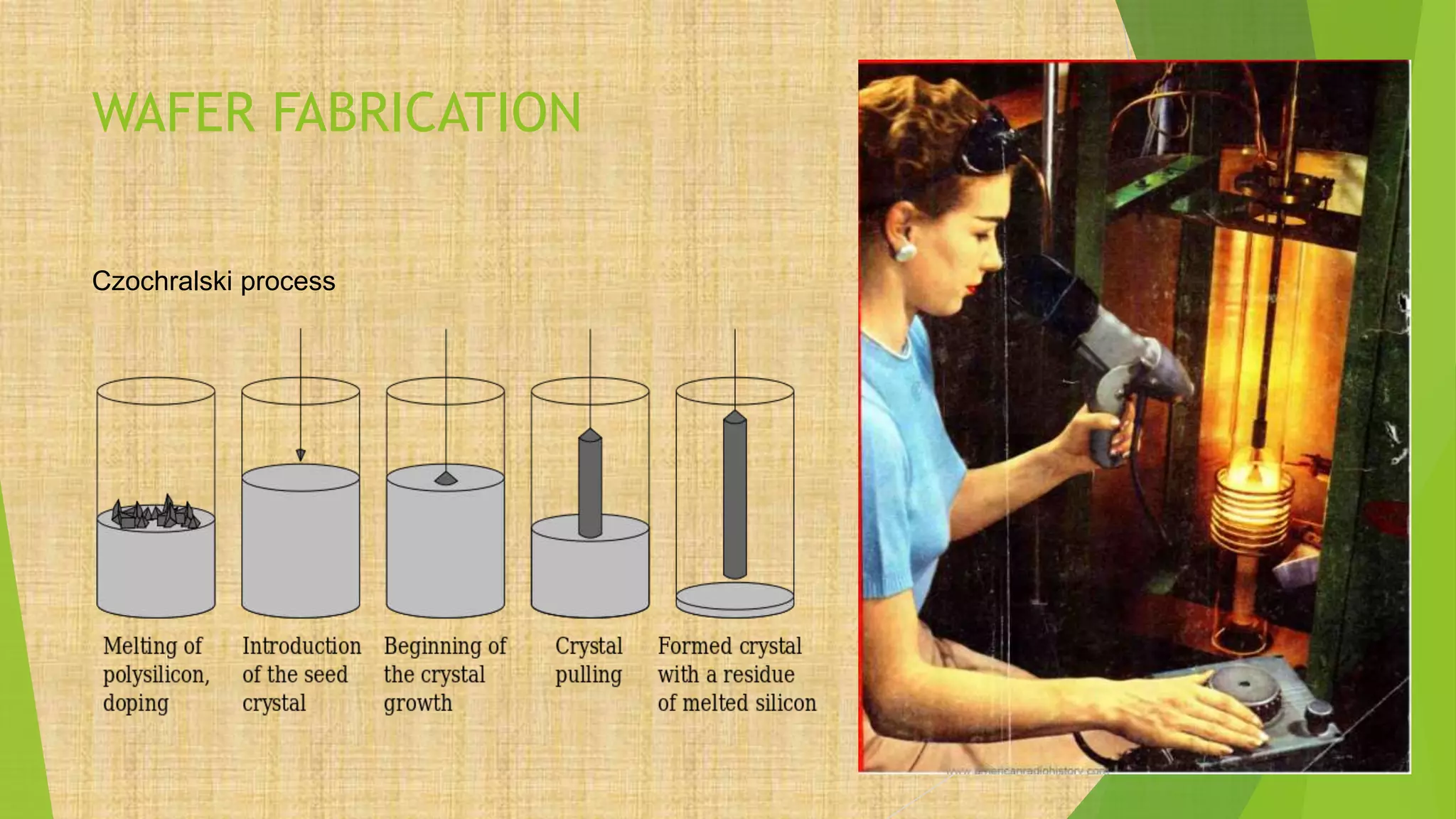
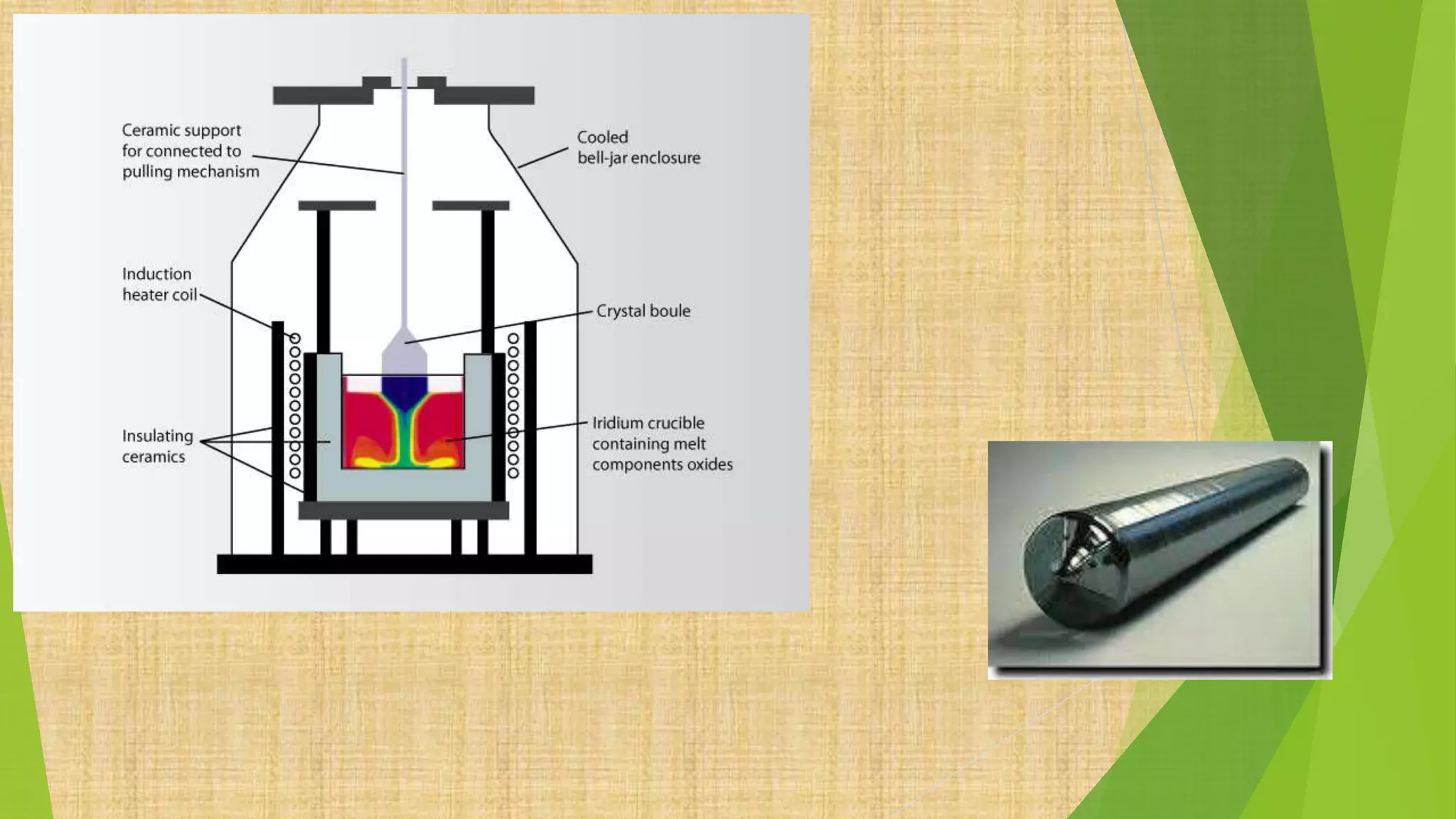
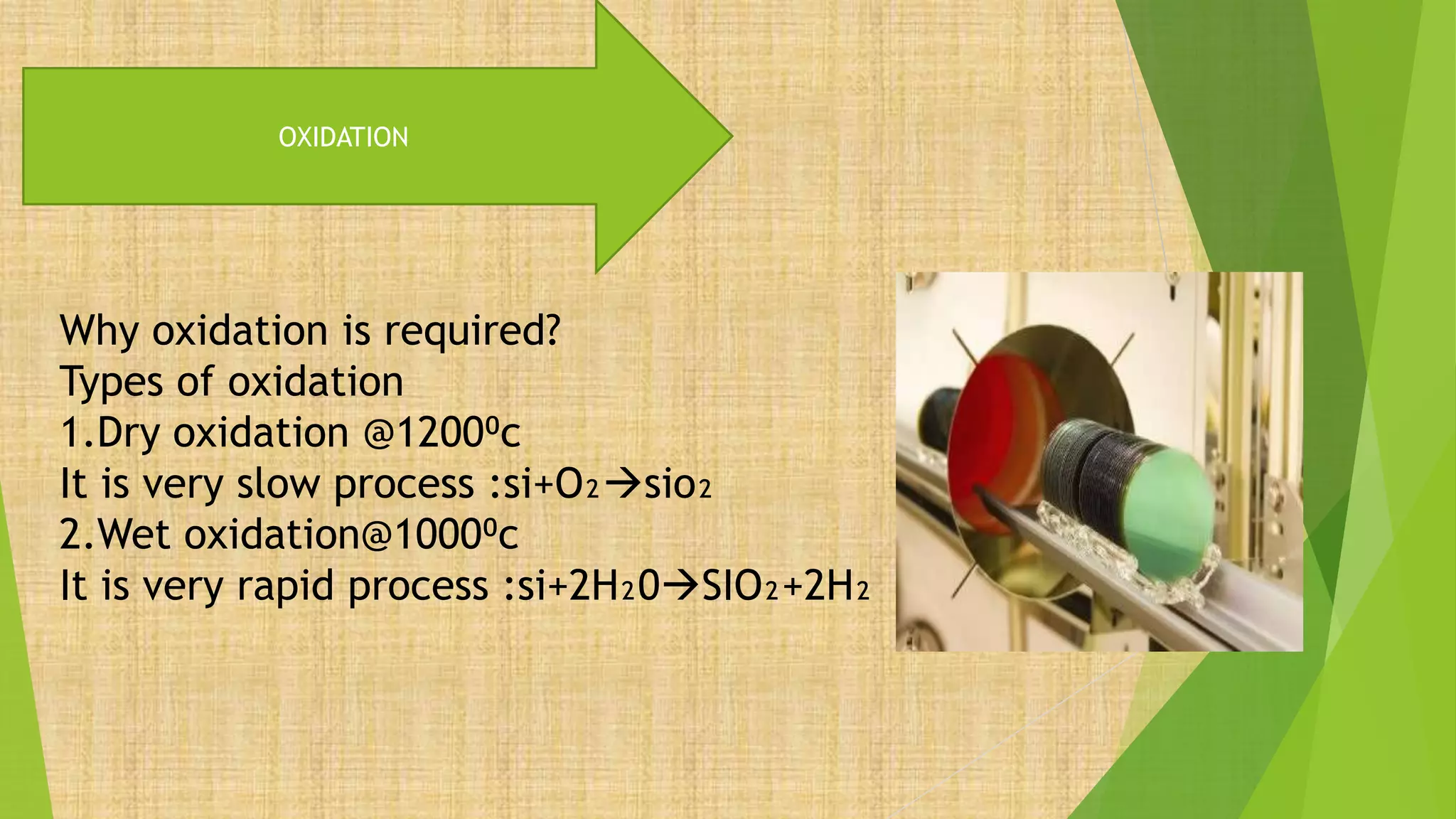
