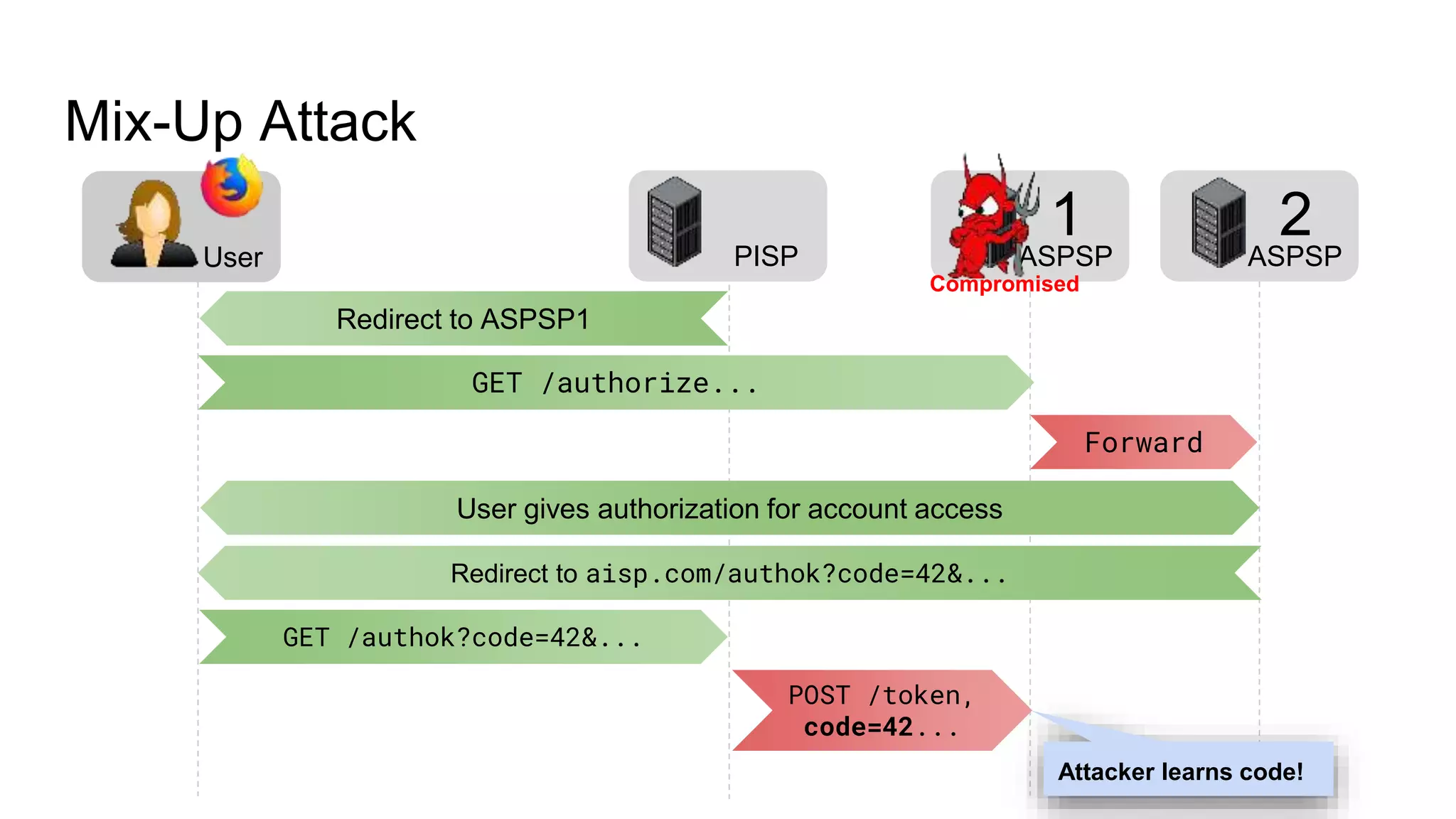
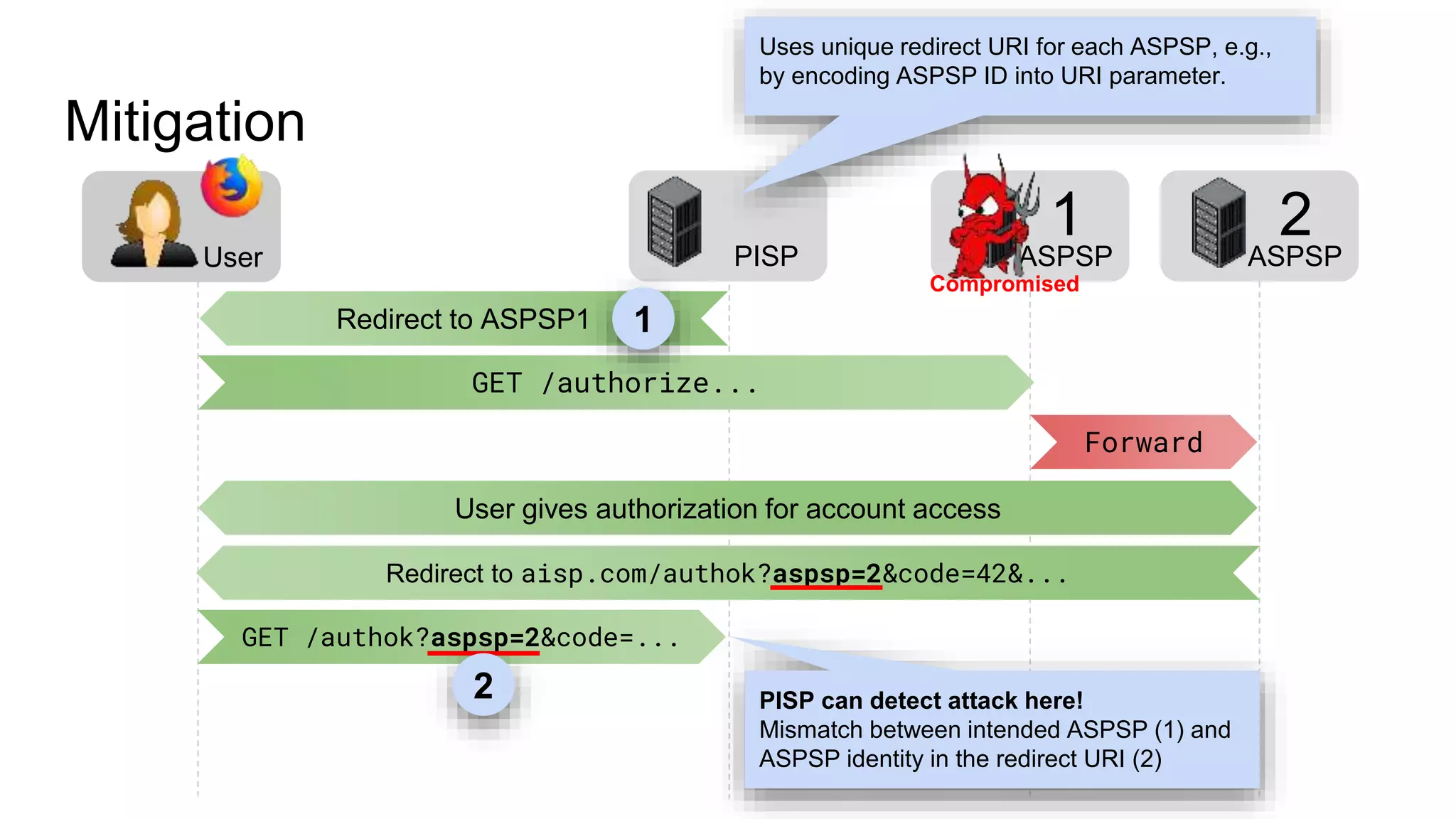
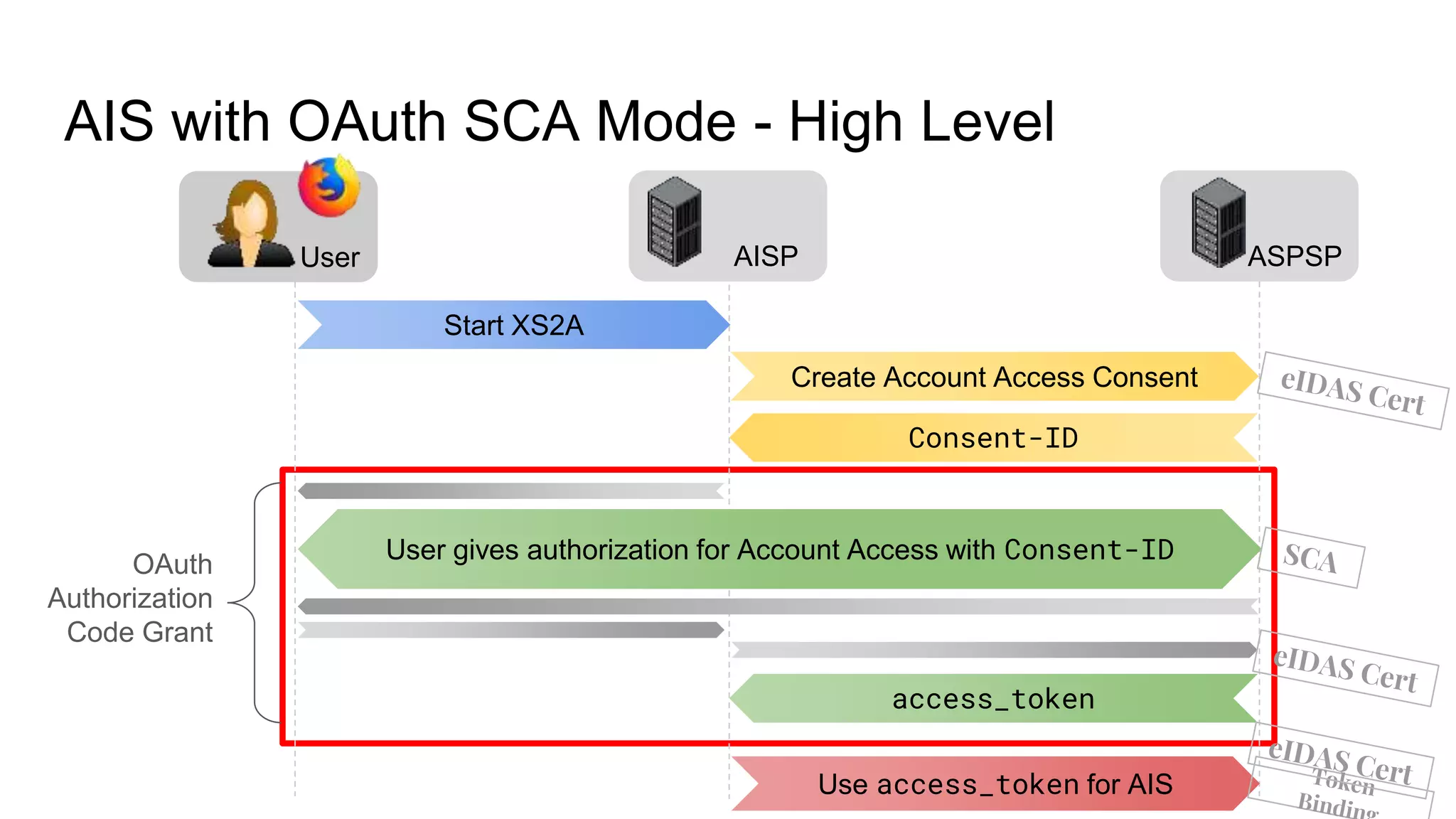
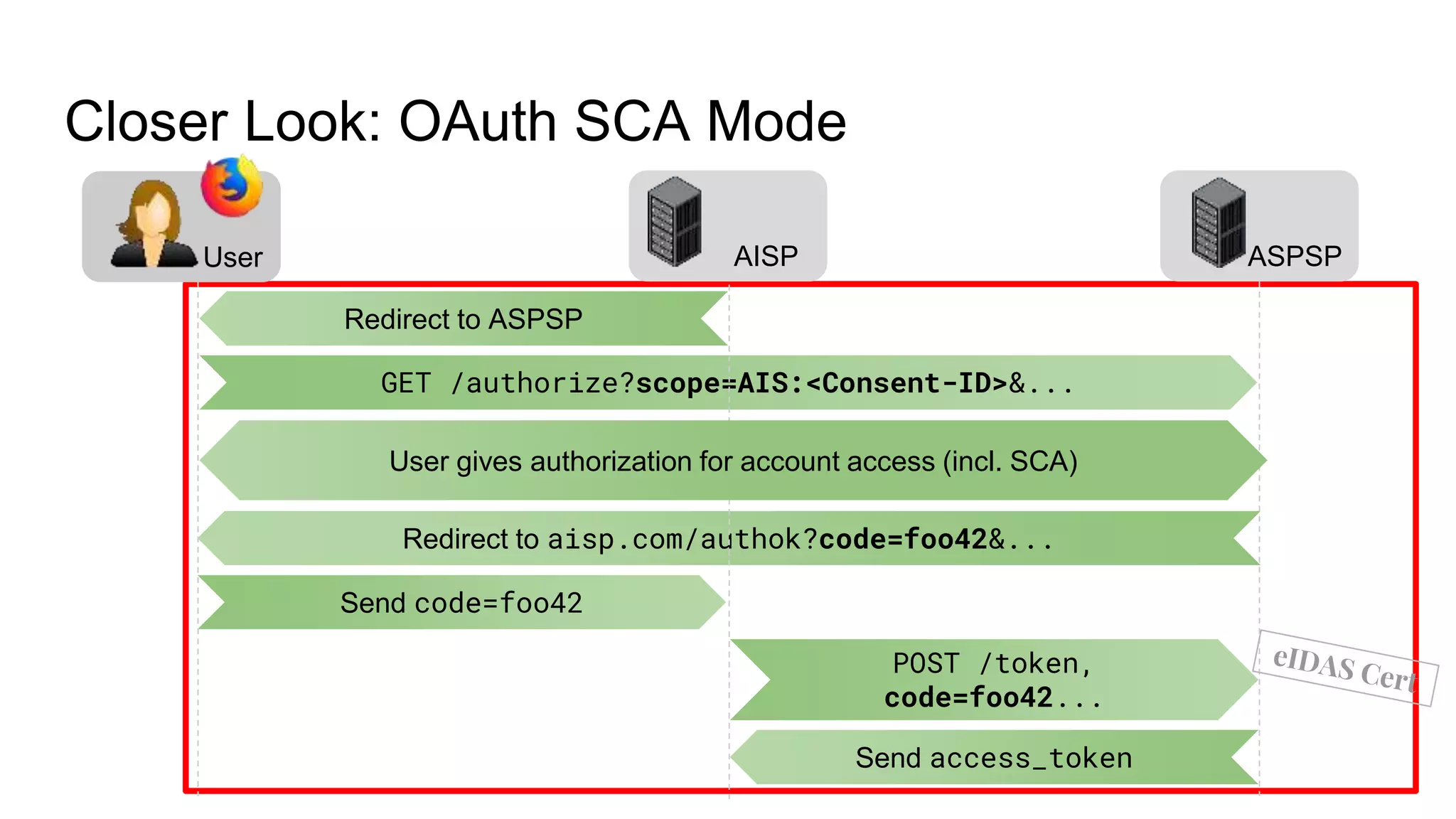
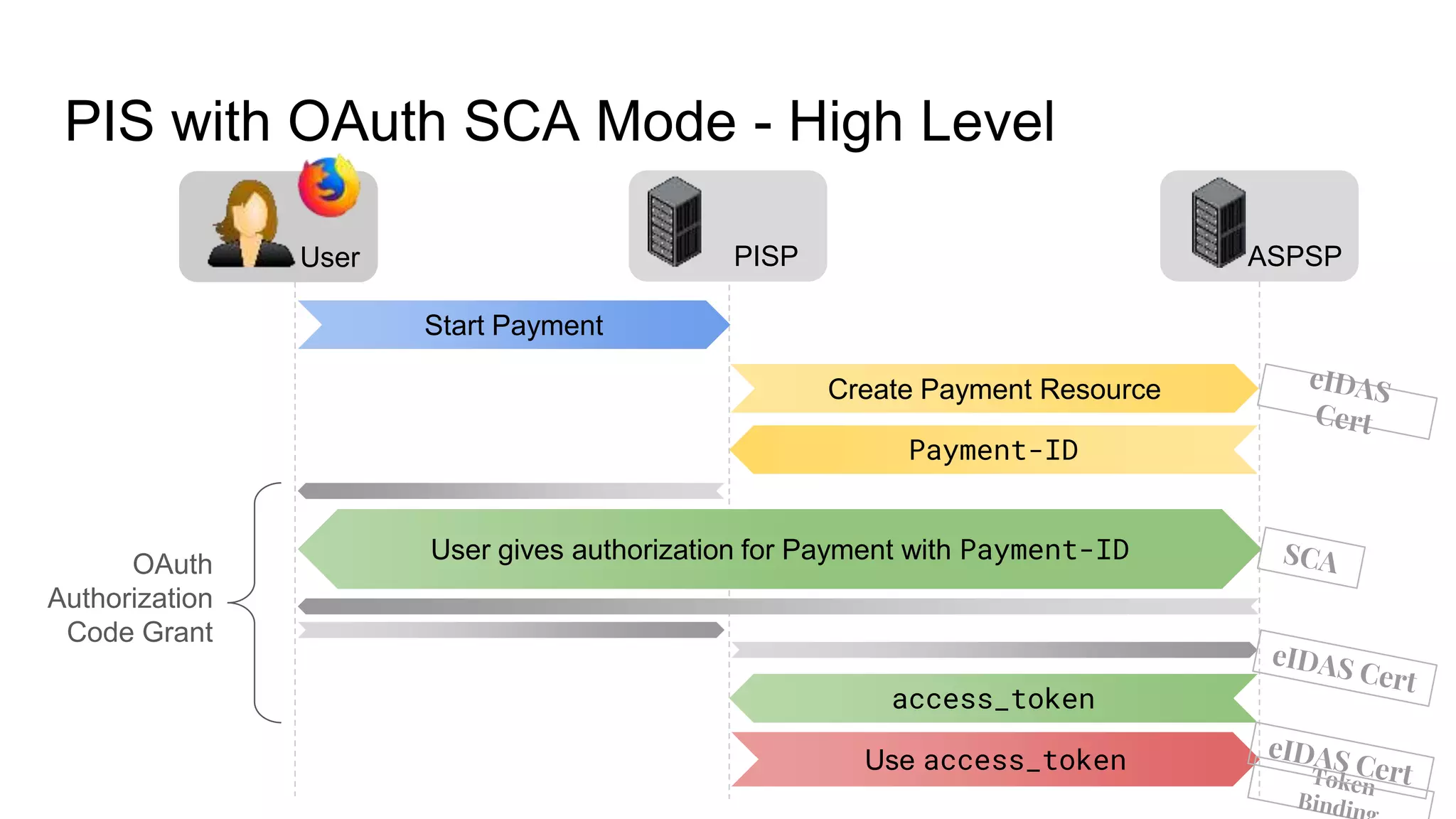
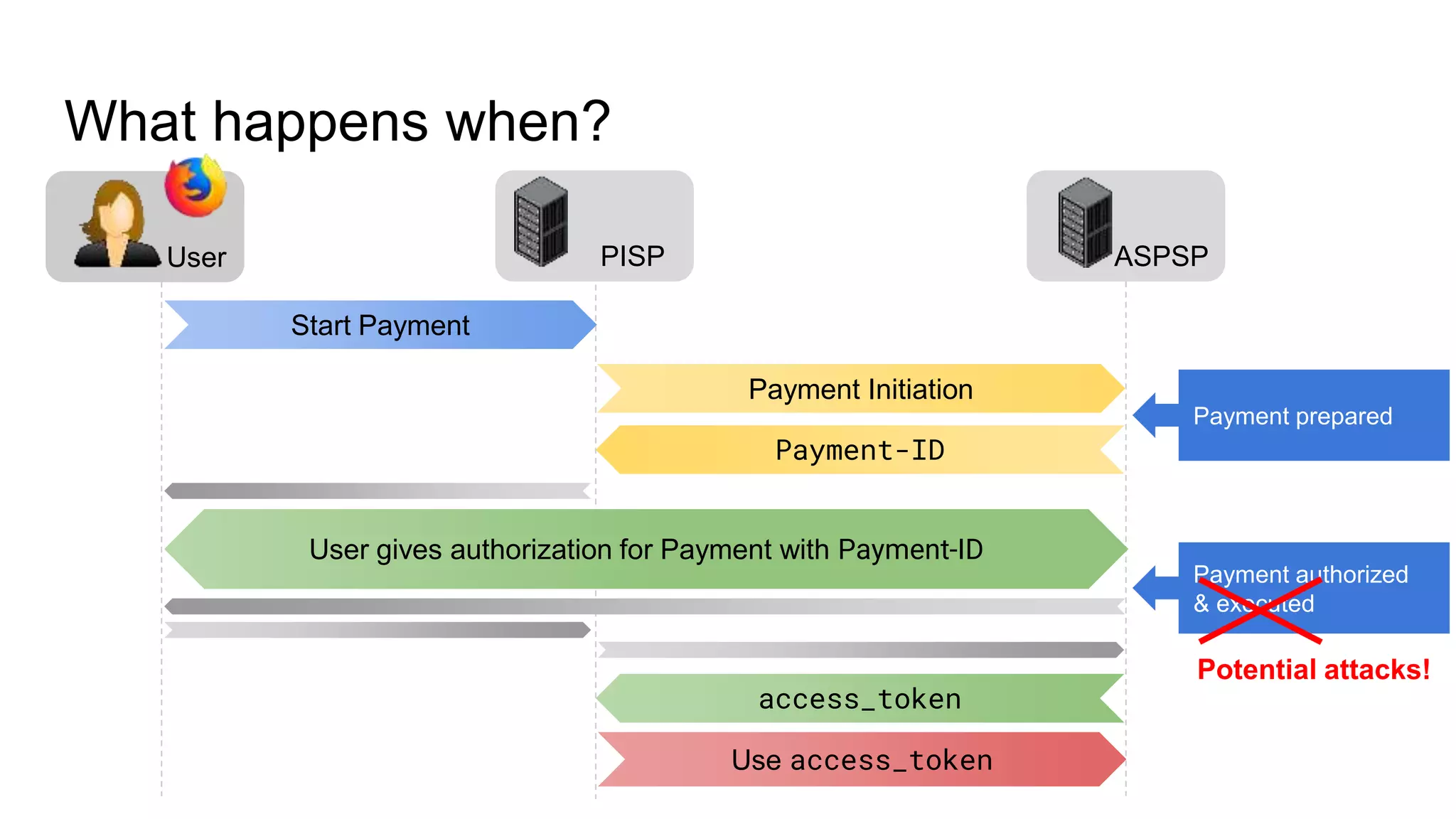
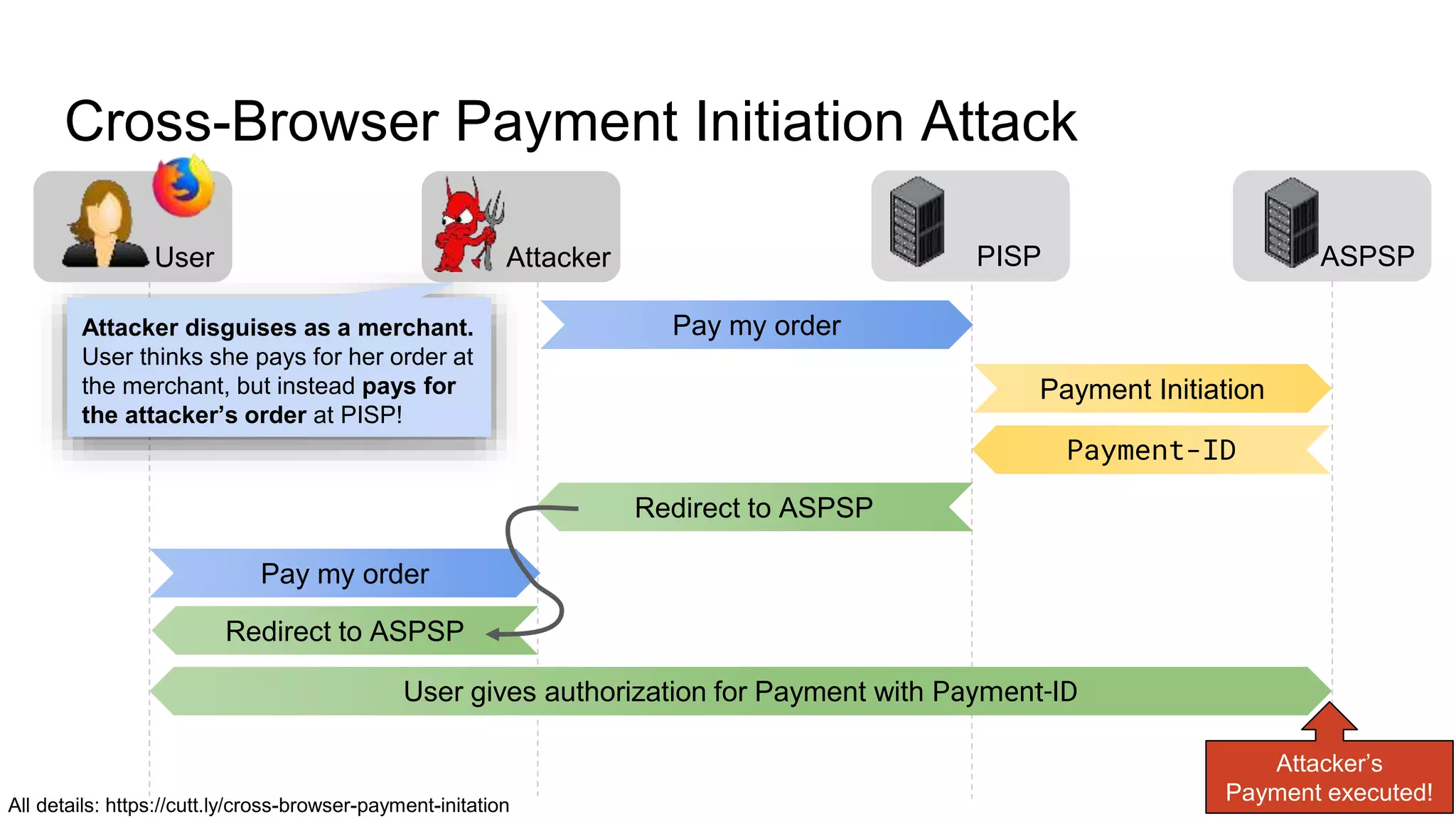
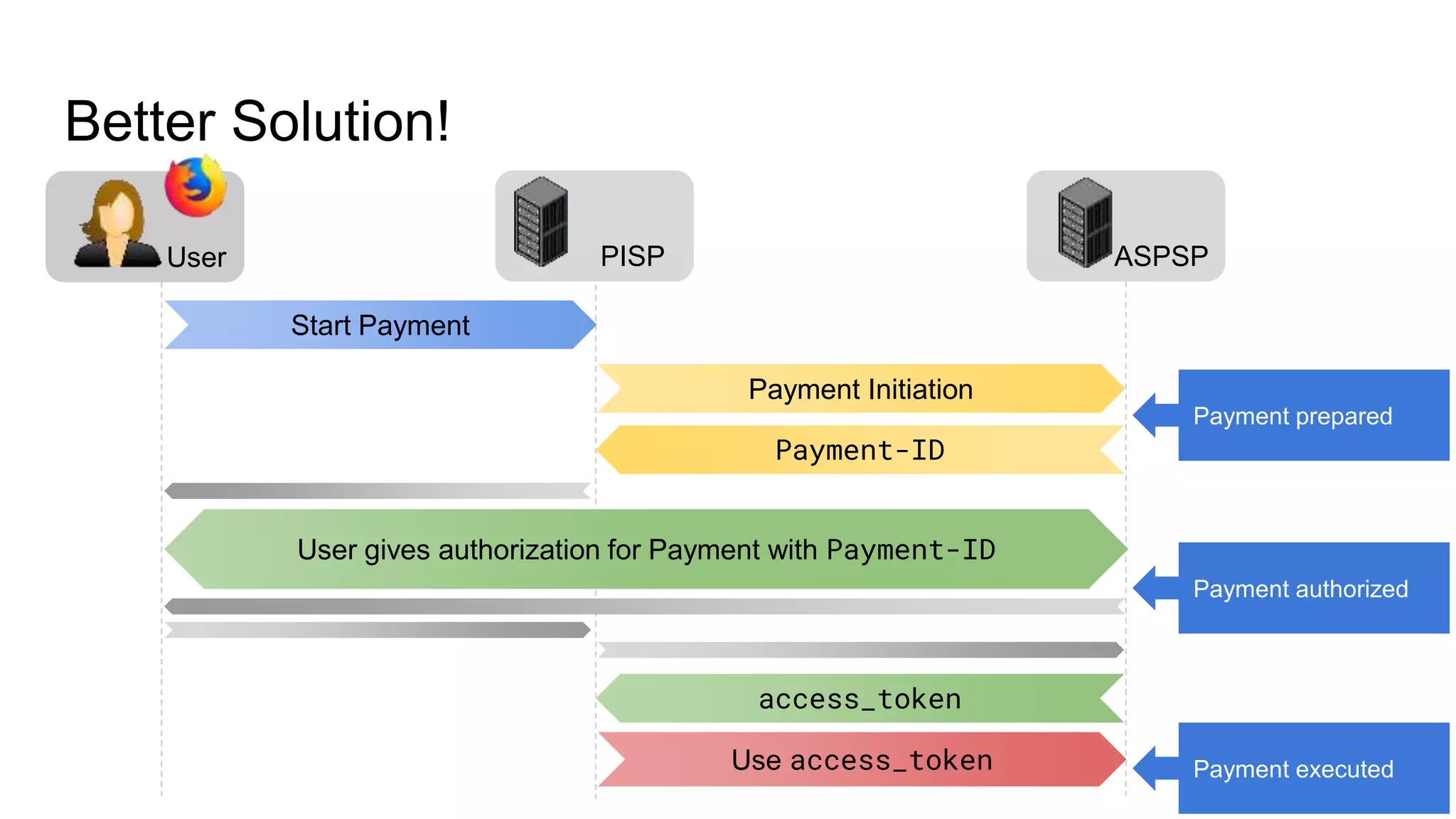
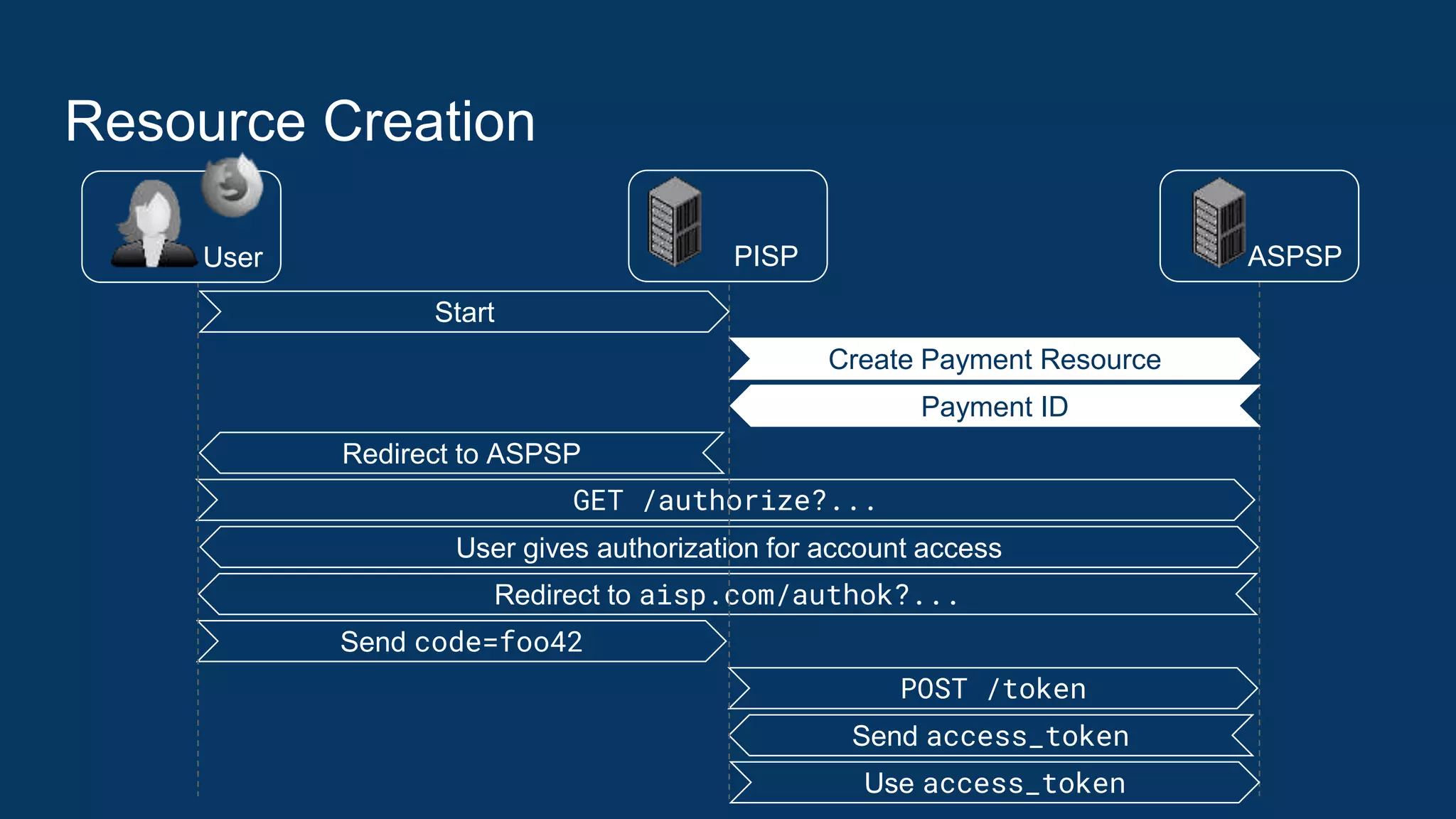
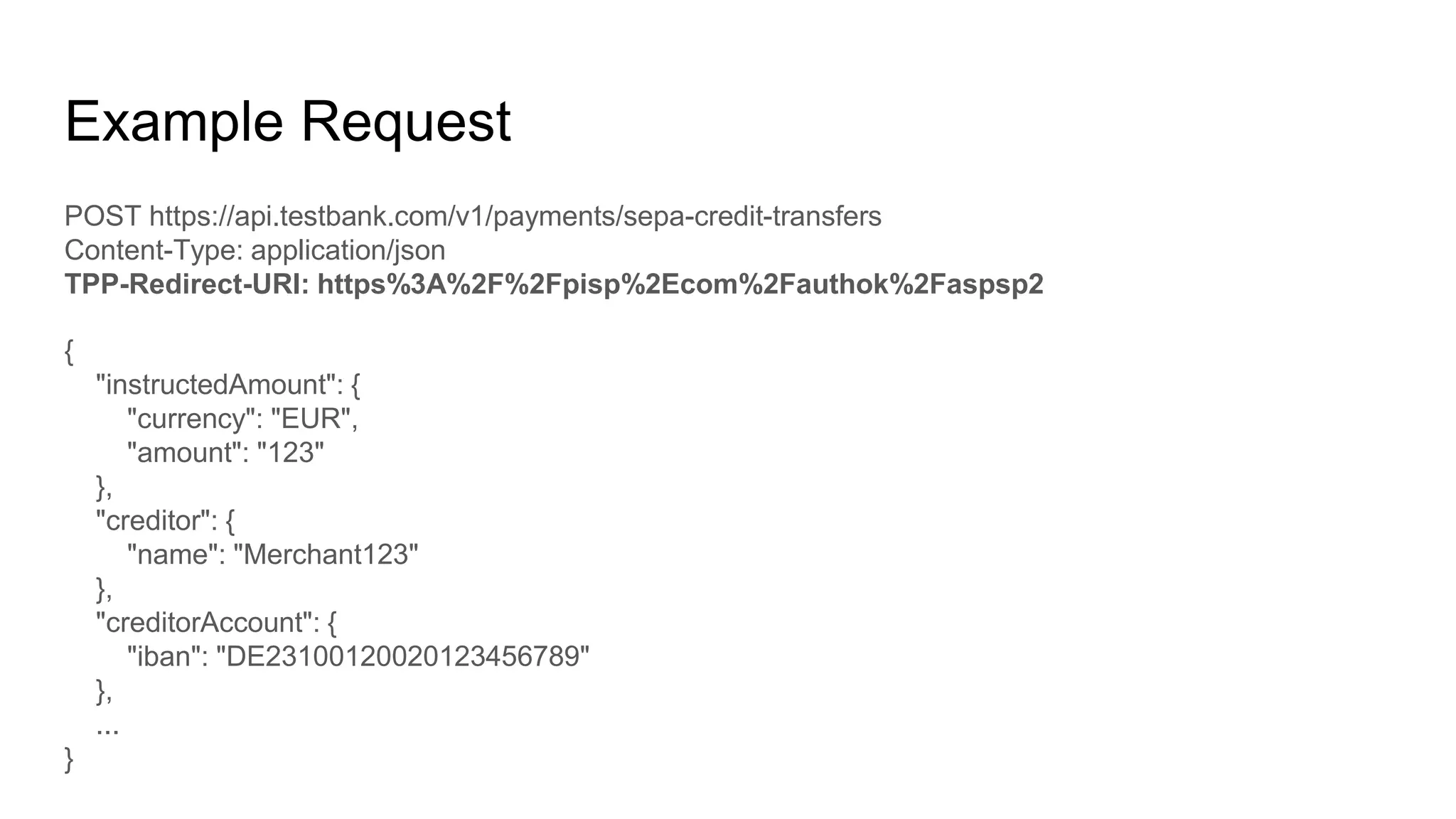
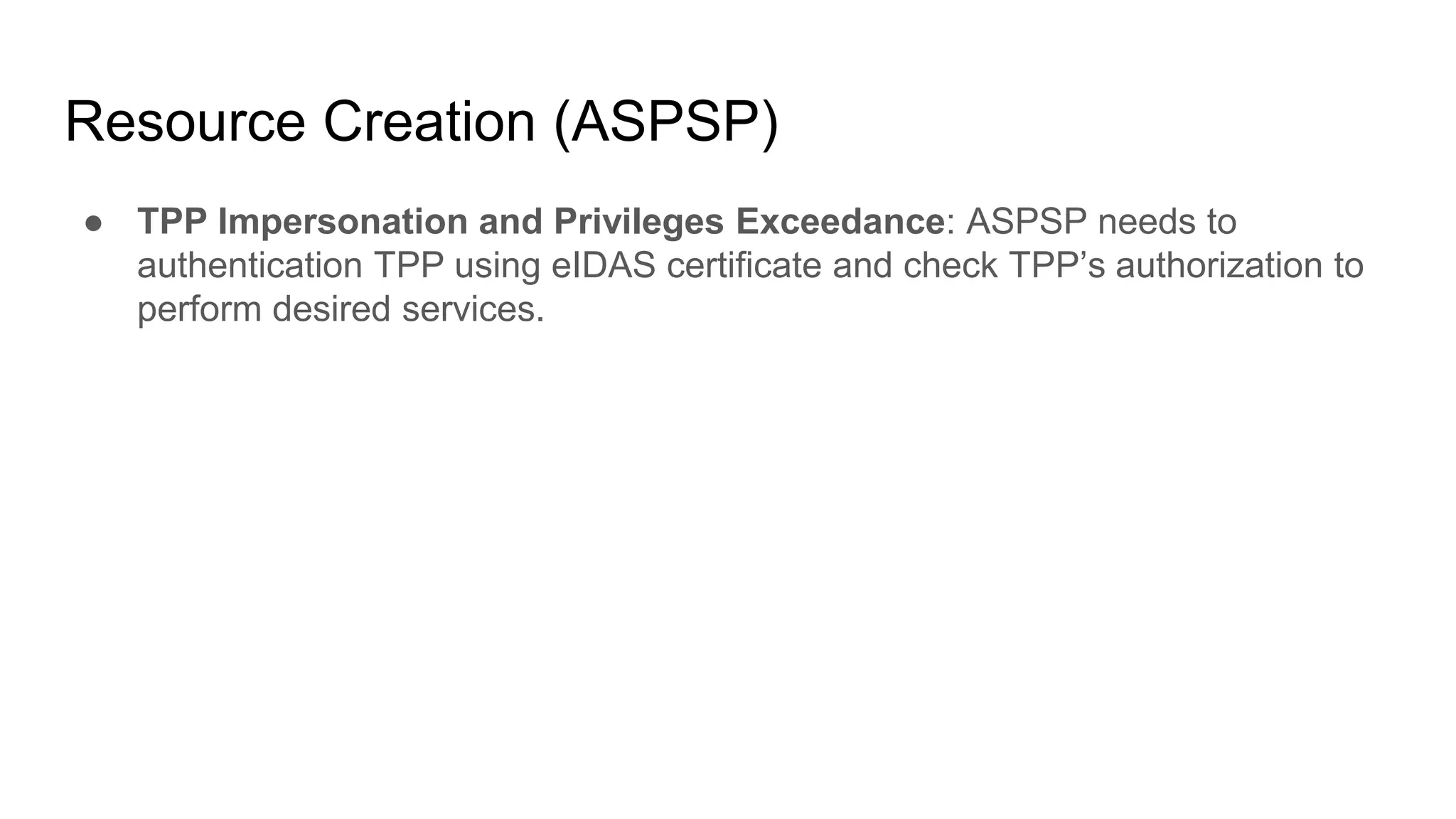
