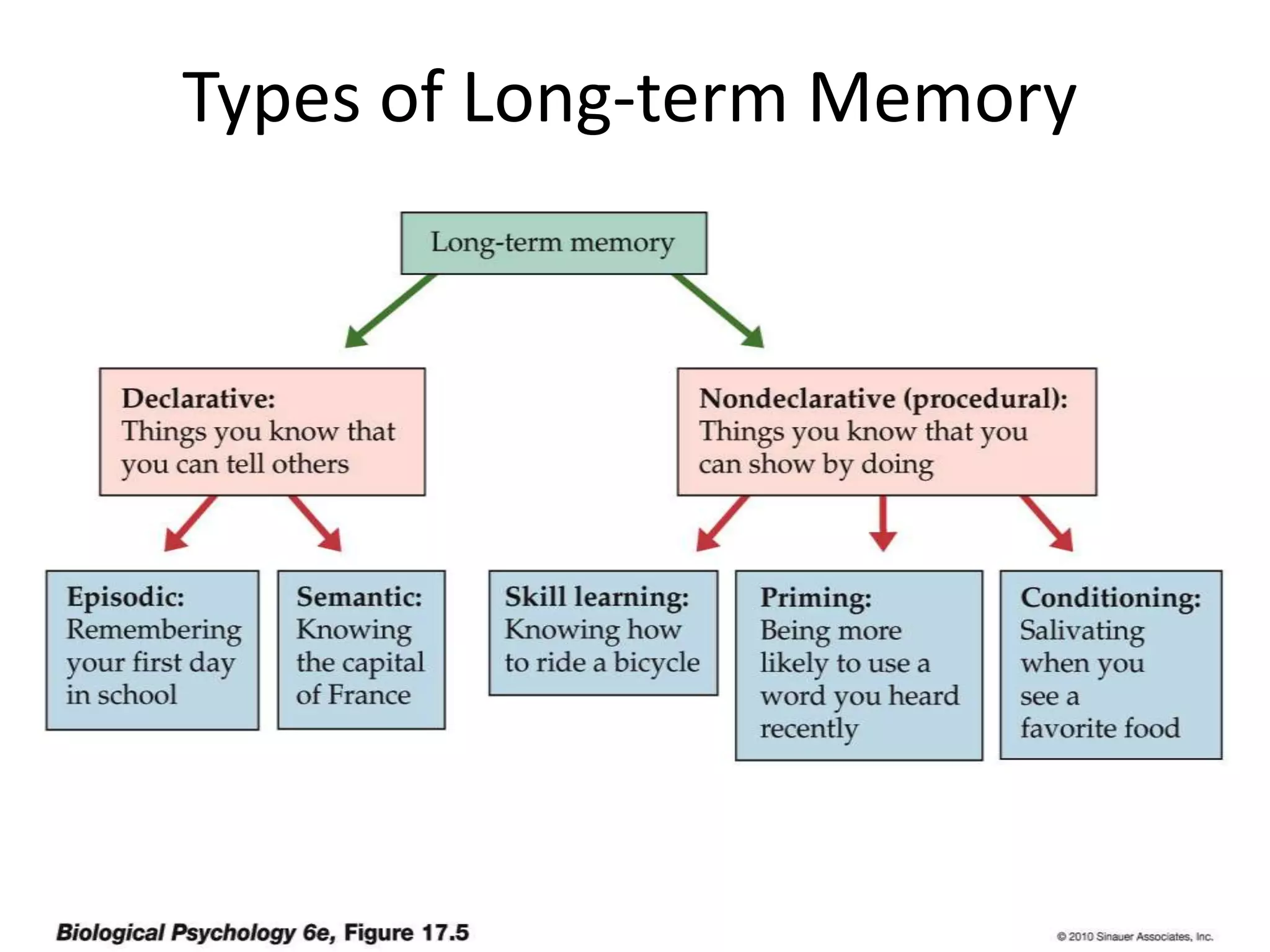