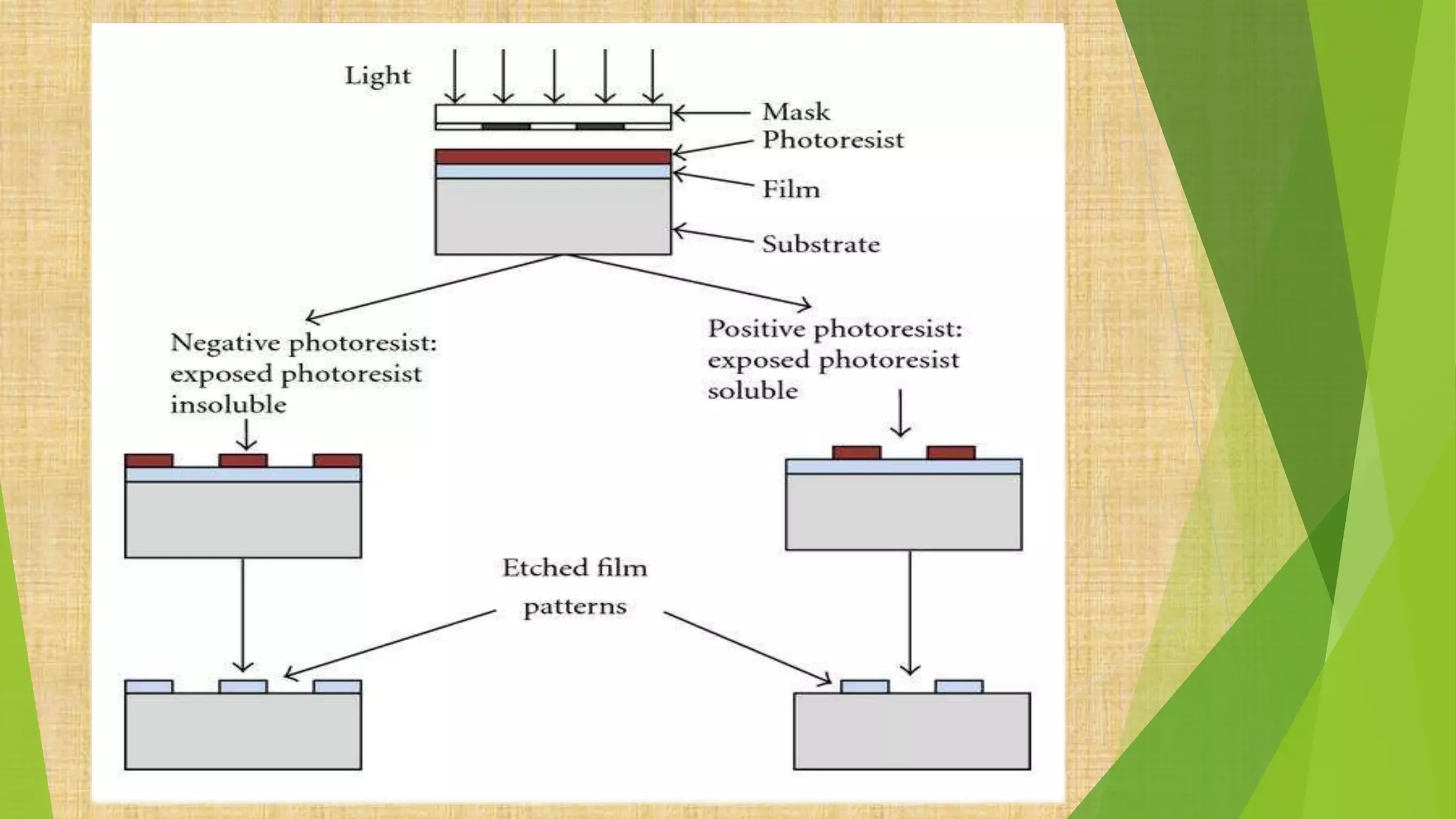
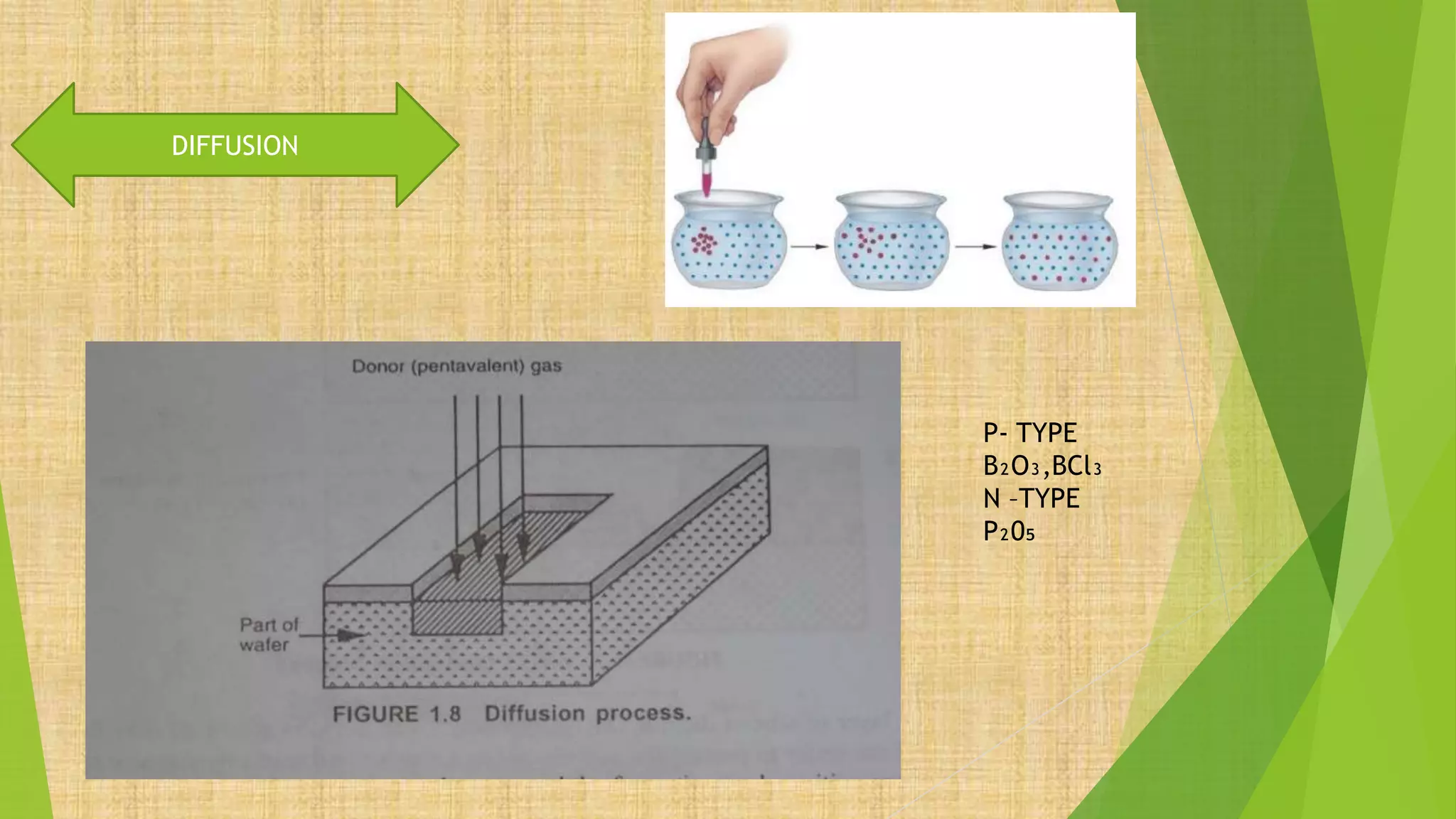
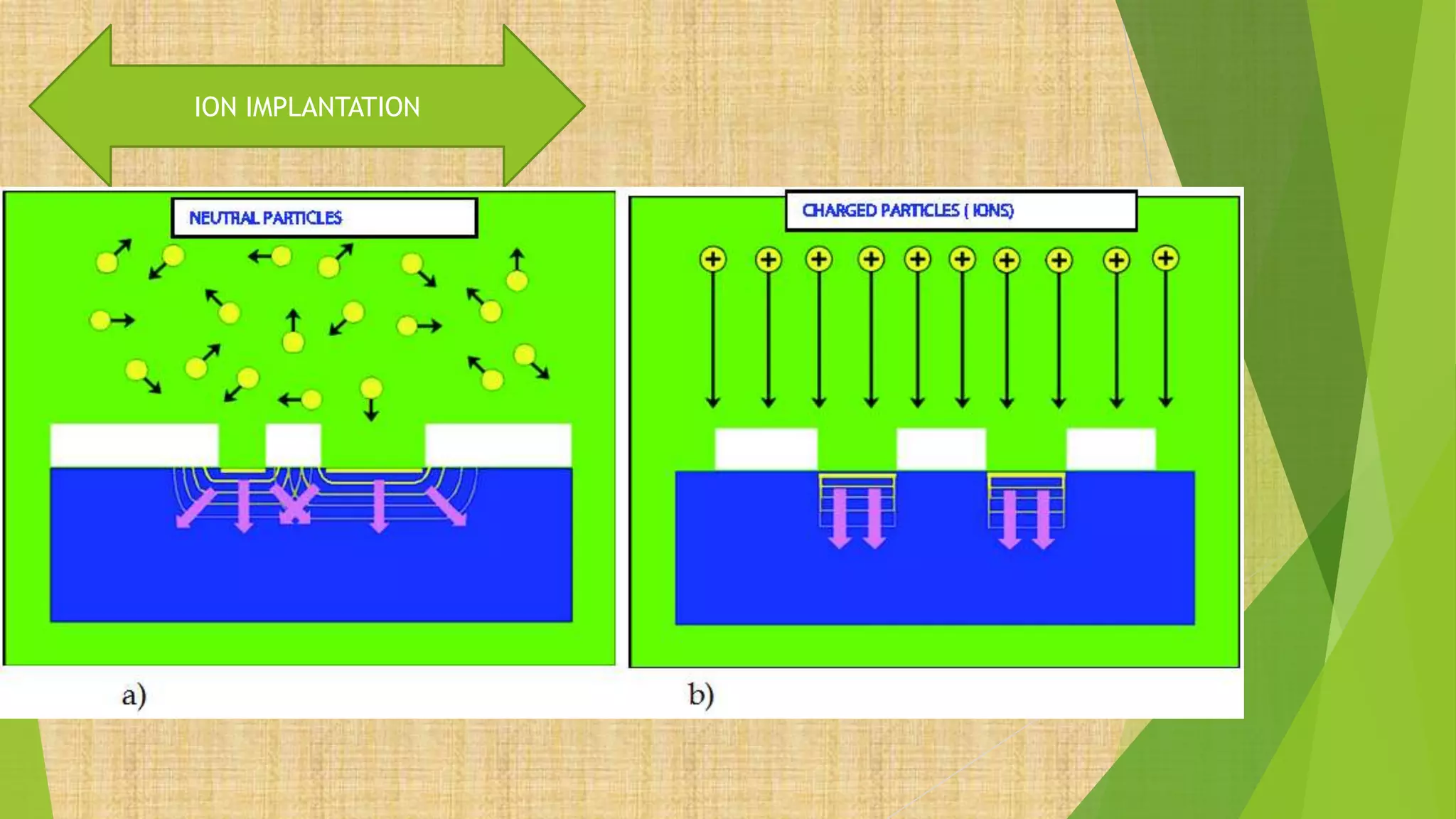
