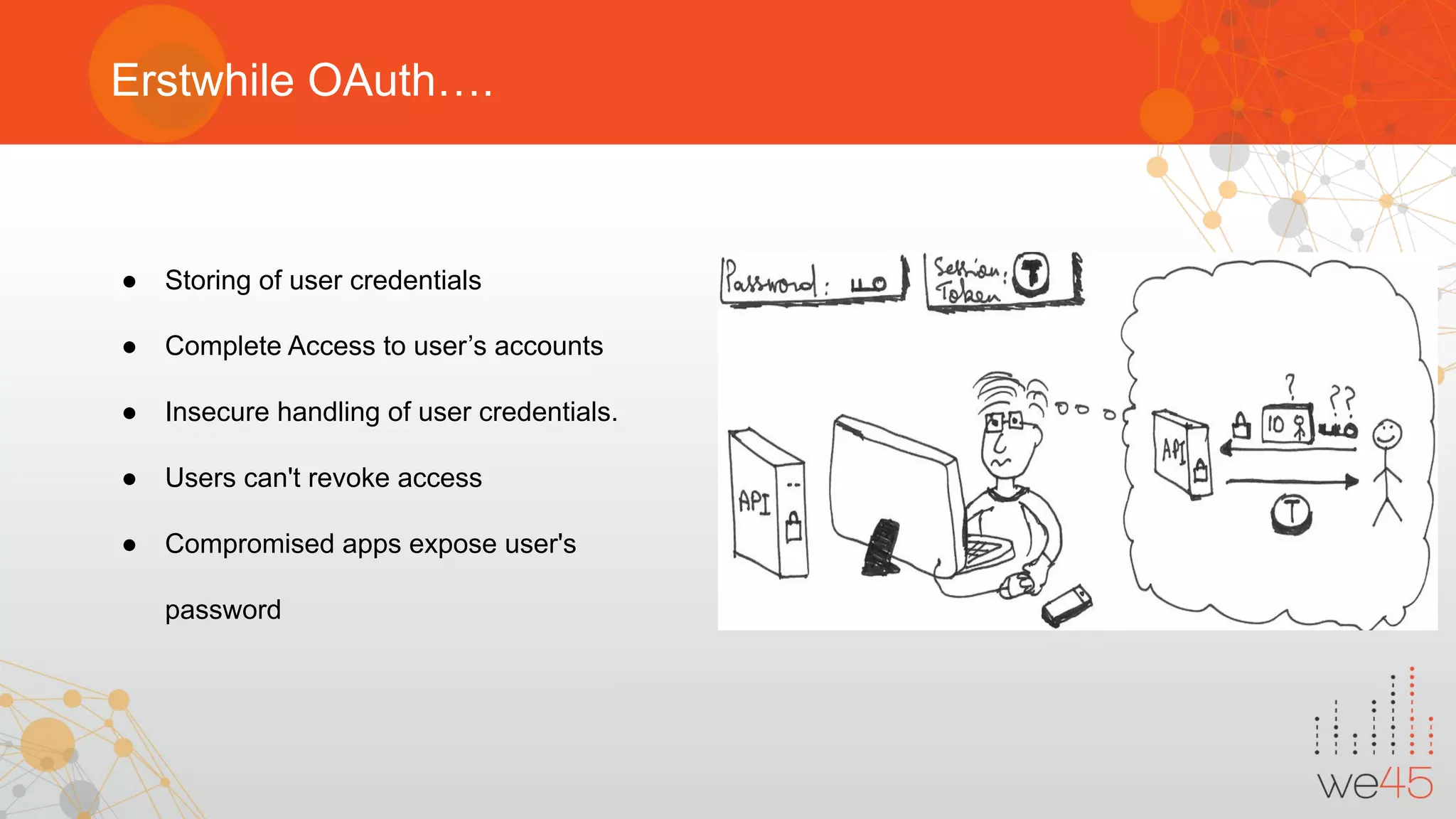
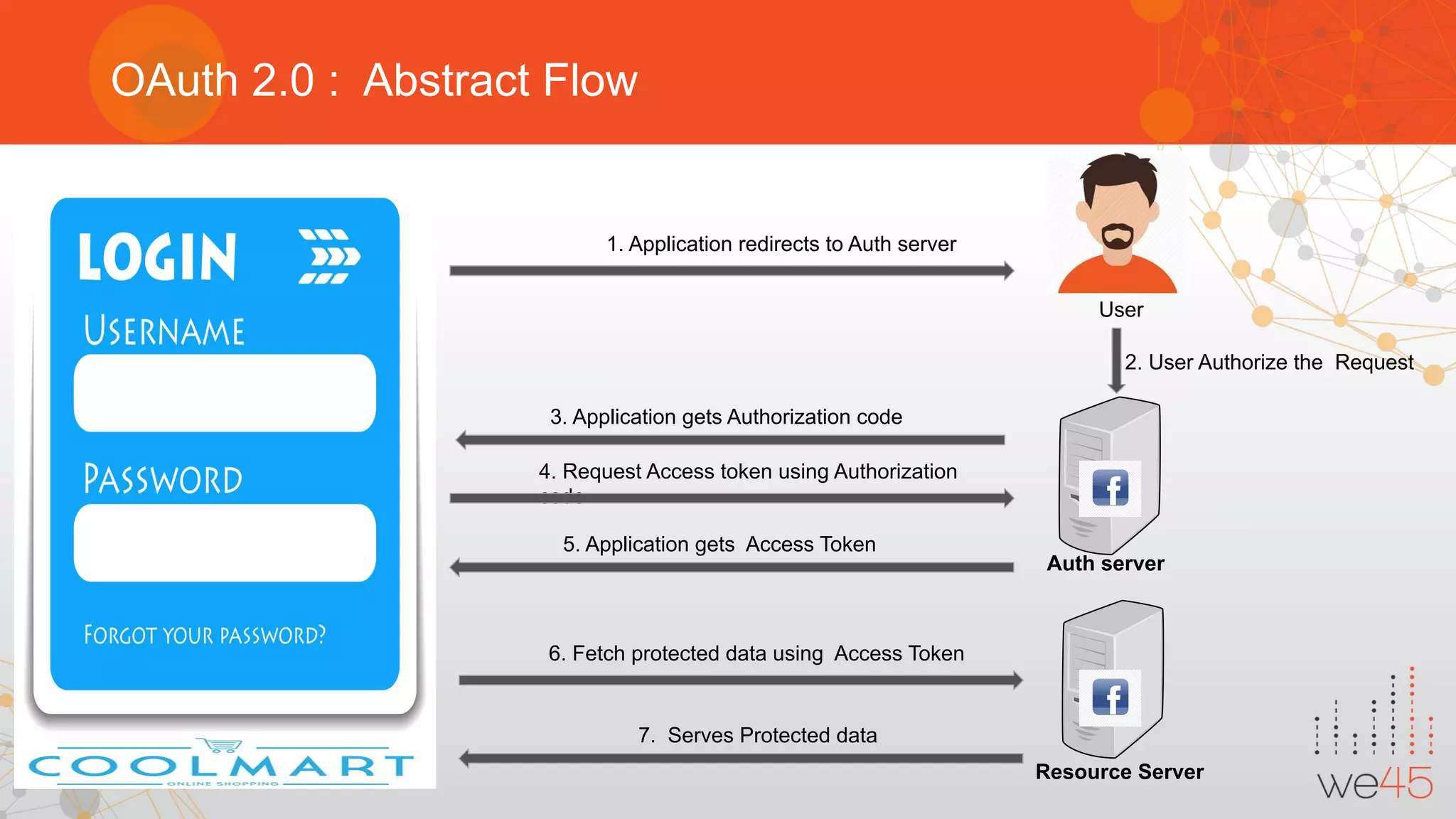
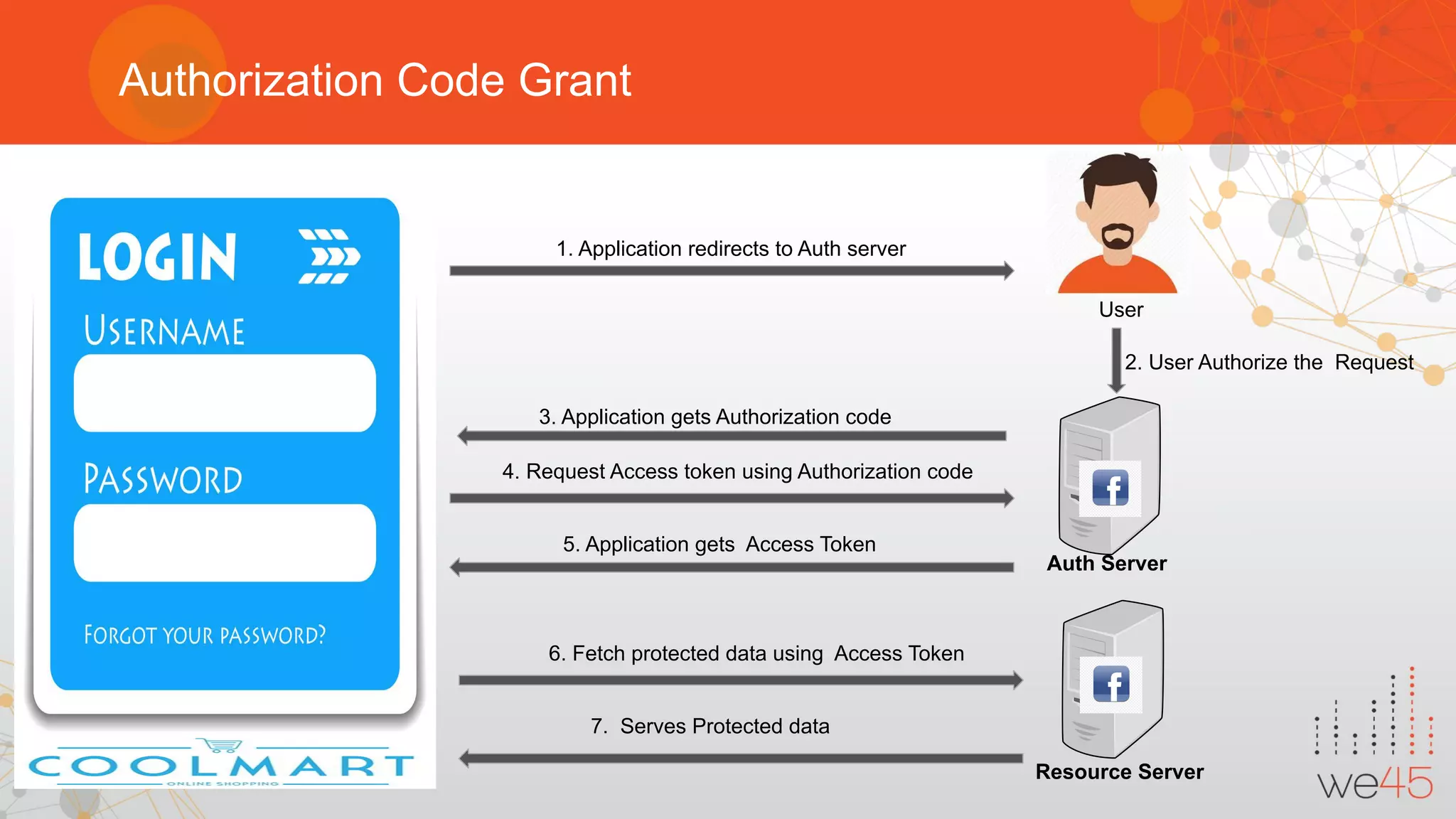
