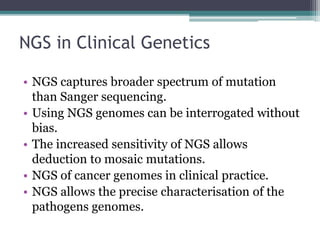
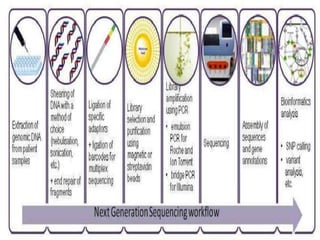
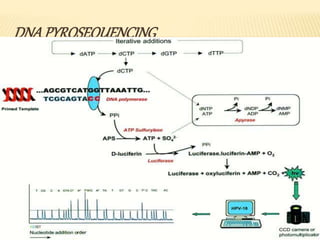
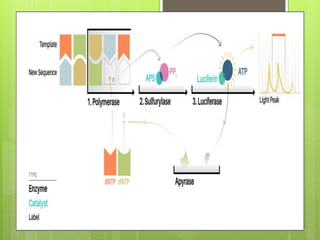
This document discusses DNA sequencing and next generation sequencing (NGS) technologies. It provides background on DNA sequencing, noting that it determines the exact order of nucleotides within a DNA molecule. Next, it introduces Frederick Sanger as the "Father of DNA Sequencing." Finally, it discusses how NGS has revolutionized genomic research by allowing entire human genomes to be sequenced in a single day and its various applications in clinical genetics and other fields.