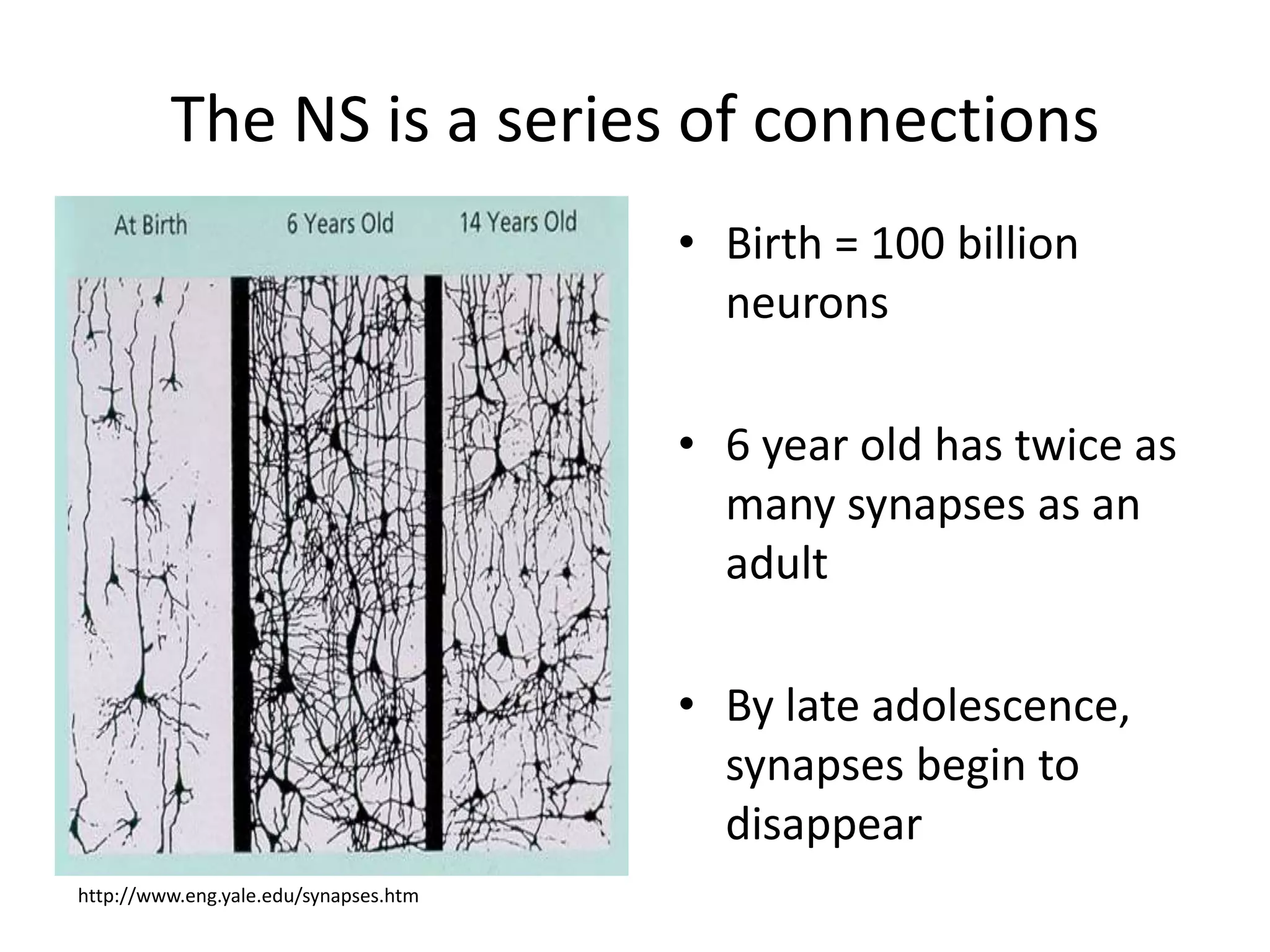
