frameworks to enable advanced analytics, machine learning, and real-time streaming, while helping organizations manage their big data workflows effectively. The document discusses Spark's architecture, features, integrations, and its role in the evolving big data landscape.















![Unifying the Pieces: GraphX
// http://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/graphx-programming-guide.html!
!
import org.apache.spark.graphx._!
import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD!
!
case class Peep(name: String, age: Int)!
!
val vertexArray = Array(!
(1L, Peep("Kim", 23)), (2L, Peep("Pat", 31)),!
(3L, Peep("Chris", 52)), (4L, Peep("Kelly", 39)),!
(5L, Peep("Leslie", 45))!
)!
val edgeArray = Array(!
Edge(2L, 1L, 7), Edge(2L, 4L, 2),!
Edge(3L, 2L, 4), Edge(3L, 5L, 3),!
Edge(4L, 1L, 1), Edge(5L, 3L, 9)!
)!
!
val vertexRDD: RDD[(Long, Peep)] = sc.parallelize(vertexArray)!
val edgeRDD: RDD[Edge[Int]] = sc.parallelize(edgeArray)!
val g: Graph[Peep, Int] = Graph(vertexRDD, edgeRDD)!
!
val results = g.triplets.filter(t => t.attr > 7)!
!
for (triplet <- results.collect) {!
println(s"${triplet.srcAttr.name} loves ${triplet.dstAttr.name}")!
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/keynote-paco-databrix-141110005808-conversion-gate01/85/Big-Data-Everywhere-Chicago-Apache-Spark-Plus-Many-Other-Frameworks-How-Spark-Fits-Into-the-Big-Data-Landscape-Databricks-25-320.jpg)