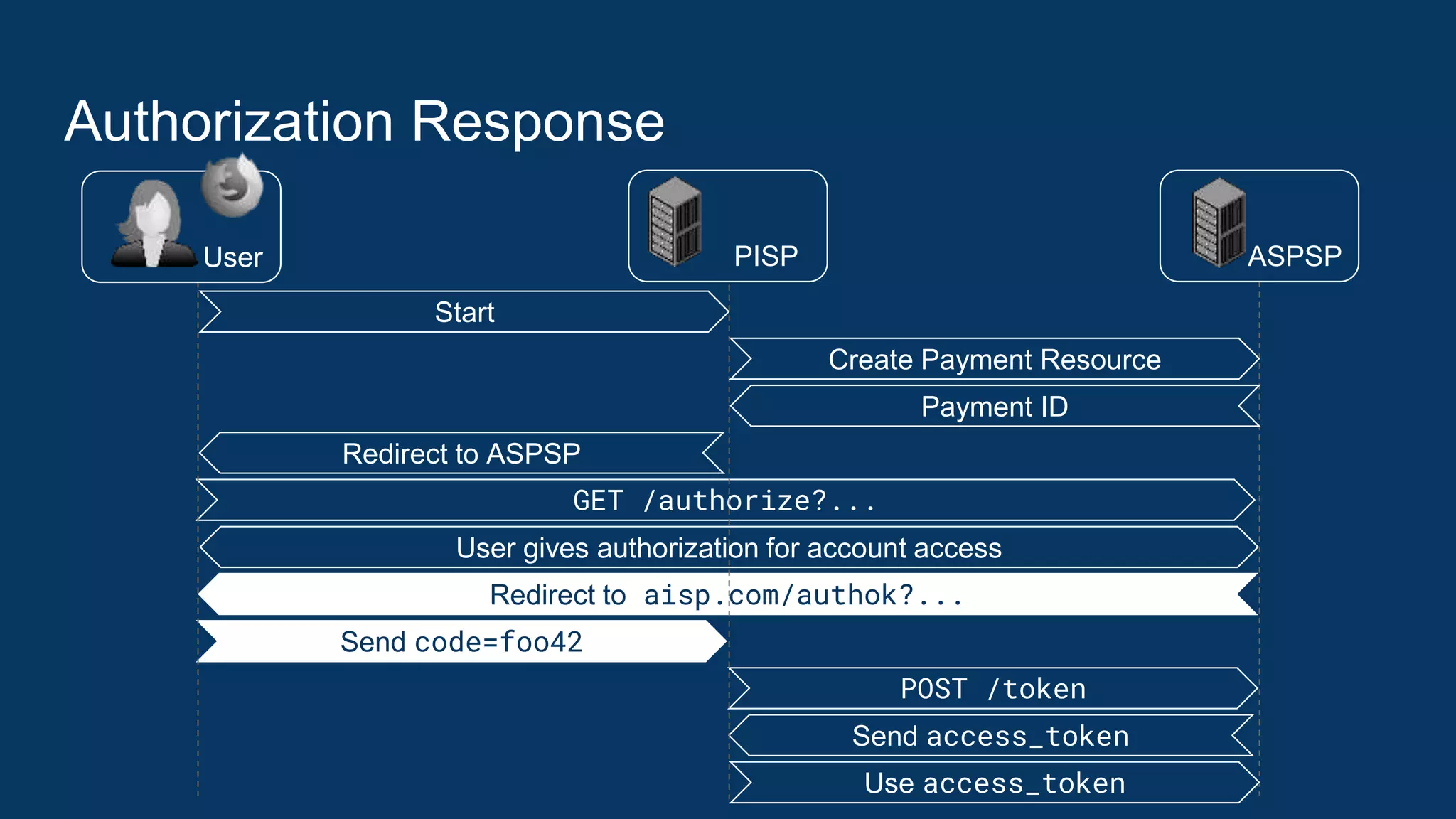
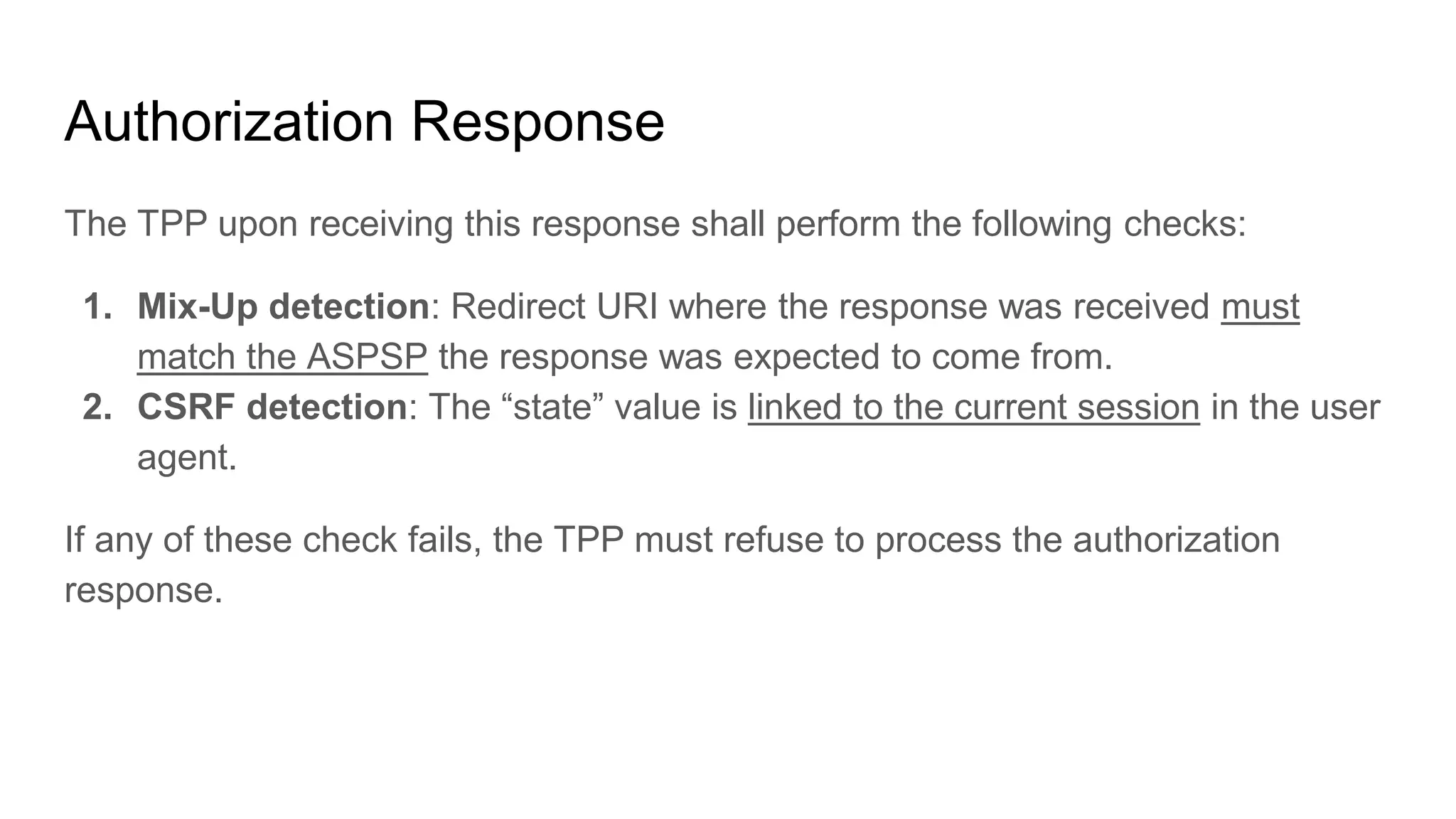
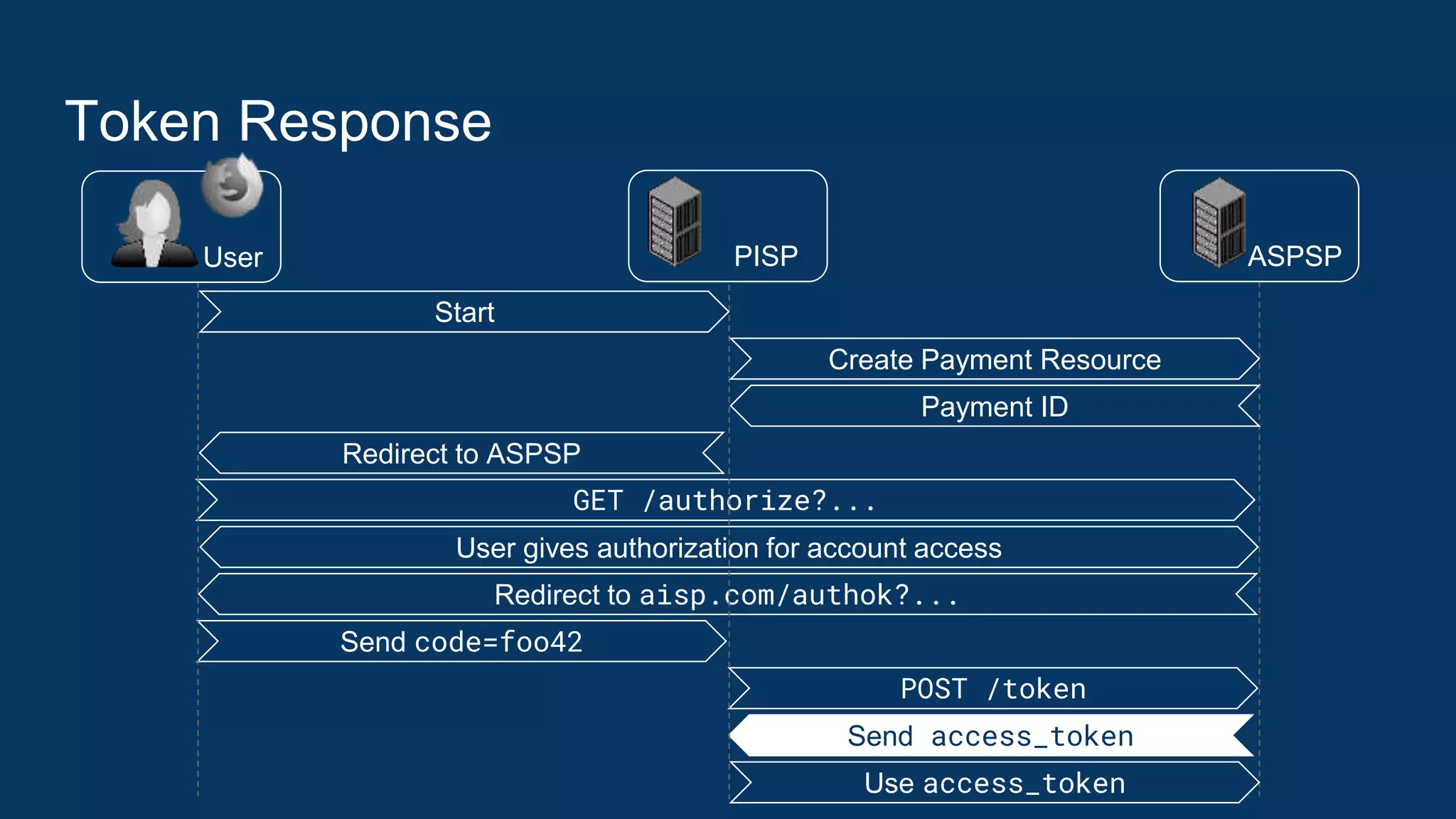
The document outlines security recommendations for implementing OAuth 2.0 in the context of payment initiation and account access using the SCA mode. Key focus areas include the separation of authentication and authorization, measures to prevent security threats such as impersonation and replay attacks, and the need for TPP (Third