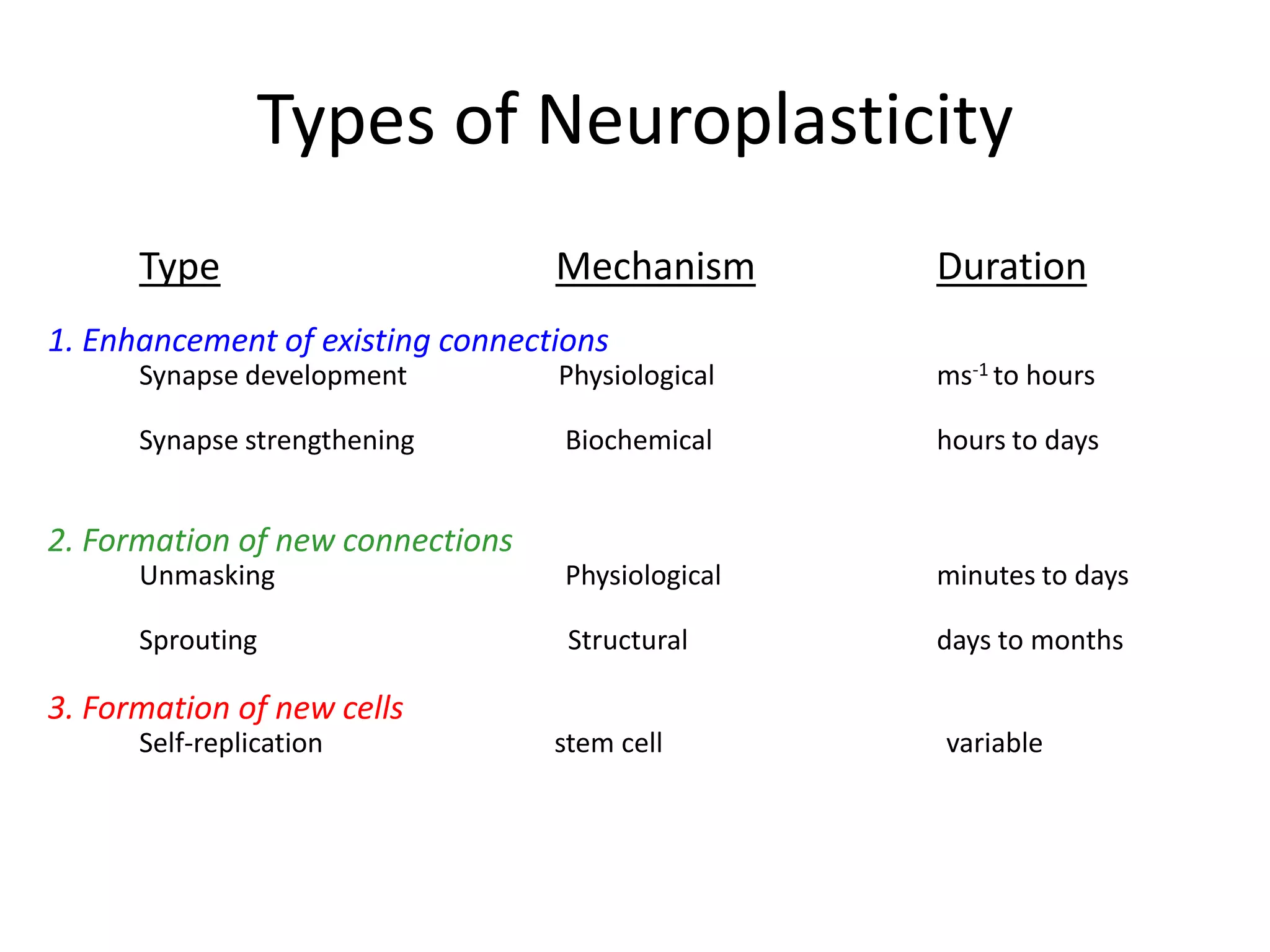
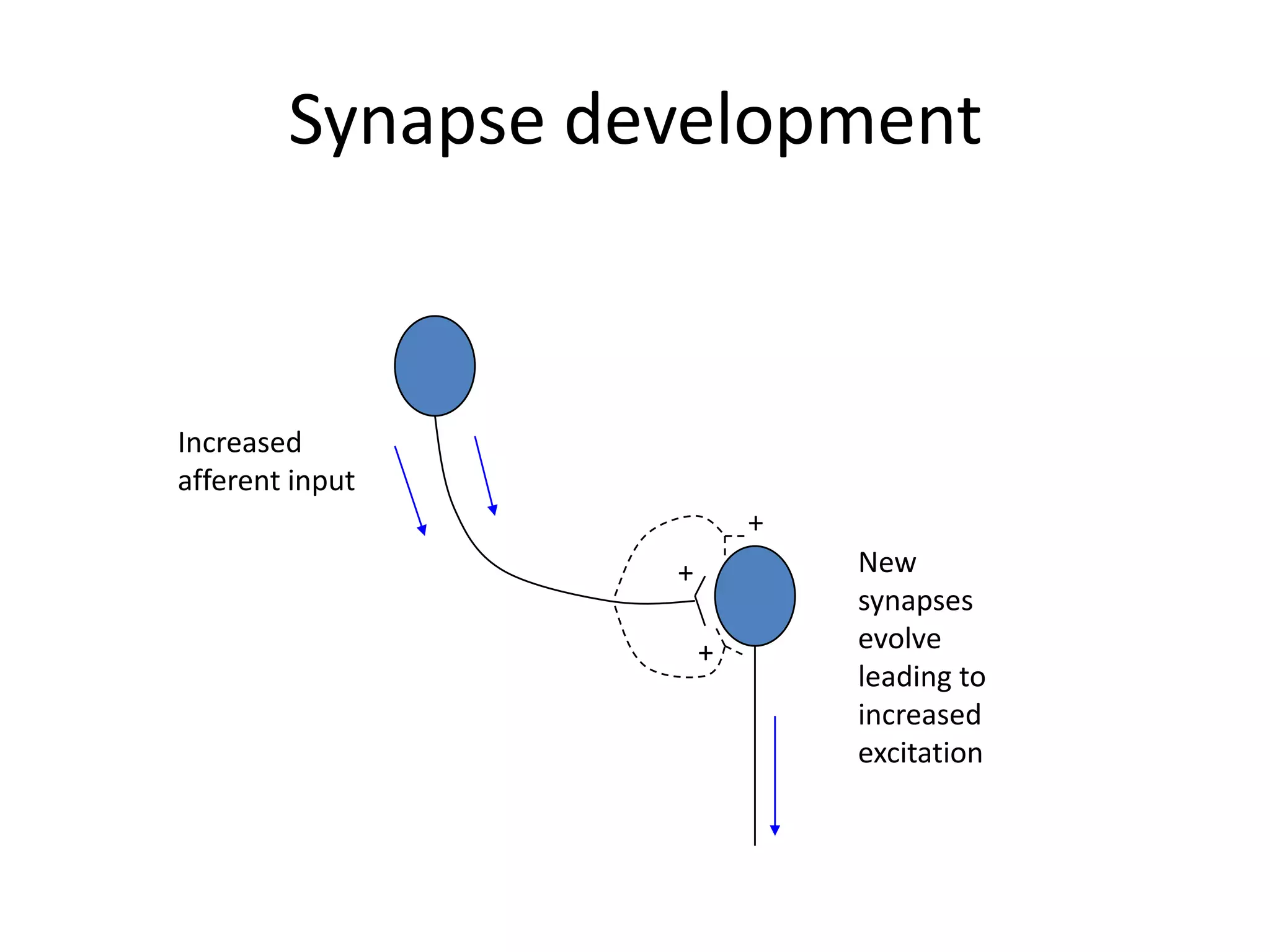