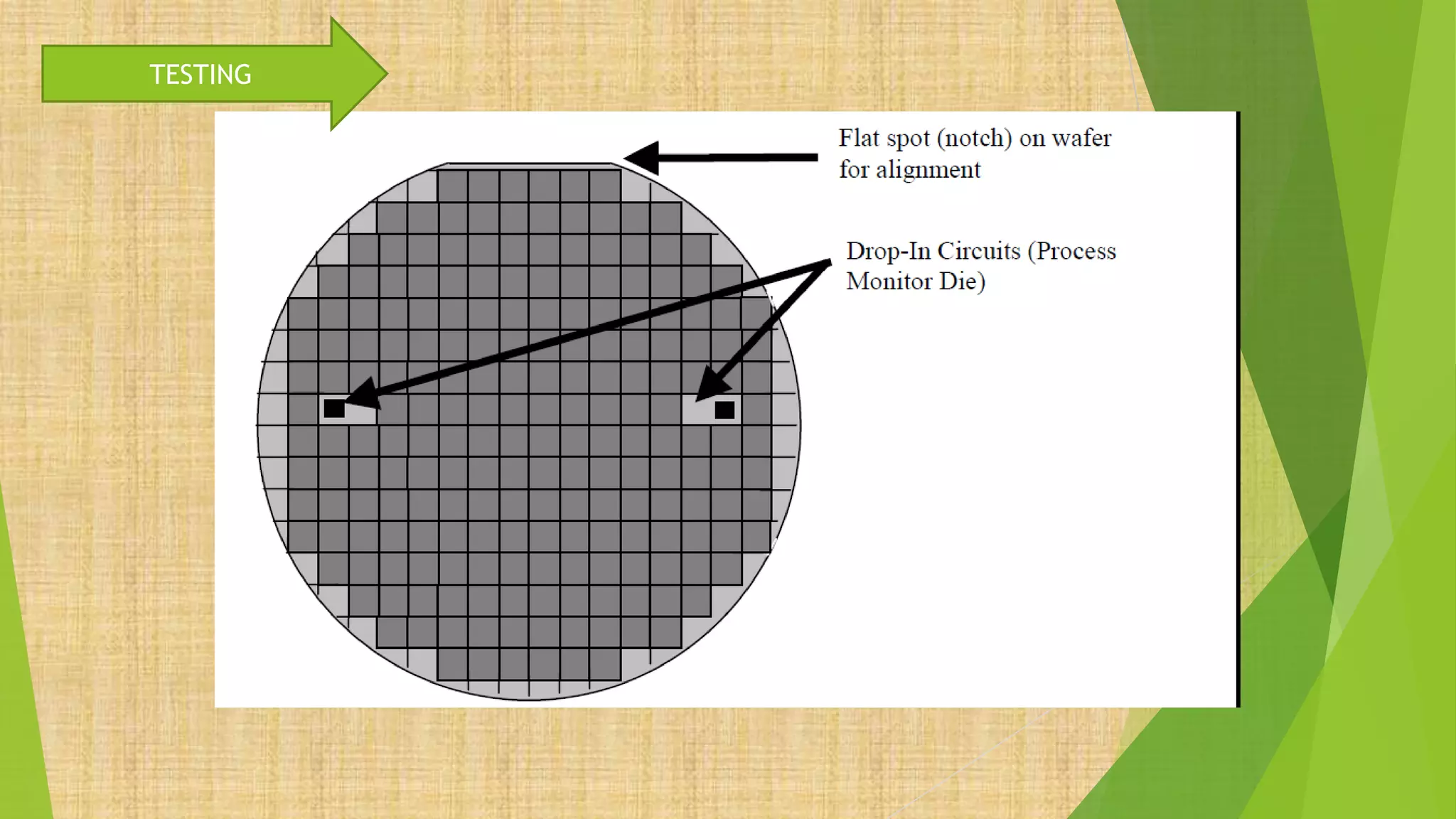
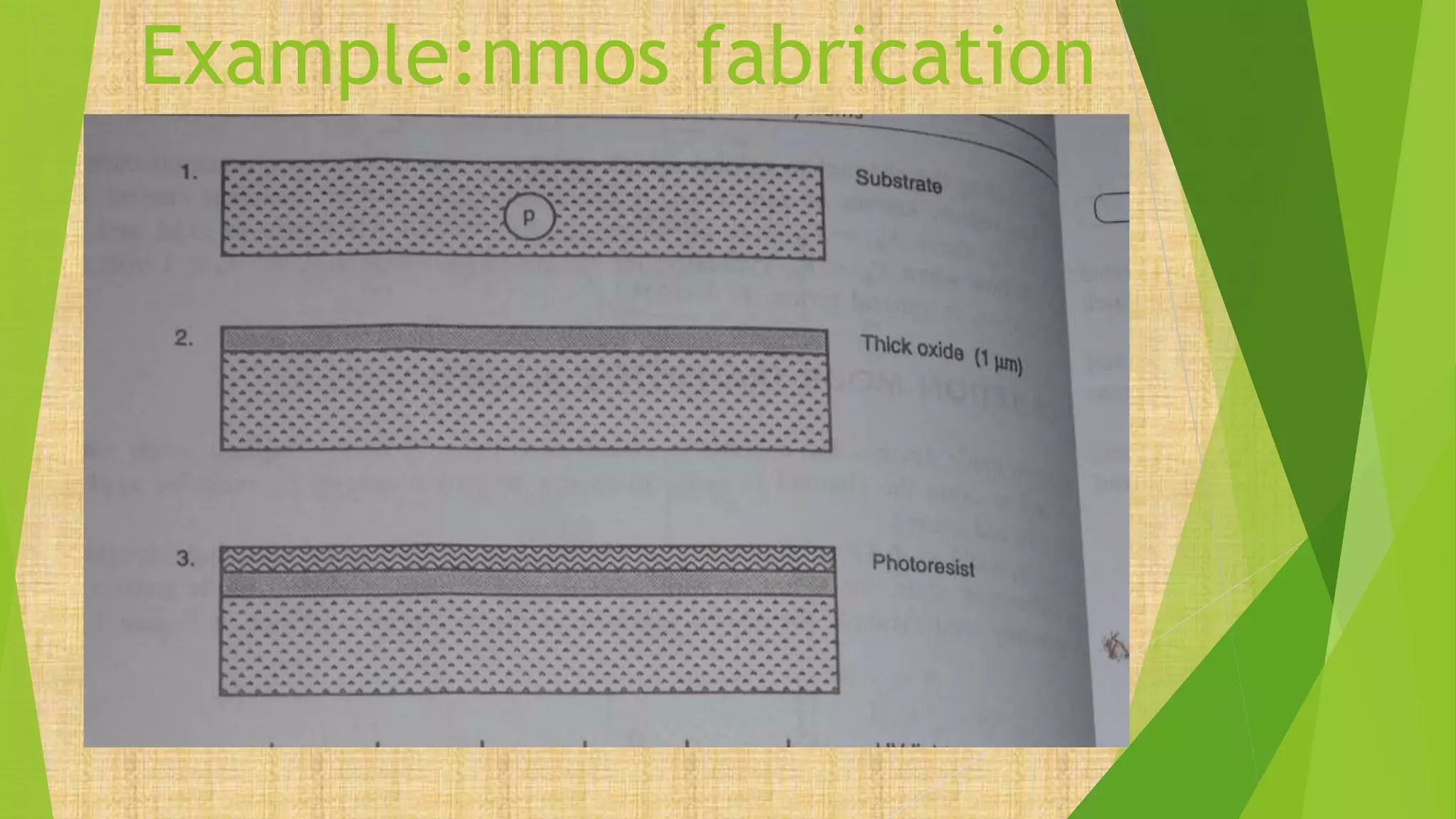
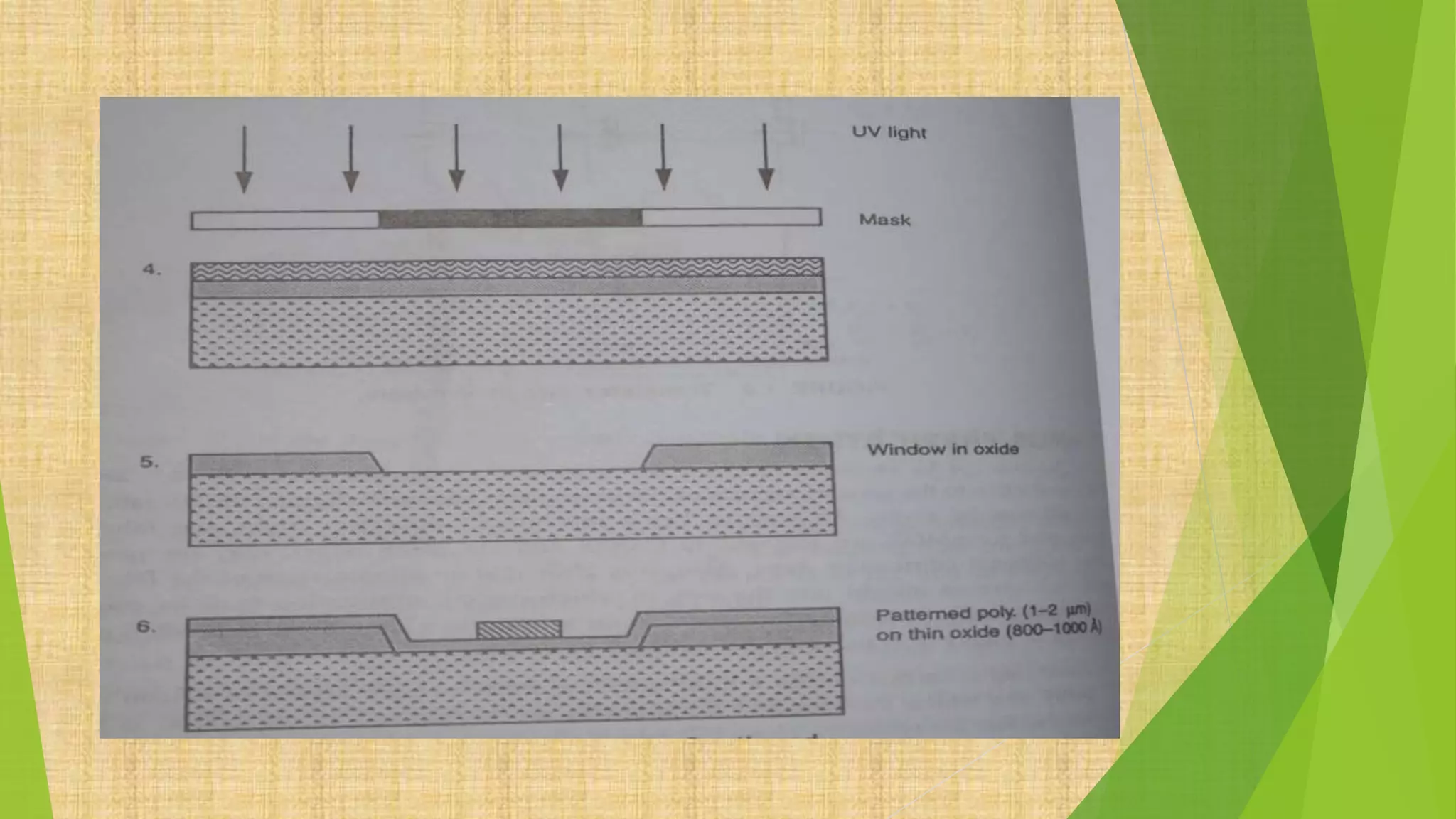
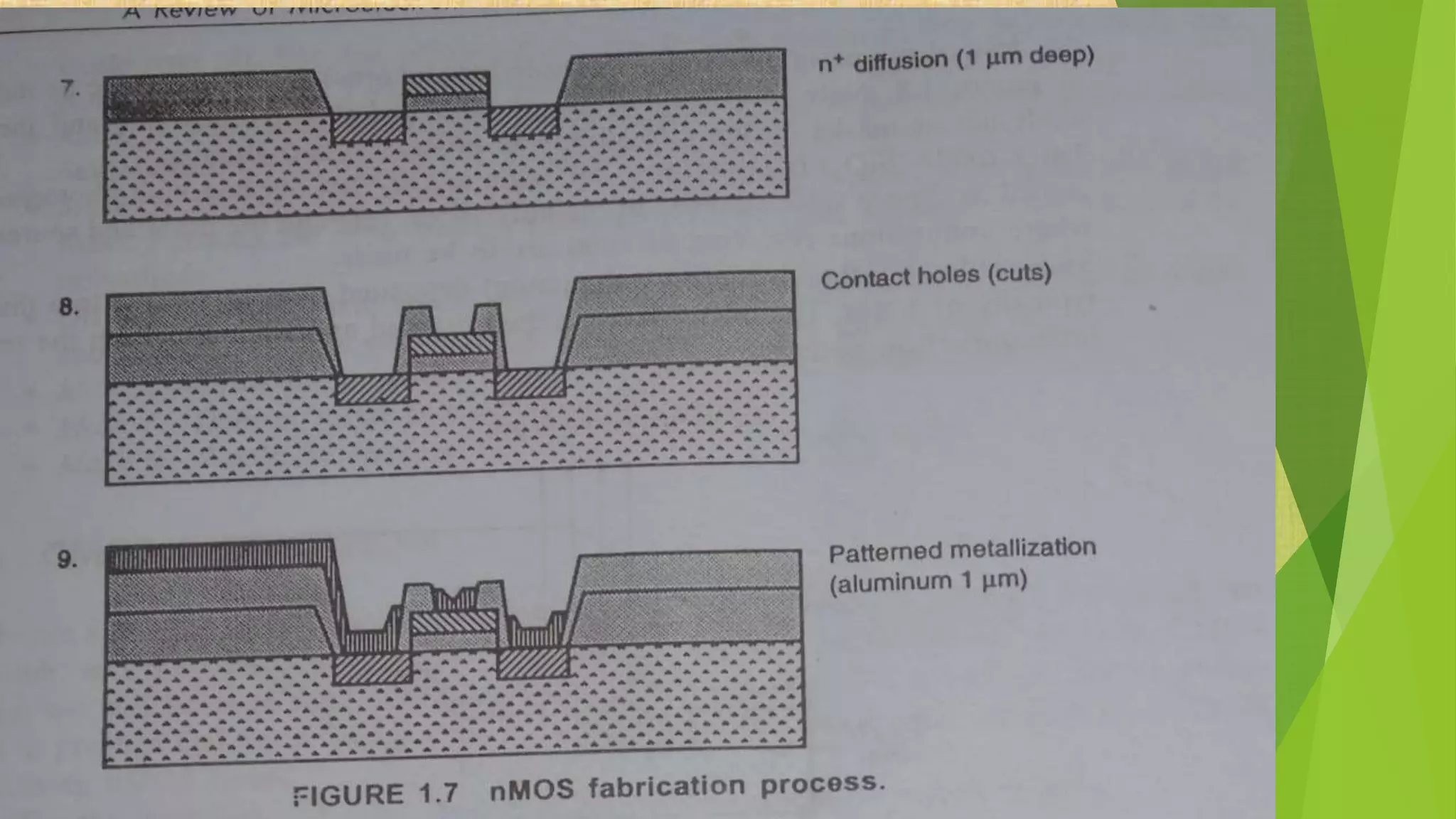