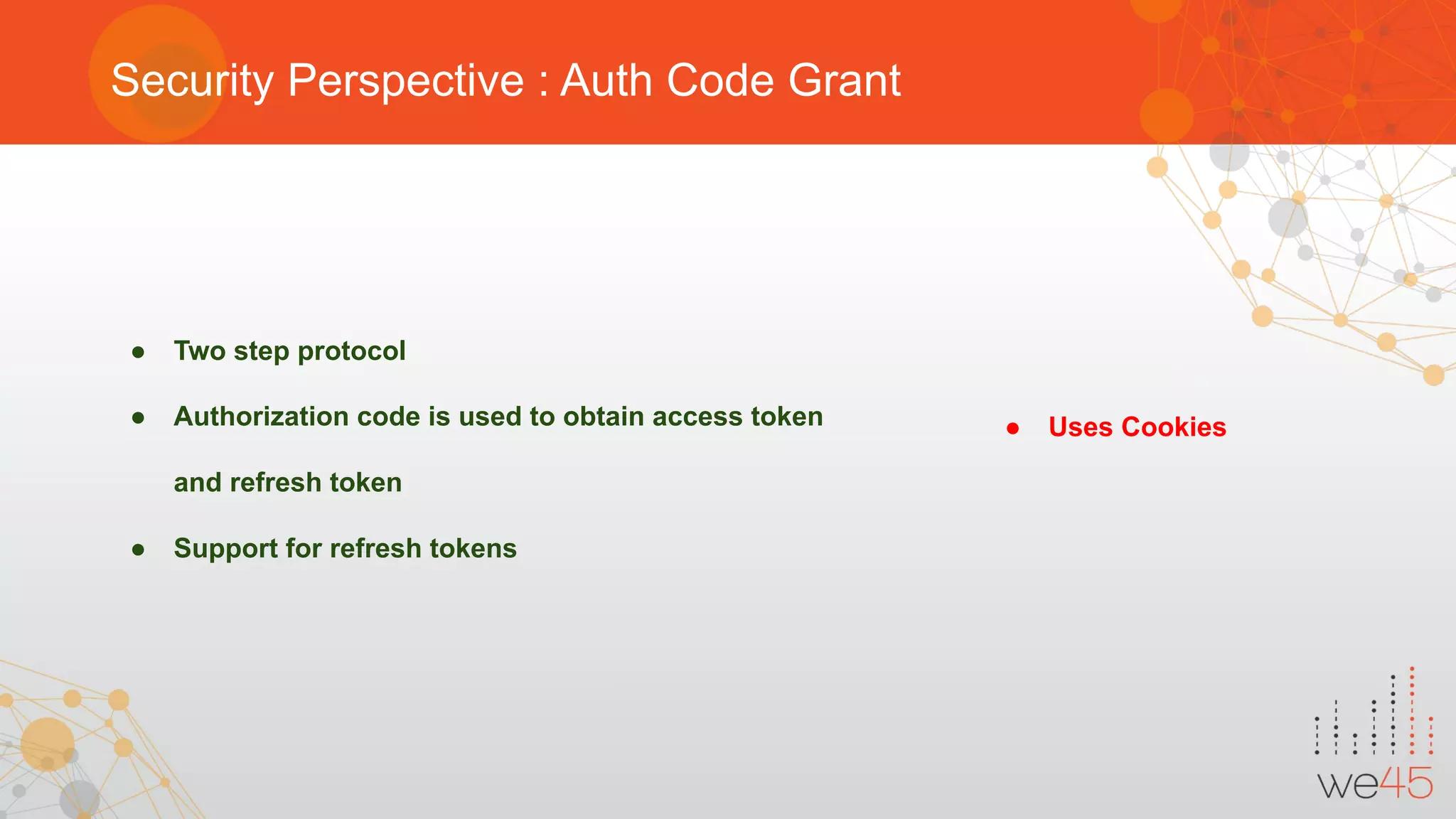
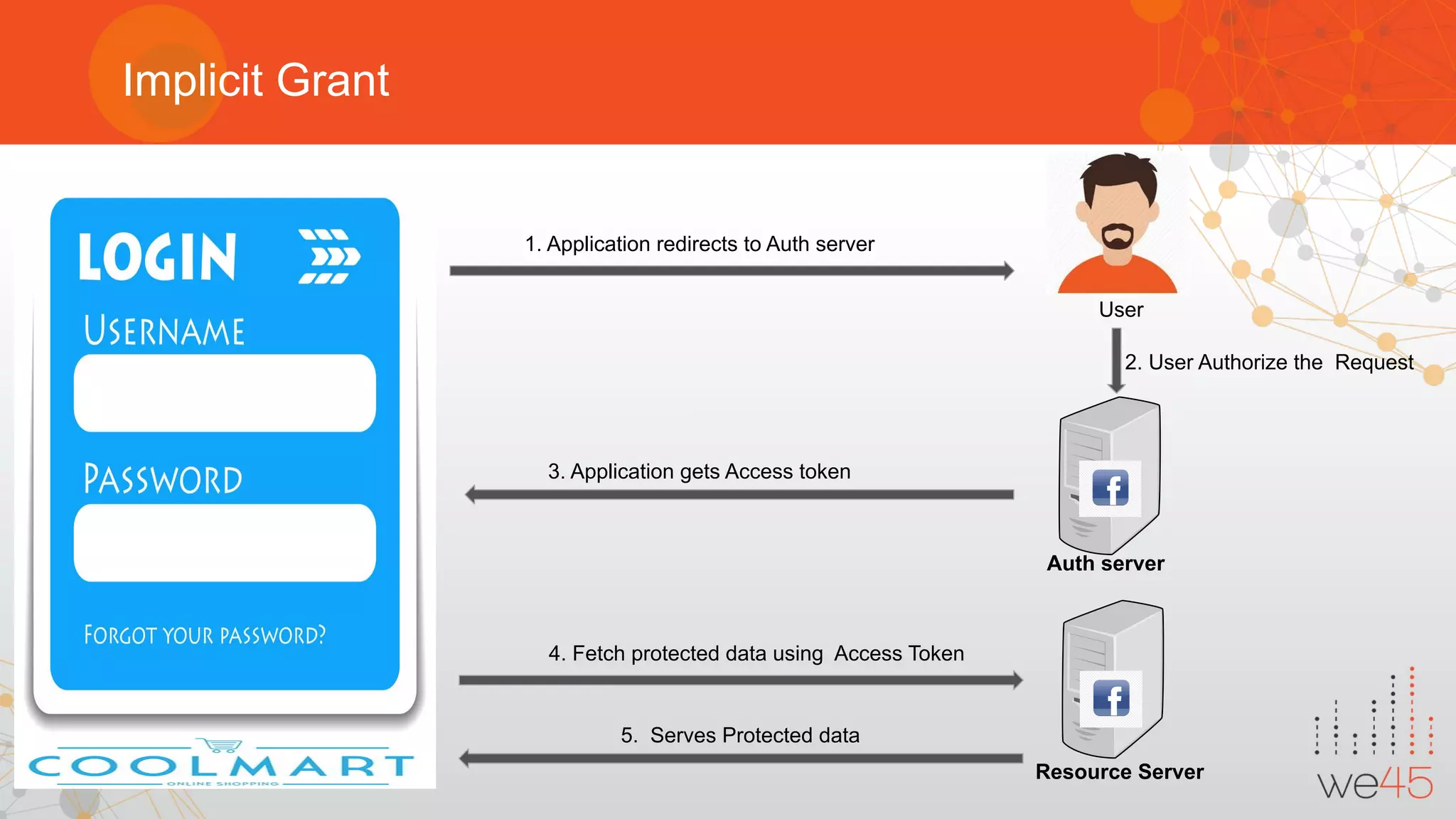
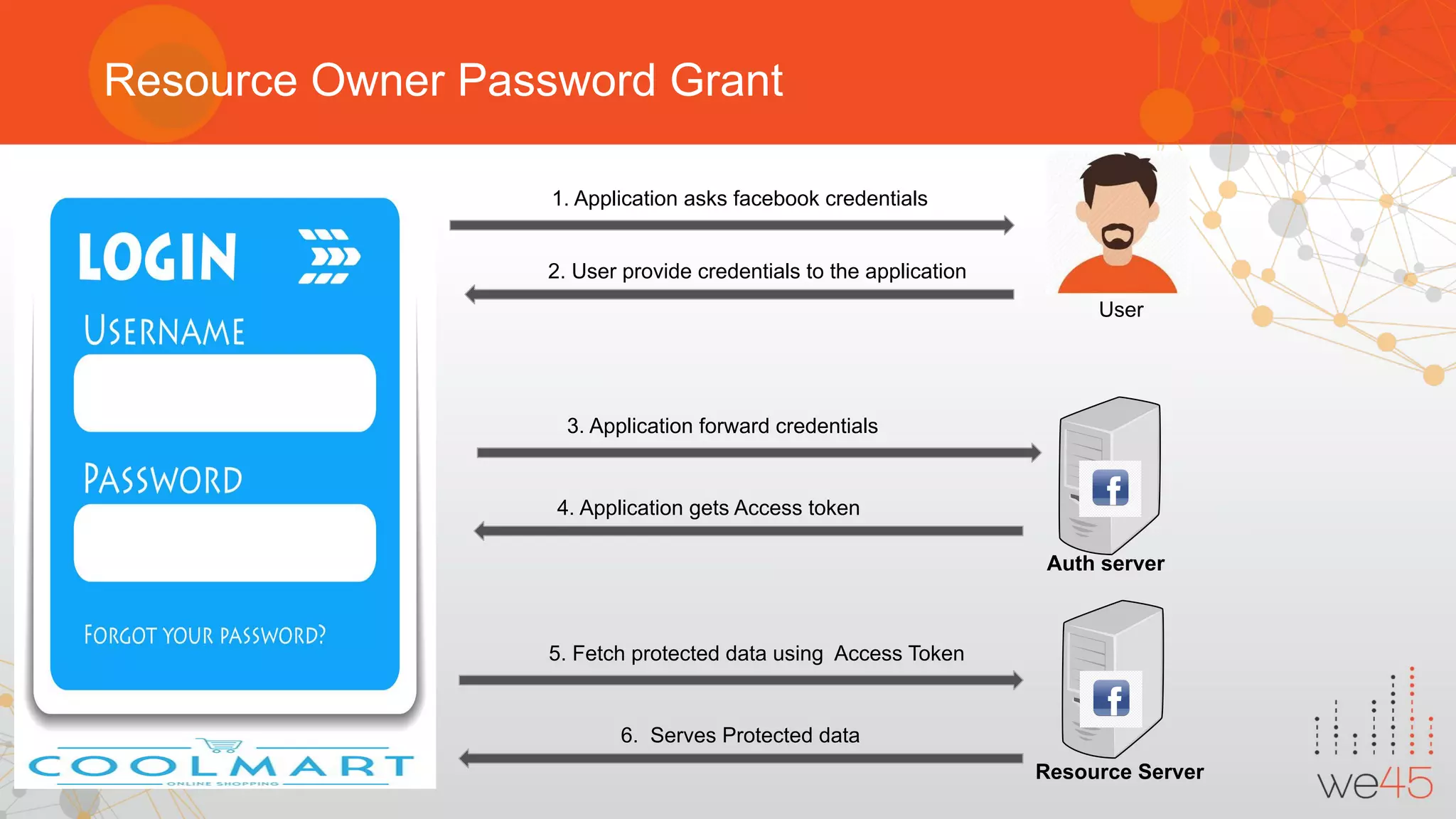
