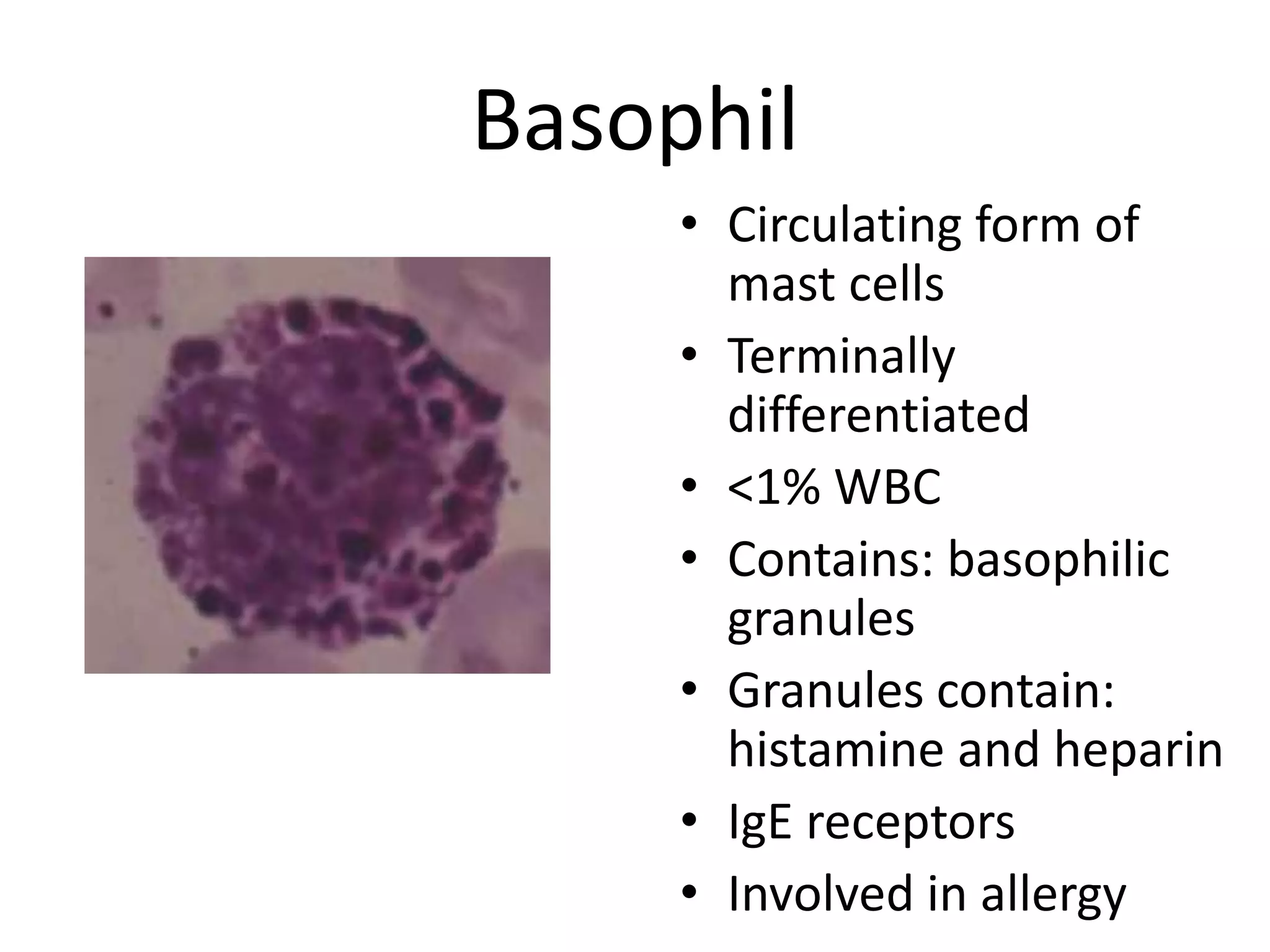
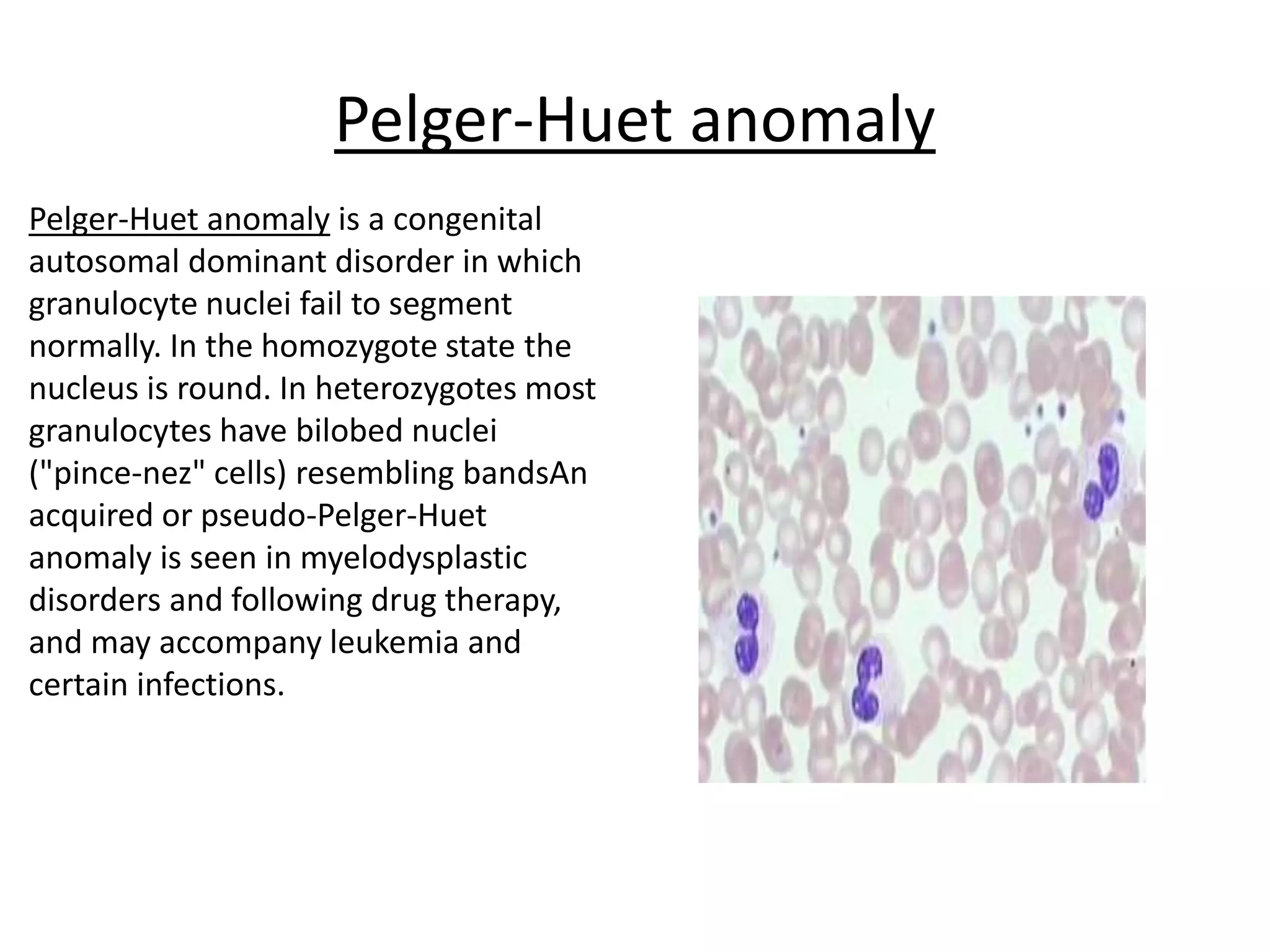
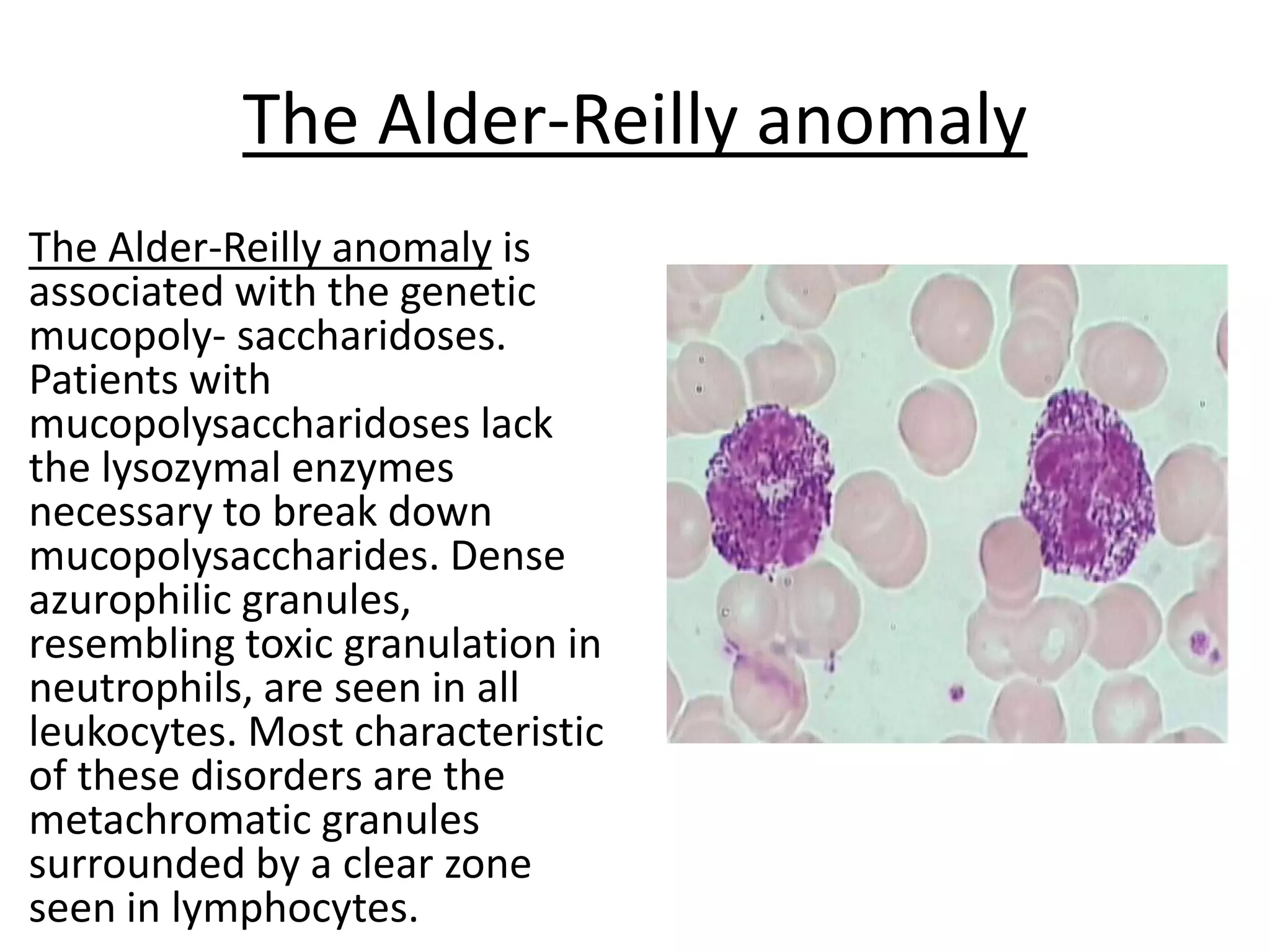
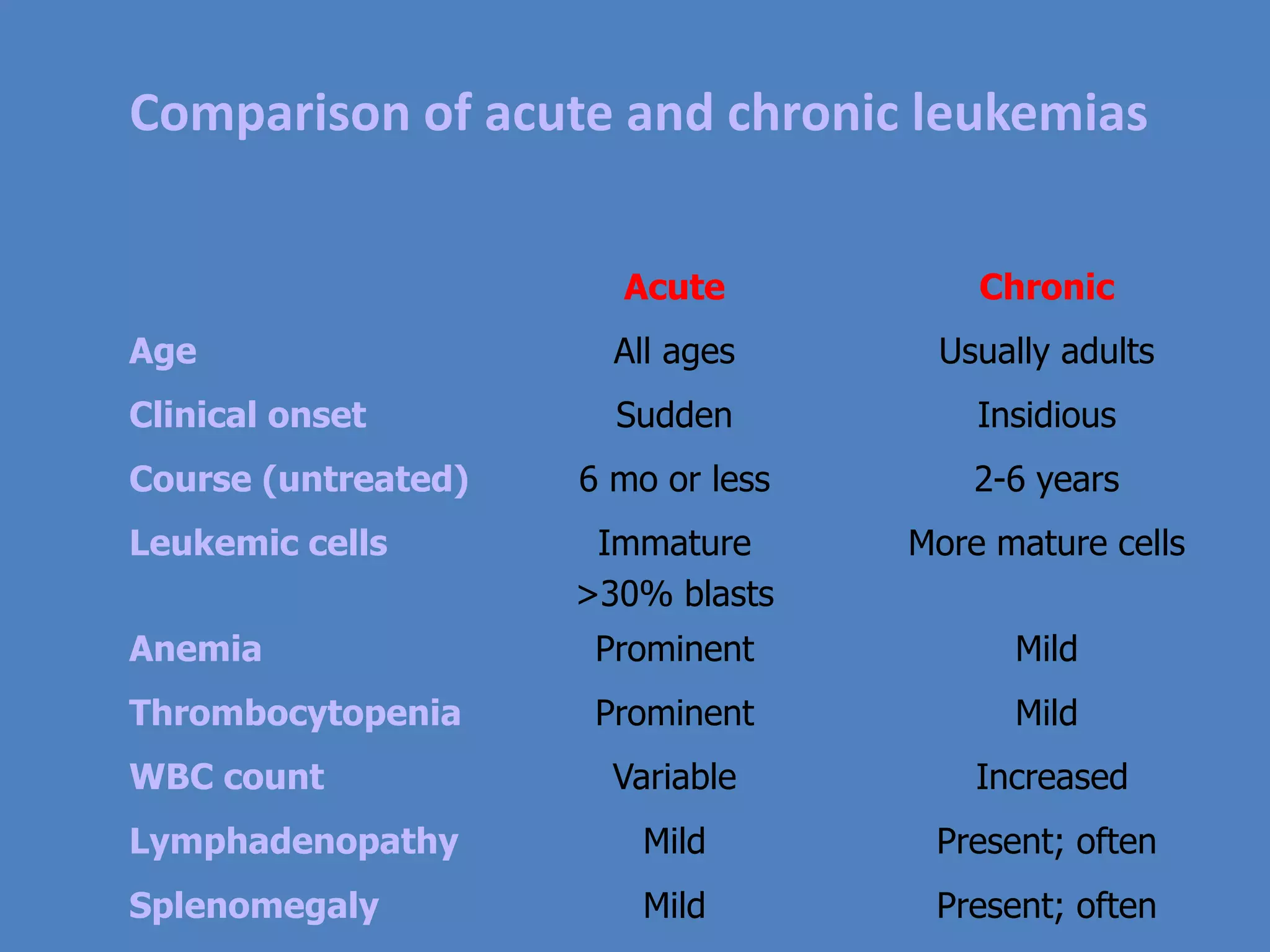
This document summarizes the morphology of normal white blood cells and some abnormalities. It describes the main types of granulocytes (neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils) and their characteristics. It also discusses monocytes/macrophages and lymphocytes. Causes of conditions like leukocytosis, neutrophilia, lymphocytosis, and eosinophilia are provided. Some morphological abnormalities of white blood cells like toxic granulation and Pelger-Huet anomaly are also summarized.