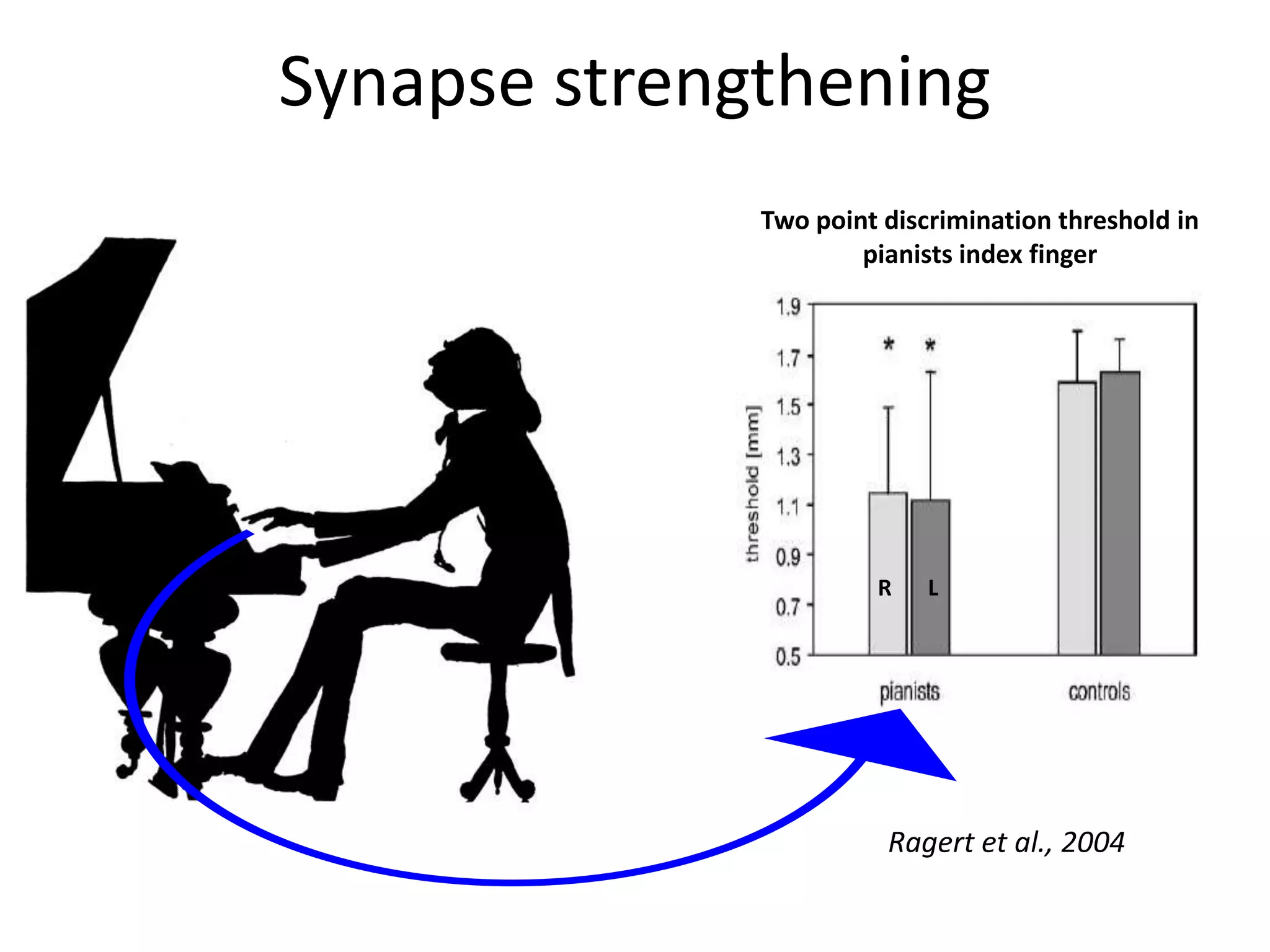