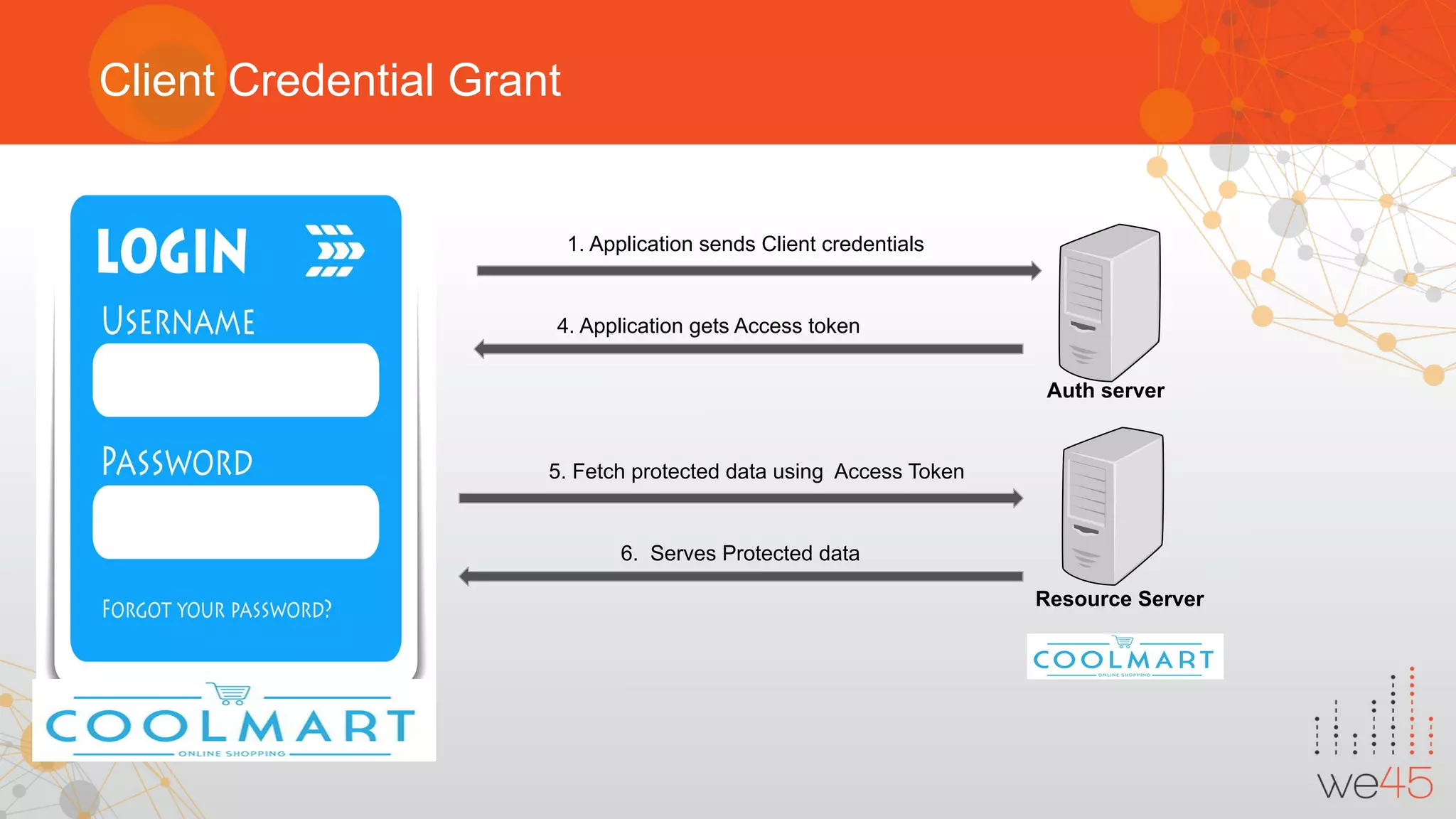
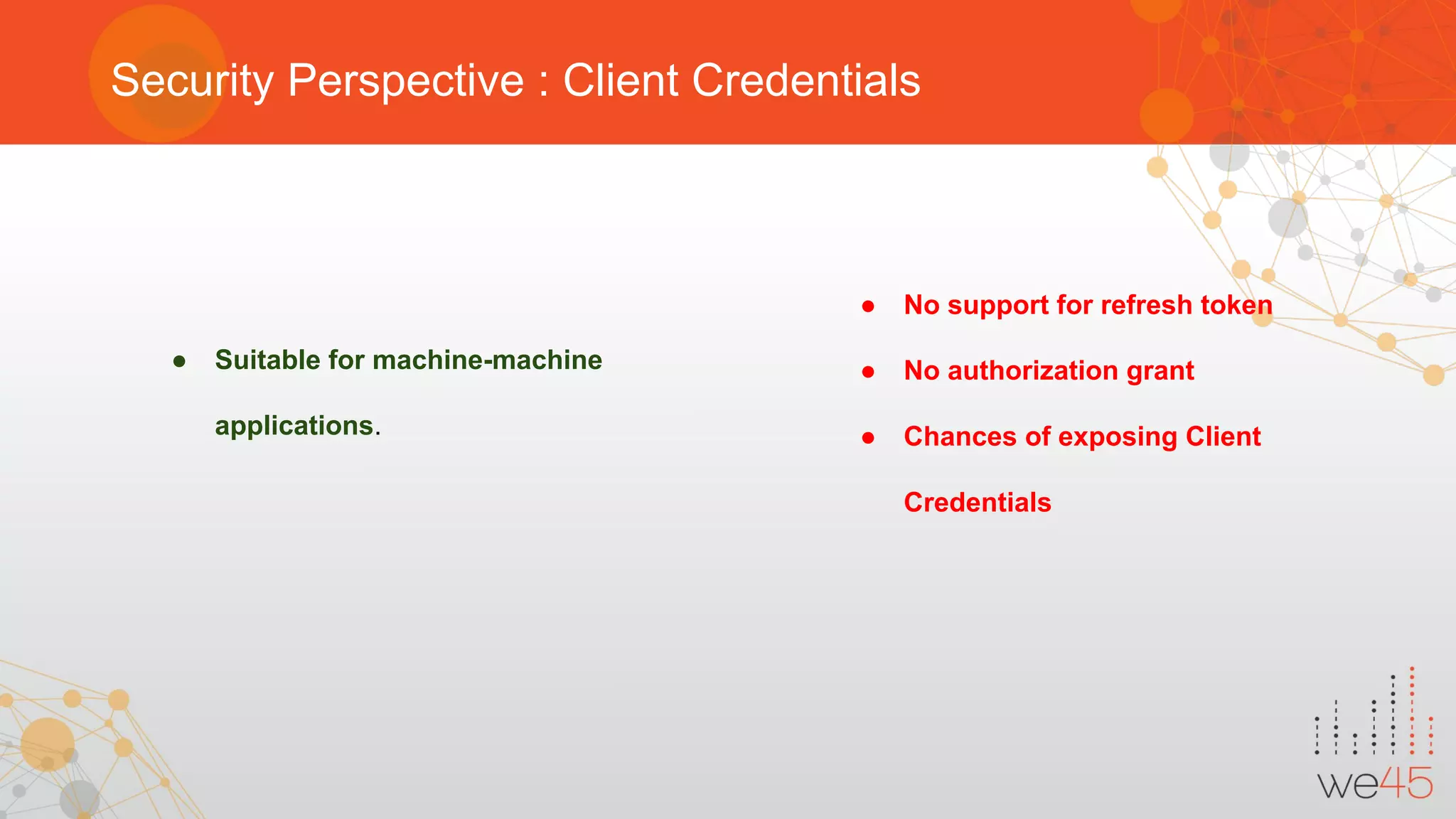
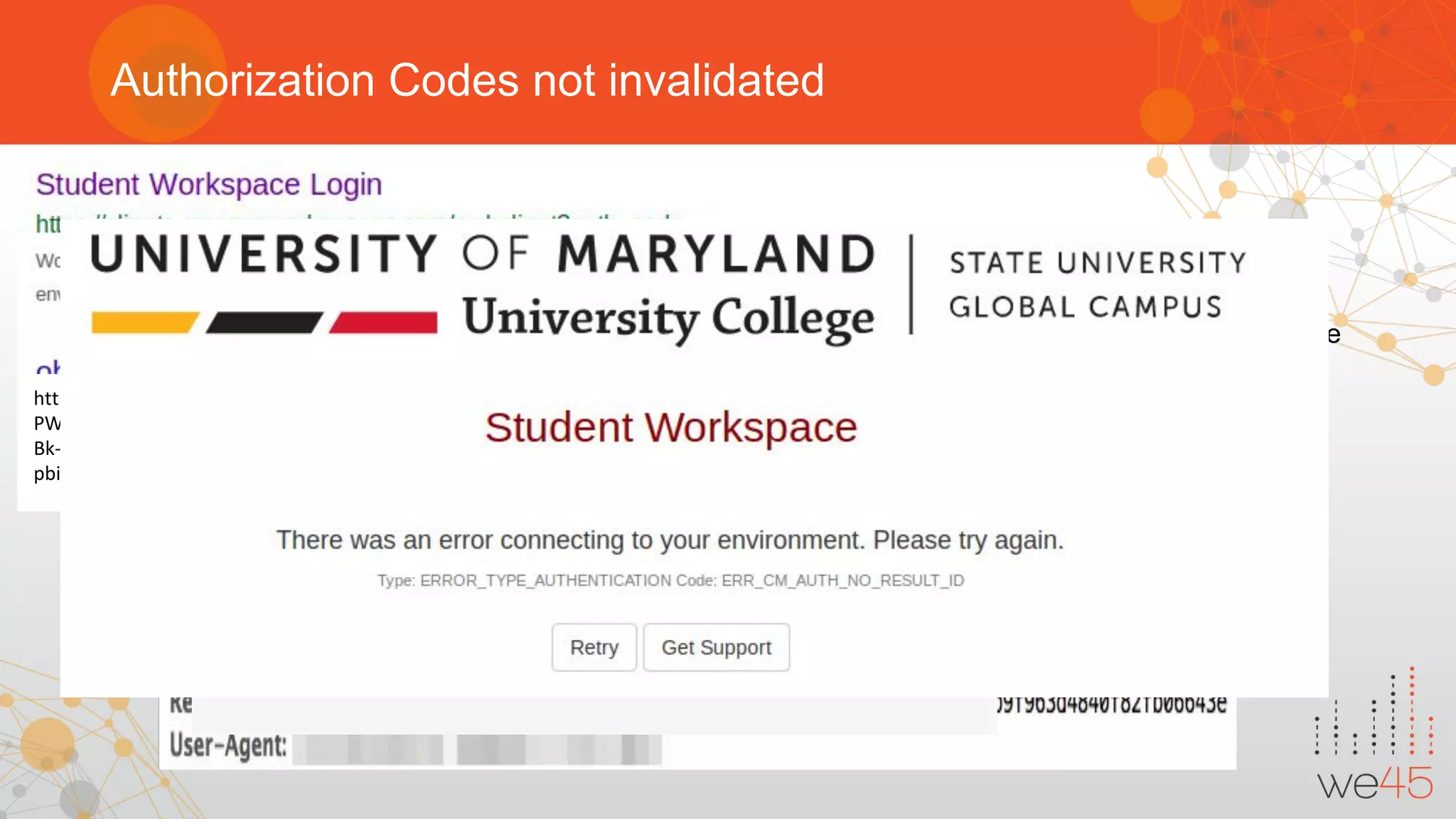