Party Provider) authentication through eIDAS certificates. Detailed procedures for managing authorization requests, token issuance, and API interaction are provided to mitigate risks associated with cross-browser attacks and unauthorized access.









![Example oauth-authorization-server
{
"issuer": "https://as.testbank.com",
"authorization_endpoint": "https://as.example.com/authorize",
"token_endpoint": "https://as.example.com/token",
"token_endpoint_auth_methods_supported": ["tls_client_auth",”self_signed_tls_client_auth”],
"scopes_supported": ["pis","ais","offline_access"],
"response_types_supported": ["code"],
"grant_types_supported": "authorization_code",
"code_challenge_methods_supported": "S256",
...
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nextgenpsd2oauthscamodesecurityrecommendations2-191025145143/75/NextGenPSD2-OAuth-SCA-Mode-Security-Recommendations-19-2048.jpg)




![Token Request
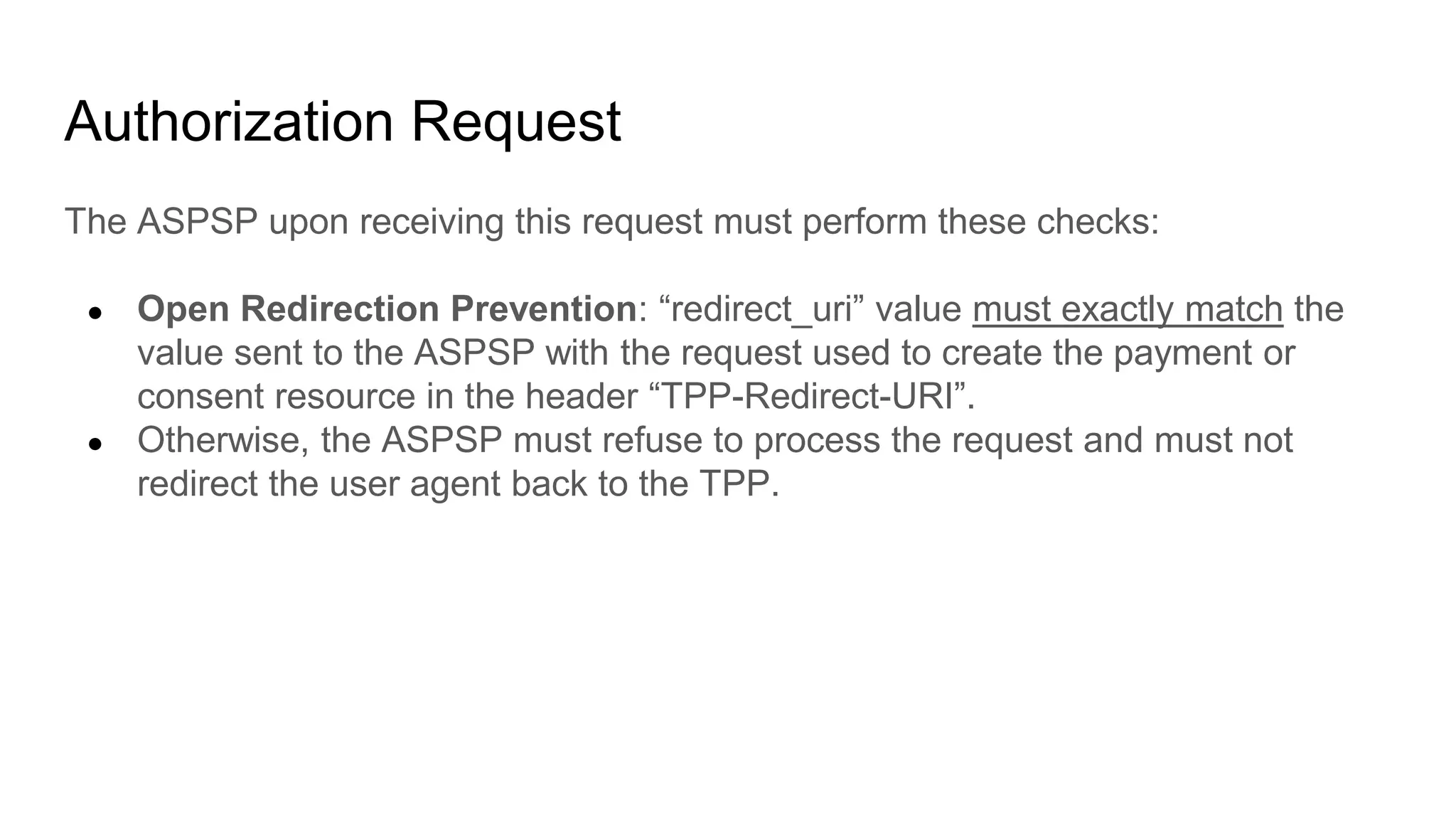
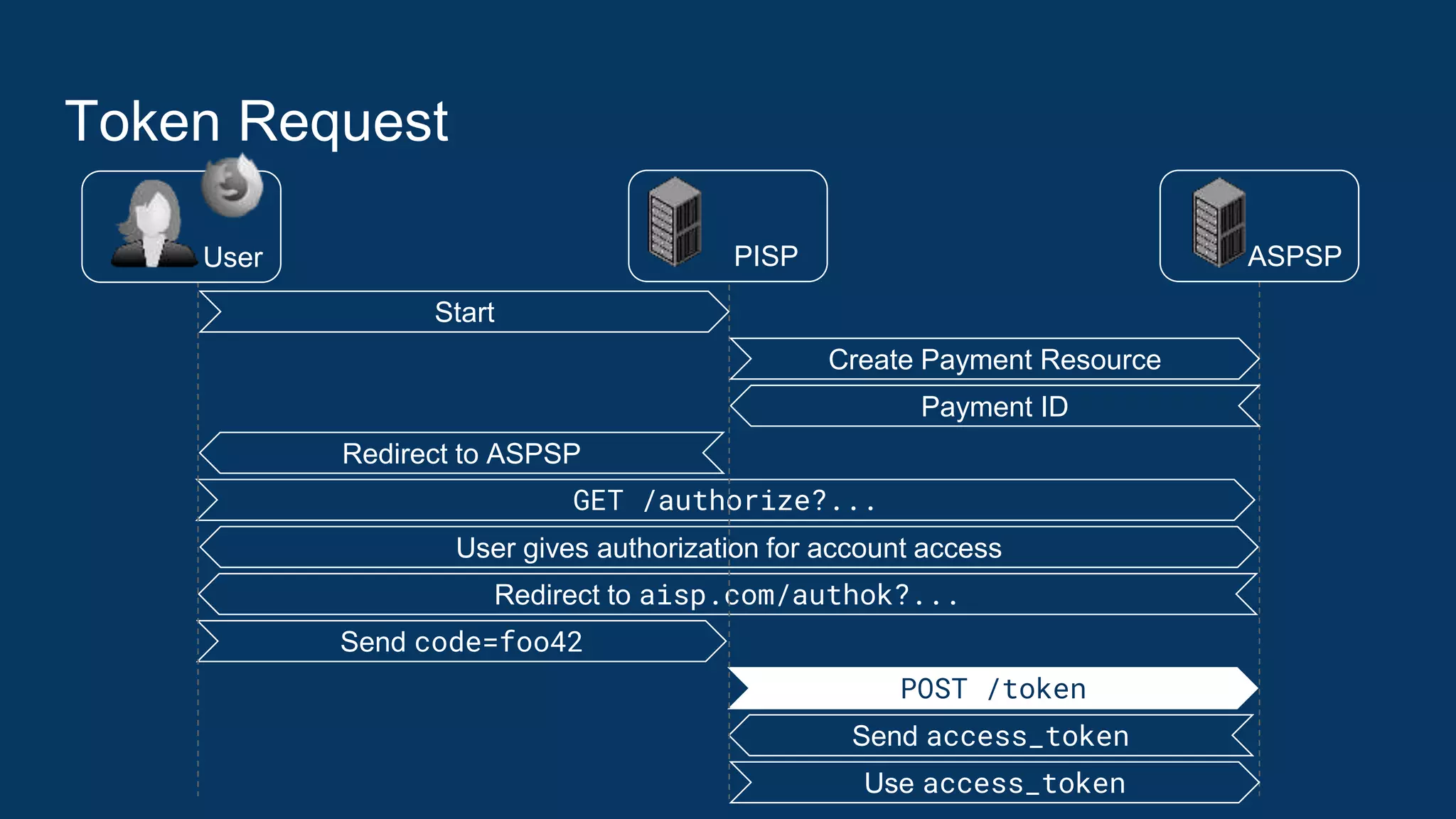
The ASPSP upon receiving the request shall perform the following checks:
1. TPP impersonation detection: Authenticate TPP with eIDAS certificate
2. Code leakage and replay detection: Check that code is bound to the TPP
(client_id), is still valid, and was sent to exactly the redirect URI conveyed in
the “redirect_uri” request parameter.