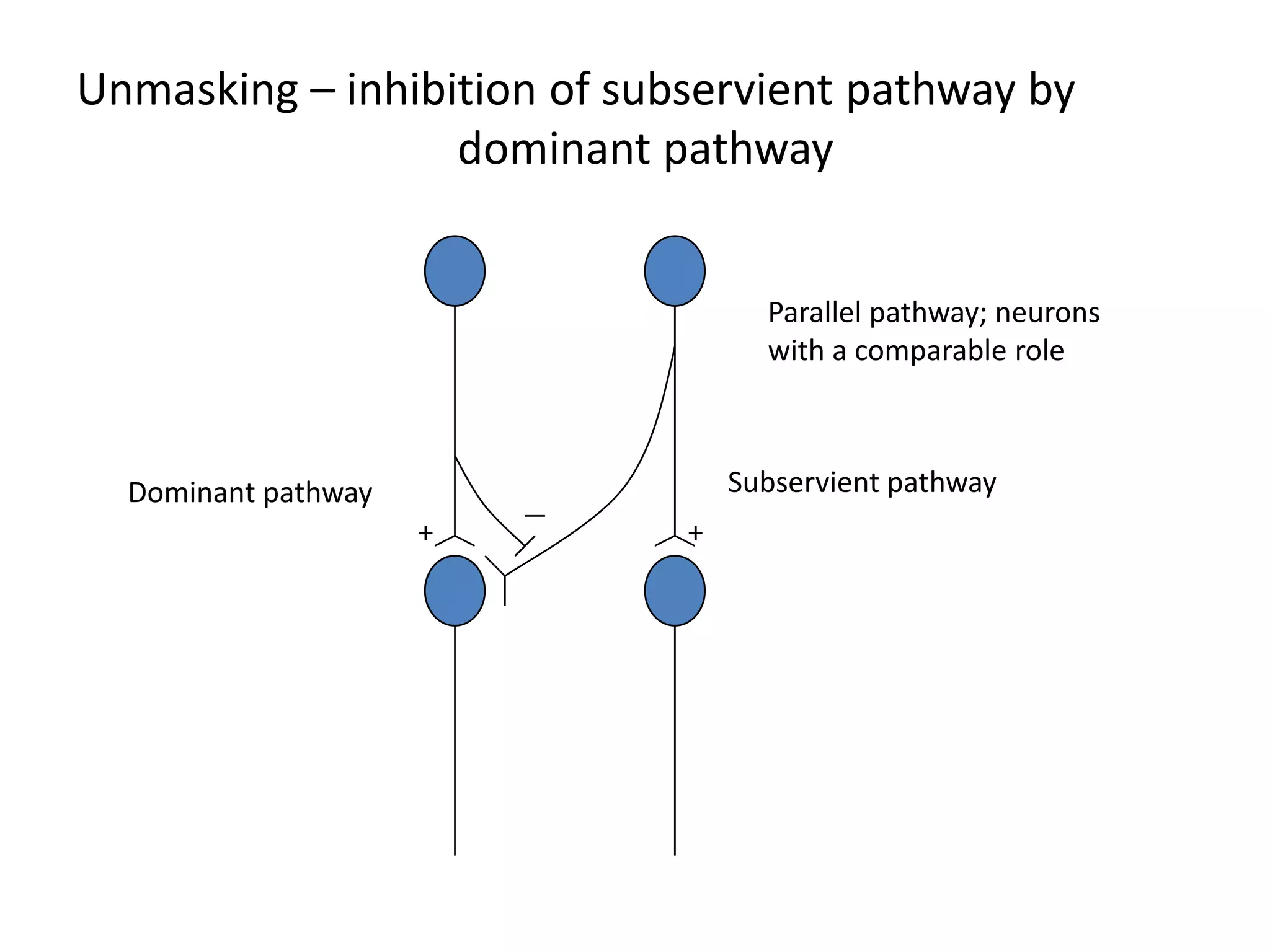
