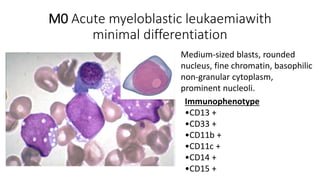
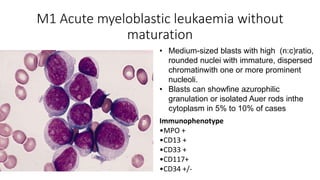
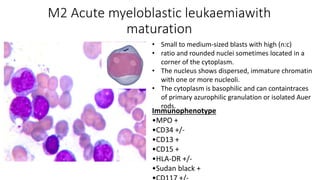
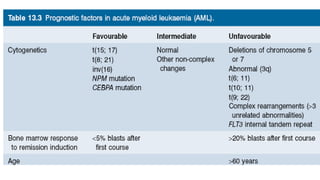
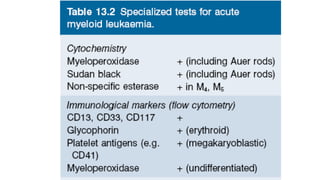
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a heterogeneous clonal disorder characterized by rapid growth of abnormal white blood cells that accumulate in the bone marrow. It has a peak incidence in the seventh decade. AML presents with anemia, fatigue, fever, infections, bruising and bleeding due to bone marrow failure. Common genetic abnormalities in AML include t(8;21), inv(16) or t(16;16), and t(15;17) which are associated with specific subtypes and have implications for diagnosis and treatment.