3. Code injection detection: “code_verifier” value, when hashed with S256,
matches the “code_challenge” value the code parameter is bound to (see
[RFC7636], Section 4.6).
If any of these check fails, the ASPSP must refuse to process the token request.
See [RFC6749], Section 10 and [OAuth 2.0 Security BCP], Section 2.1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nextgenpsd2oauthscamodesecurityrecommendations2-191025145143/75/NextGenPSD2-OAuth-SCA-Mode-Security-Recommendations-28-2048.jpg)



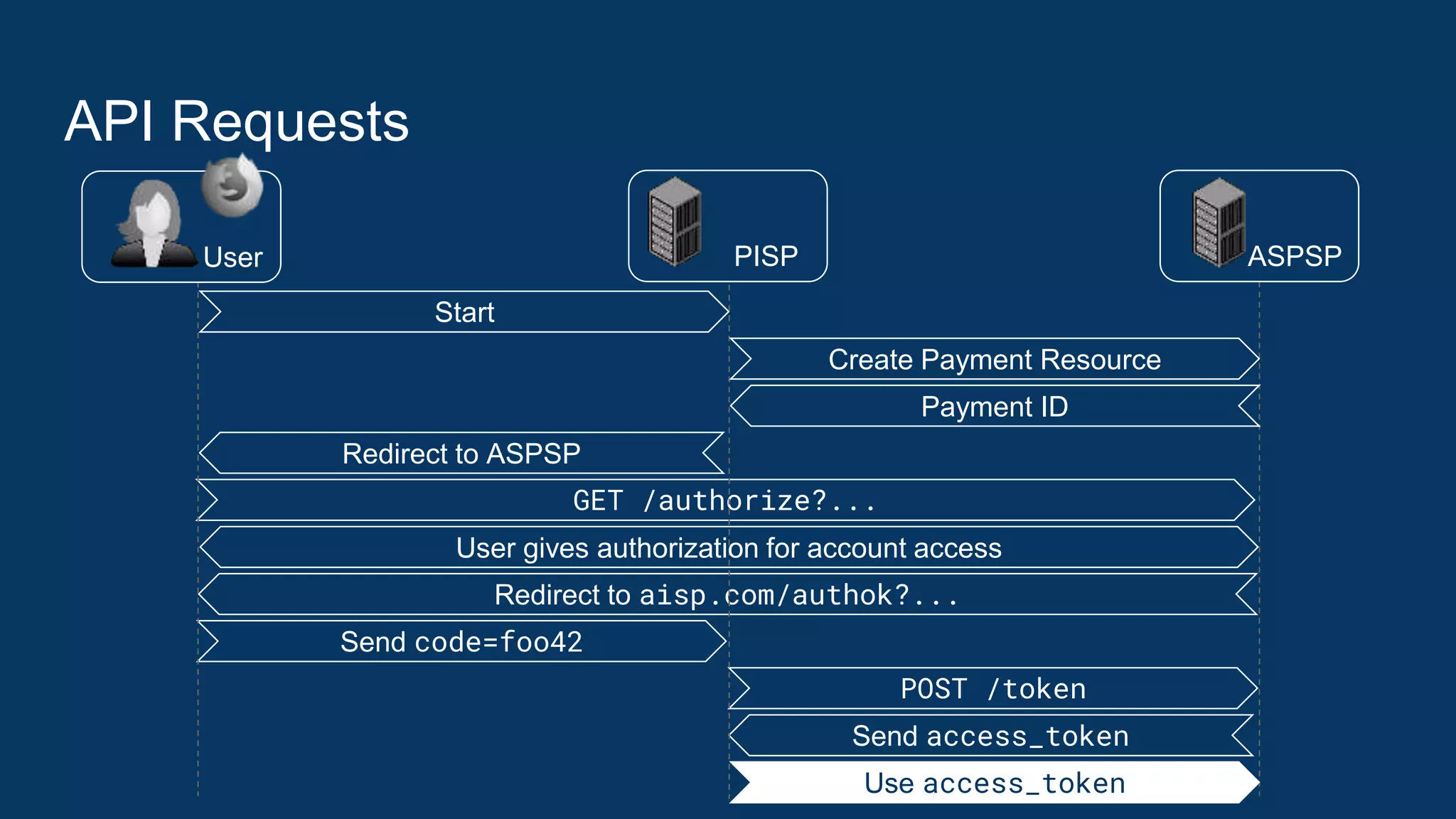
![API Requests
● Access Token Replay Detection
○ On every API request, the TPP shall authenticate using TLS client authentication and its
eIDAS certificate according to [mTLS], Section 3.
○ The resource server must check whether the certificate used for TLS Client Authentication
matches the certificate the access token is bound to (see [mTLS], Section 3).
● Authorization: The ASPSP must also check that the access token is still
valid and whether the permission associated with the access token entitles
the TPP to perform the specific request.
● If any of these checks fails, the request must be refused by responding with a
suitable HTTP Status code.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nextgenpsd2oauthscamodesecurityrecommendations2-191025145143/75/NextGenPSD2-OAuth-SCA-Mode-Security-Recommendations-34-2048.jpg)