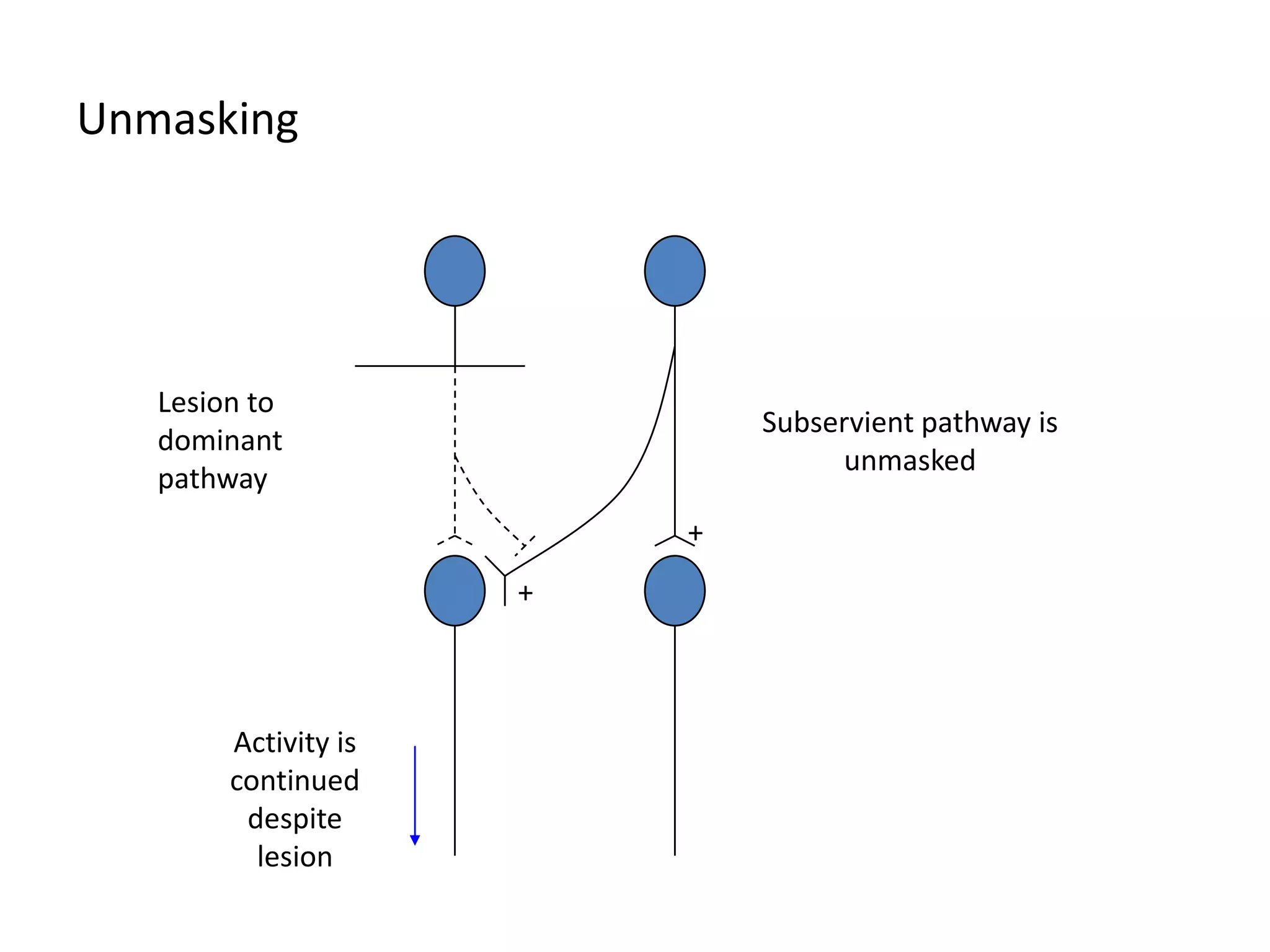
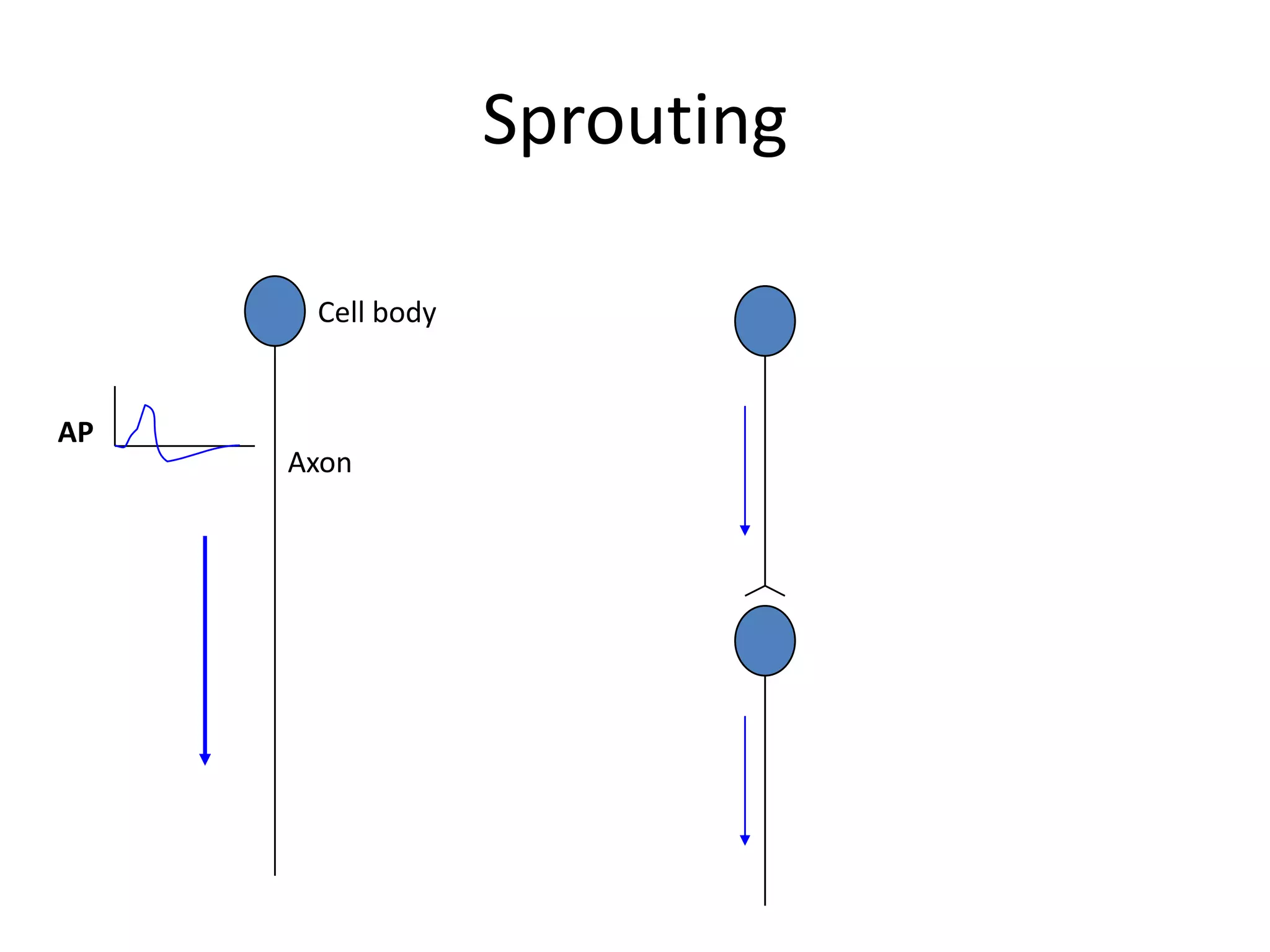