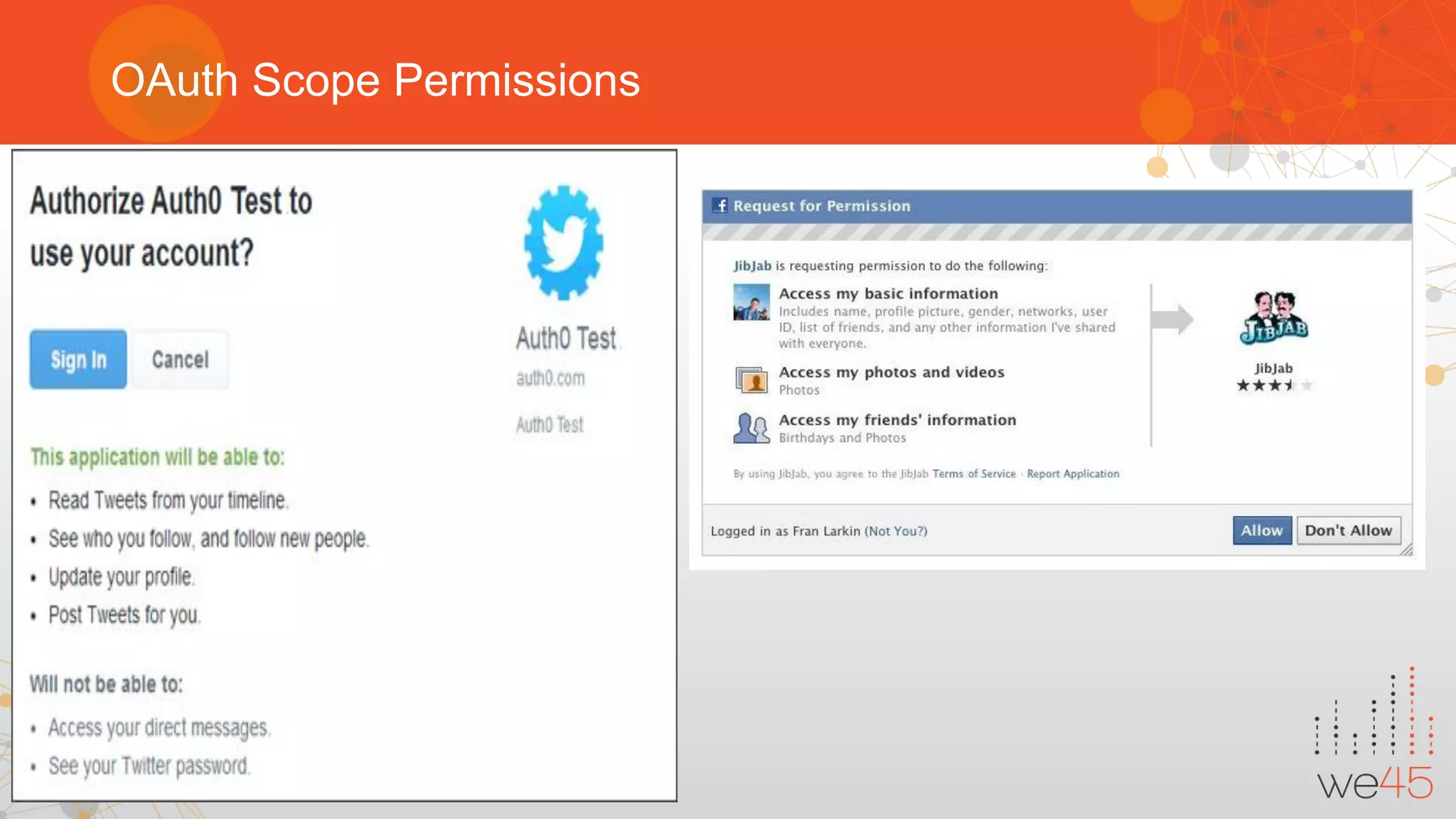
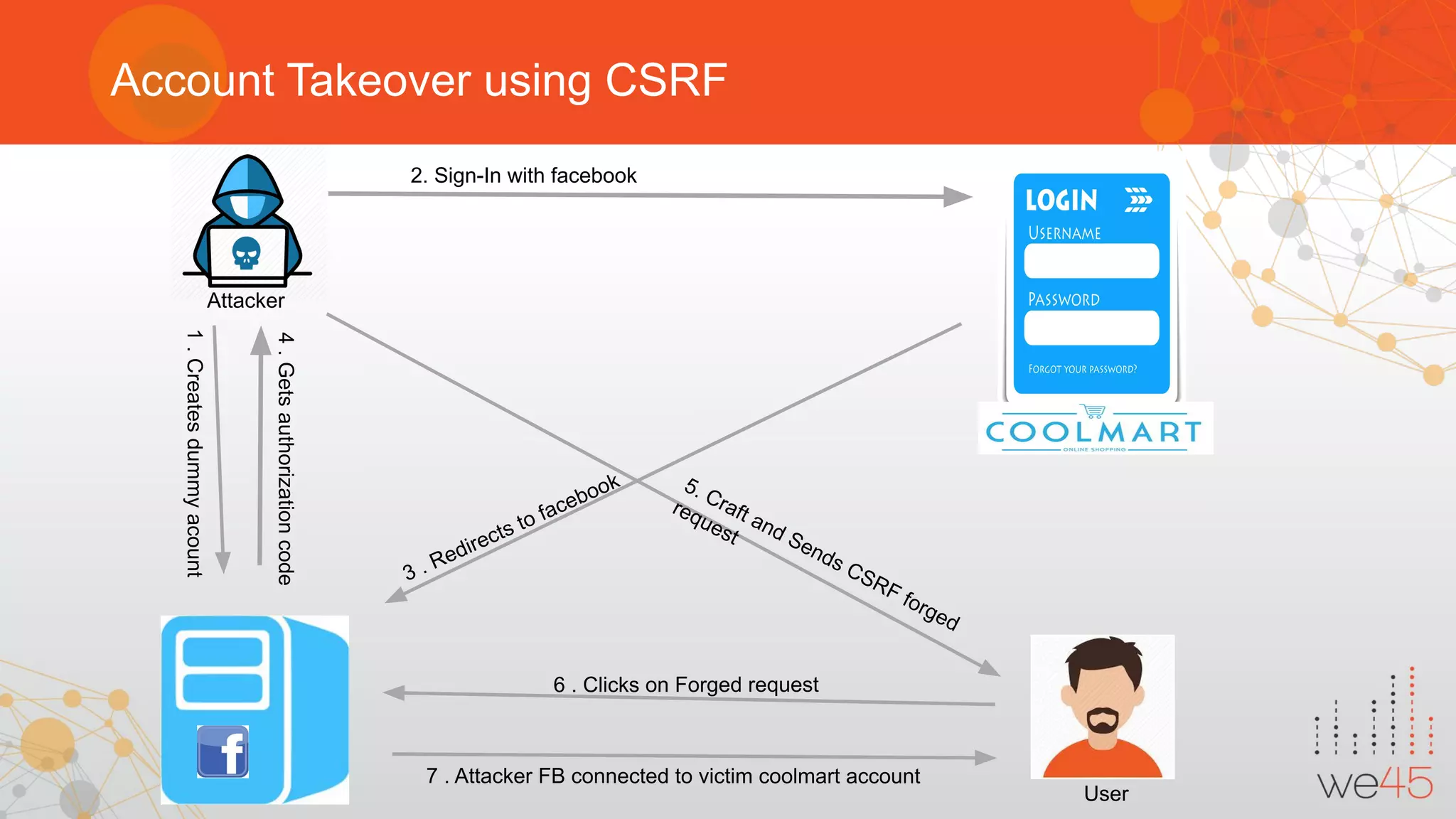
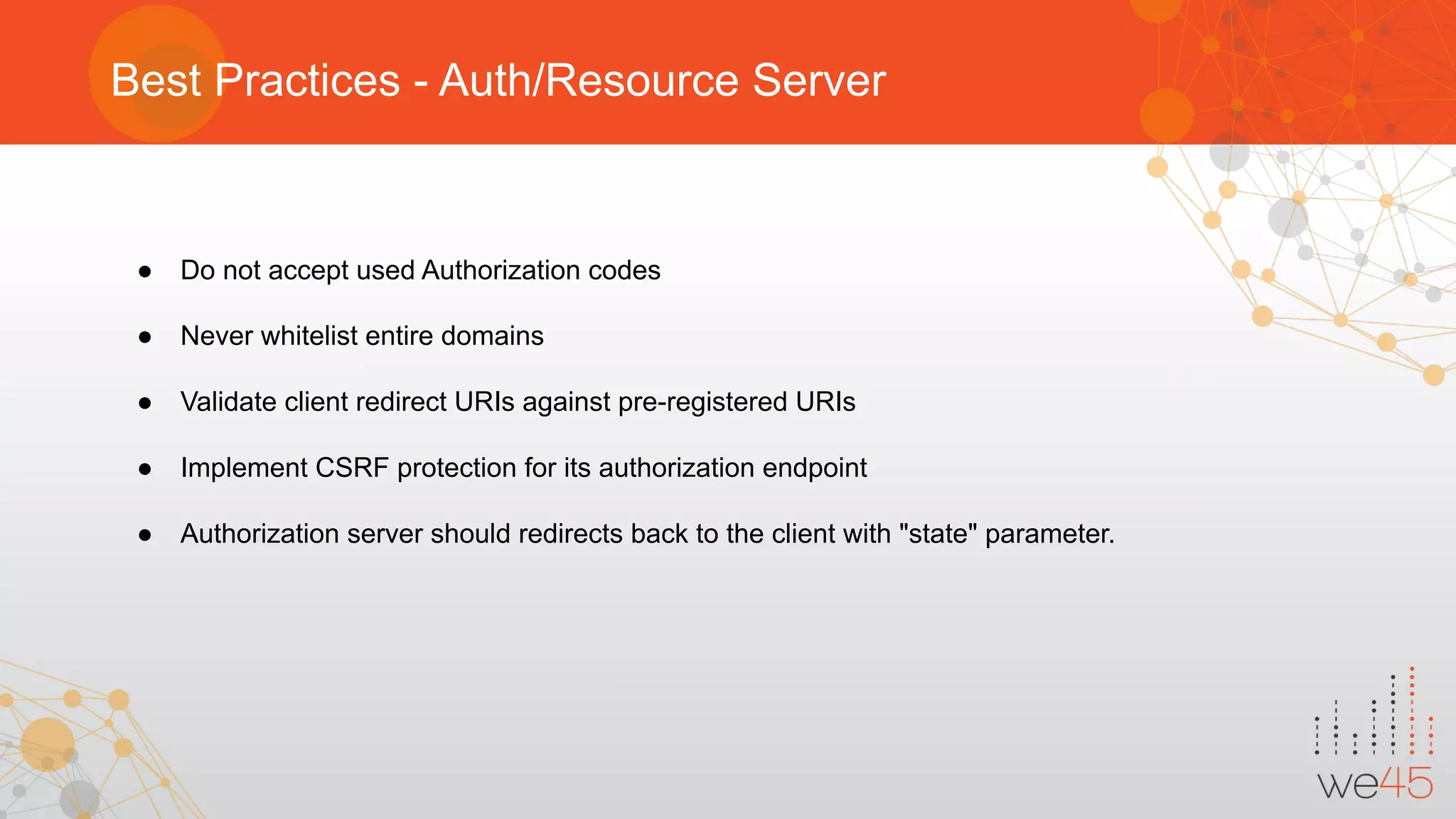
The document provides an overview of OAuth 2.0 authorization framework and discusses common security issues. It begins with introducing the speaker and their background in security. The main topics covered include the history and core elements of OAuth, common grant types and flows, and vulnerabilities like insecure storage of secrets, CSRF attacks during authorization, scope permission issues, and account takeover risks. Best practices for clients and authorization servers to mitigate these threats are also outlined.