The document provides an overview of protecting web APIs using OAuth 2.0, focusing on the use of bearer tokens to authenticate requests. It details the handling of token statuses such as missing, invalid, or insufficient privileges, and outlines two types of token encodings. Additionally, it covers the OAuth 2.0 grant types, the role of authorization servers in issuing tokens, and introduces OpenID Connect as an identity layer on top of OAuth 2.0.

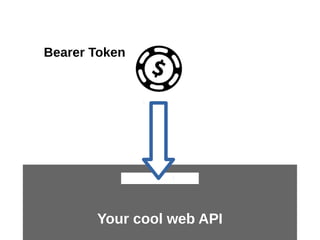
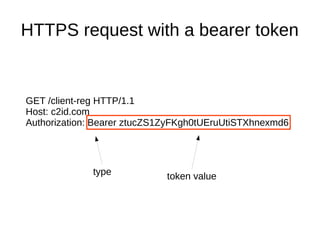




![To learn more about
bearer token usage
See RFC 6750
[ http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6750 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oauth2-export-141023142241-conversion-gate02/85/Protecting-web-APIs-with-OAuth-2-0-8-320.jpg)


![JSON Web Tokens (JWT)
Header
{ "alg": "RS256", "kid": "1" }
Claims
{ "sub": "alice",
"cid": "000123",
"iss": "https://connect2id.com",
"exp": 1414065134,
"iat": 1414064534,
"scp": [ "read", "write", "admin" ]
}
Signature (RSA)
fBZW6U9r7M53fwhoEtC9
Bxi8U1ytQvpy8pmHylvvvhEZimluNkwmDXWIoHuXIgX9ZfqMp9layftbFE7DVeo3wDpGNM9UtOo8Cc](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oauth2-export-141023142241-conversion-gate02/85/Protecting-web-APIs-with-OAuth-2-0-13-320.jpg)
![To learn more about JWT
See draft-ietf-oauth-json-web-token-29
[ http://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-ietf-oauth-json-web-token-29 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oauth2-export-141023142241-conversion-gate02/85/Protecting-web-APIs-with-OAuth-2-0-14-320.jpg)


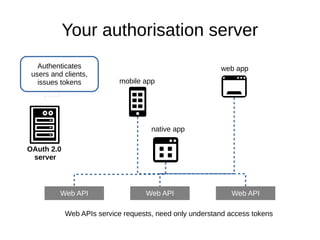

![To learn more about OAuth 2.0
See RFC 6749
[ http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6749 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oauth2-export-141023142241-conversion-gate02/85/Protecting-web-APIs-with-OAuth-2-0-19-320.jpg)

![ID token claims
{
"sub" : "alice",
"iss" : "https://connect2id.com",
"iat" : 1414076589,
"exp" : 1414077489,
"aud" : [ "000123" ],
"ip_address" : "10.20.30.40",
"acr" : "1",
"amr" : [ "ldap" ]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oauth2-export-141023142241-conversion-gate02/85/Protecting-web-APIs-with-OAuth-2-0-21-320.jpg)
![To learn more about
OpenID Connect
See
OpenID Connect 1.0 Core
OpenID Connect 1.0 Discovery
OpenID Connect 1.0 Dynamic Registration
OpenID Connect 1.0 Session Management
[ http://openid.net/connect/ ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oauth2-export-141023142241-conversion-gate02/85/Protecting-web-APIs-with-OAuth-2-0-22-320.jpg)