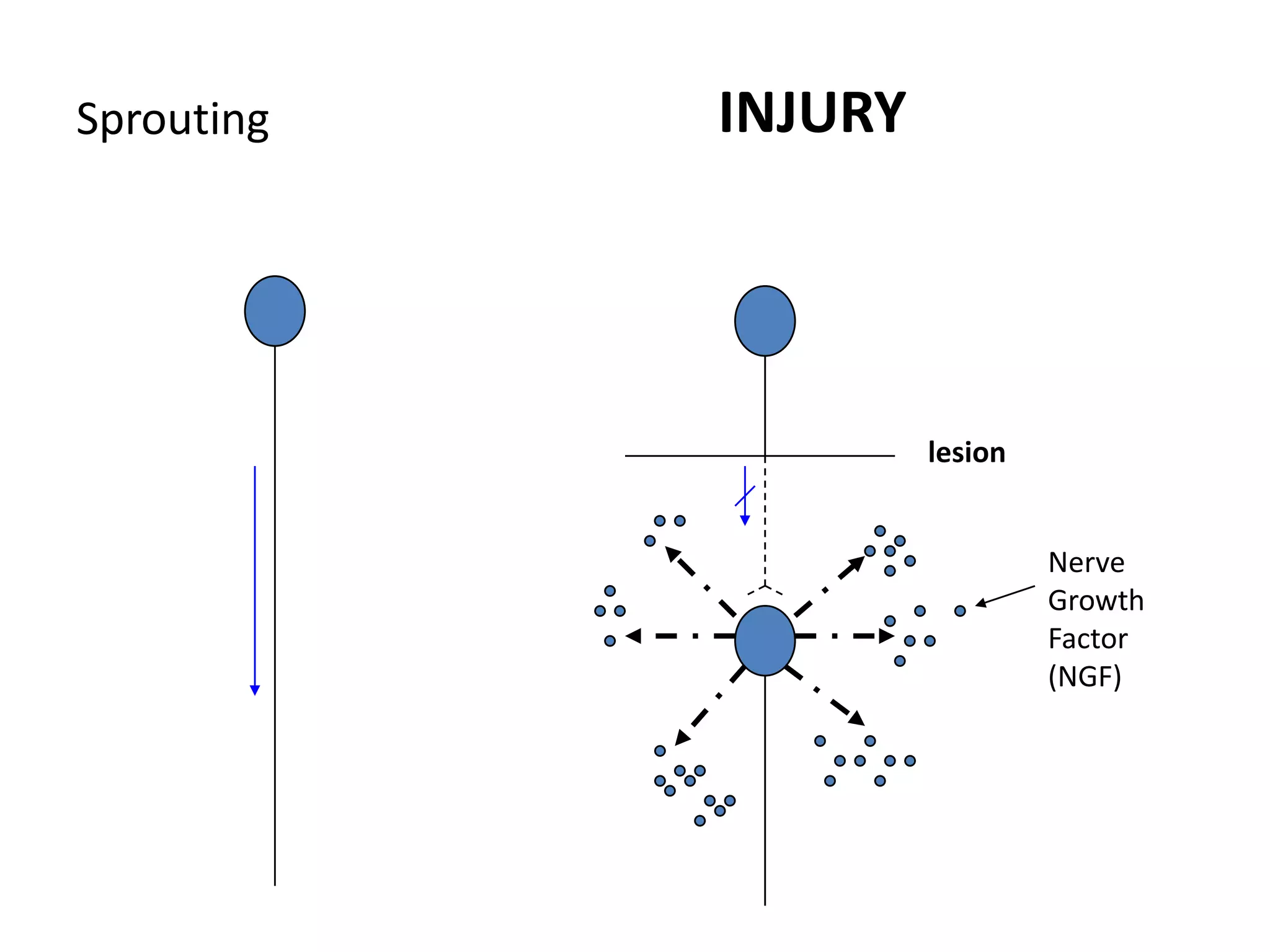