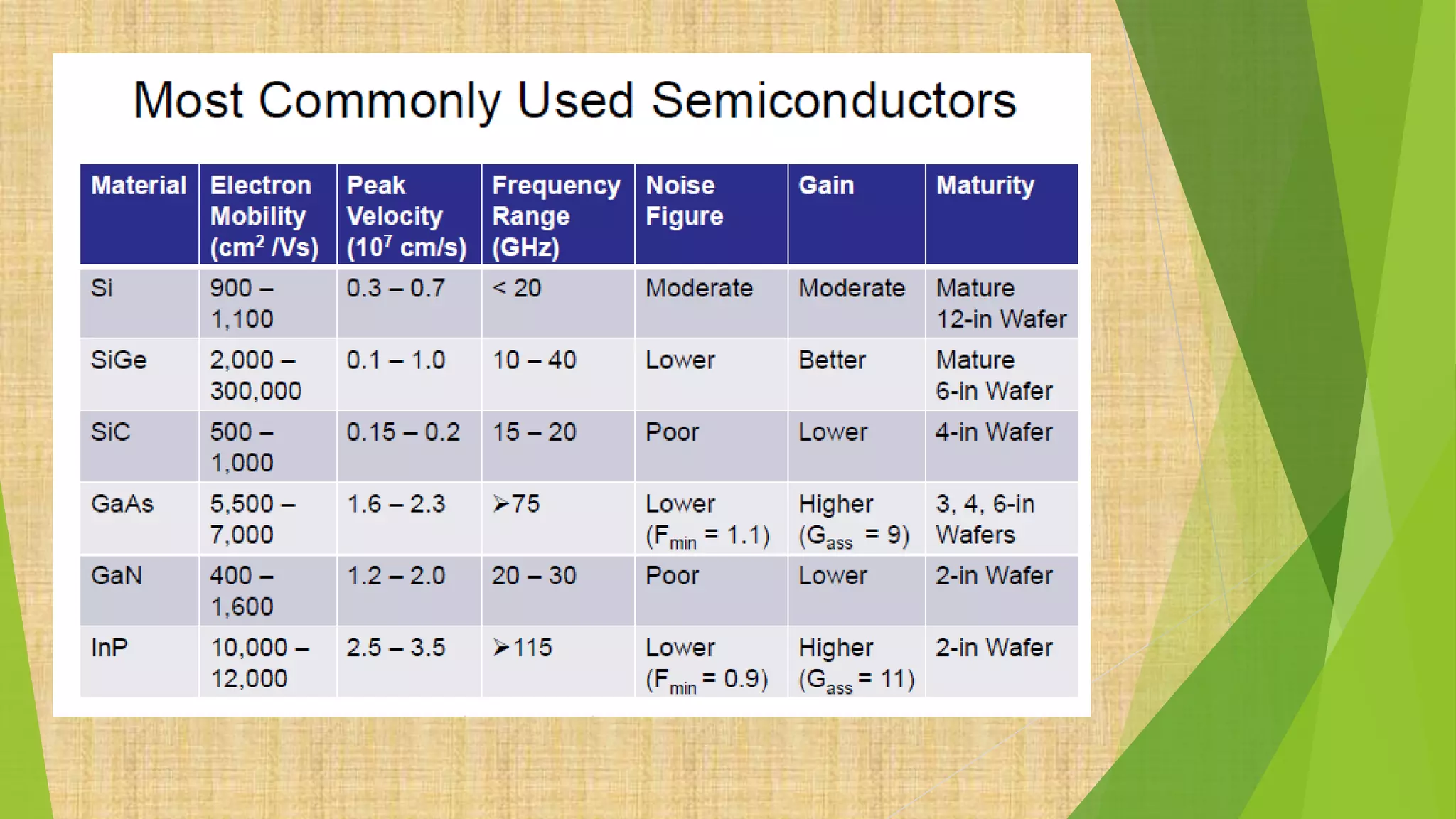
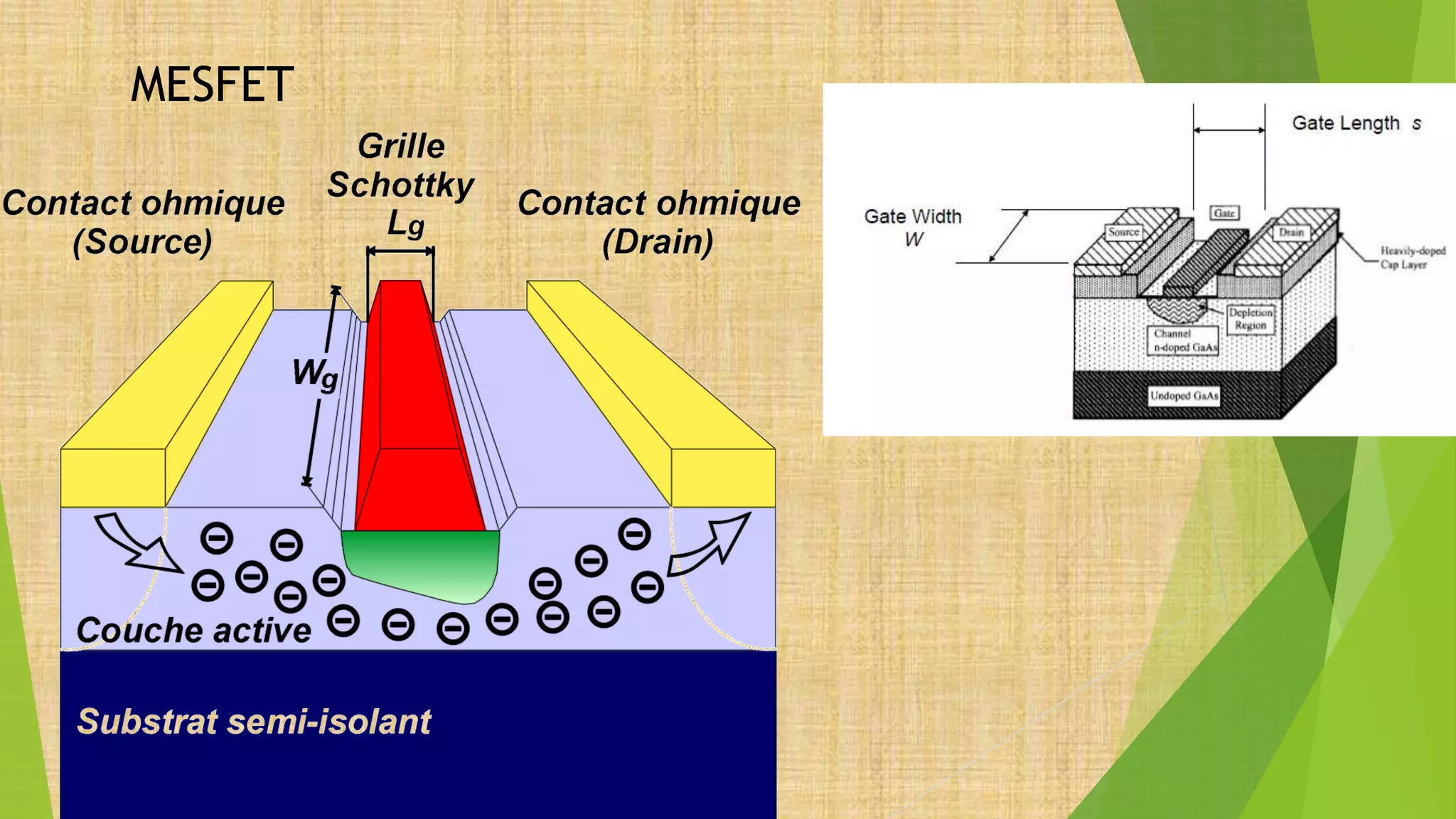
This document summarizes the key steps in integrated circuit fabrication: 1) wafer preparation through crystal growth, 2) oxidation, 3) photolithography, 4) diffusion, 5) ion implantation, 6) metallization, 7) testing, 8) passivation, and 9) packaging. It describes processes like Czochralski growth, oxidation, photolithography, diffusion, ion implantation, and metallization. It also discusses semiconductor types, apparatus used, and differences between diffusion, ion implantation, and doping. The document provides an overview of IC fabrication methods and processes.