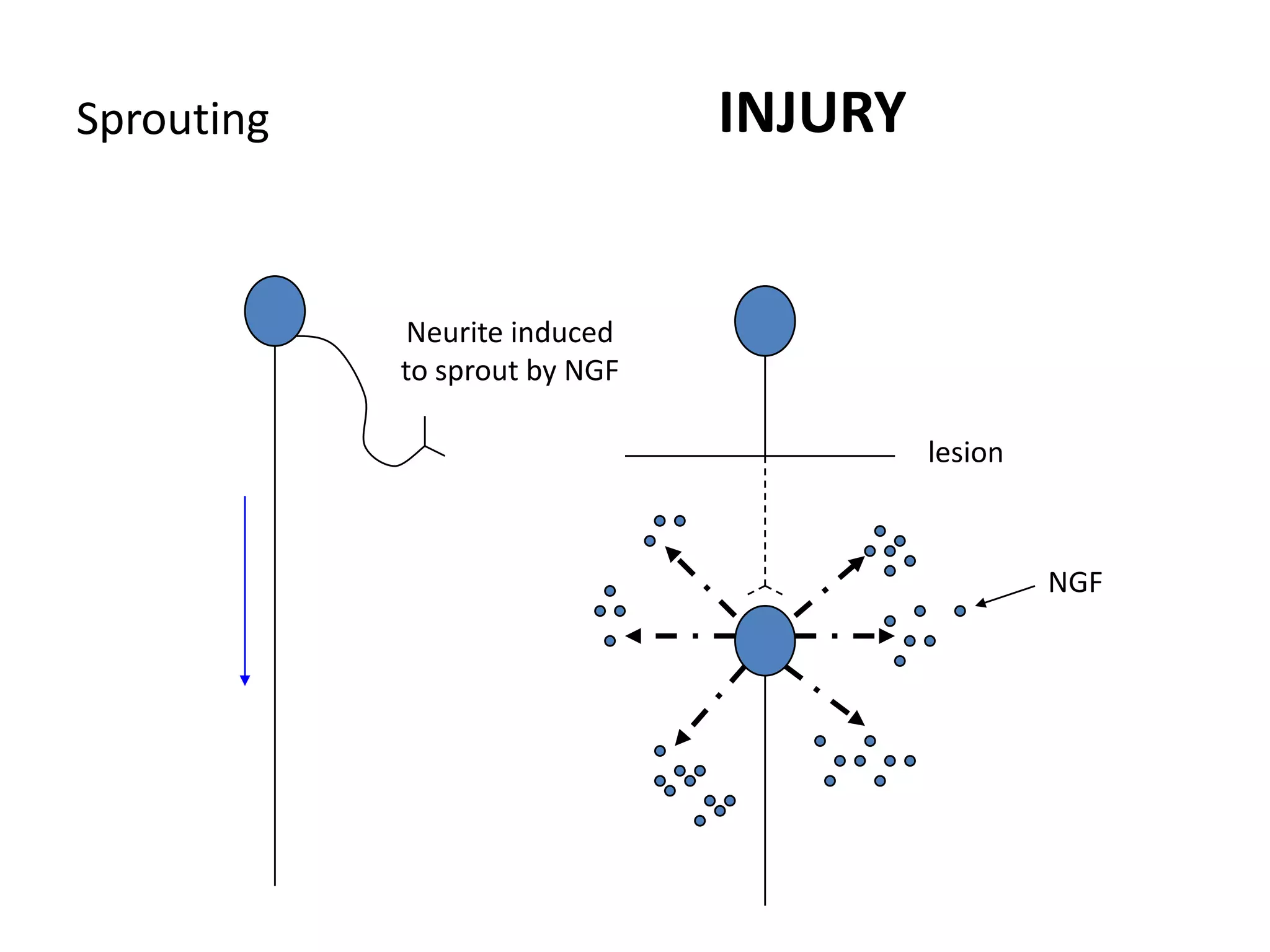
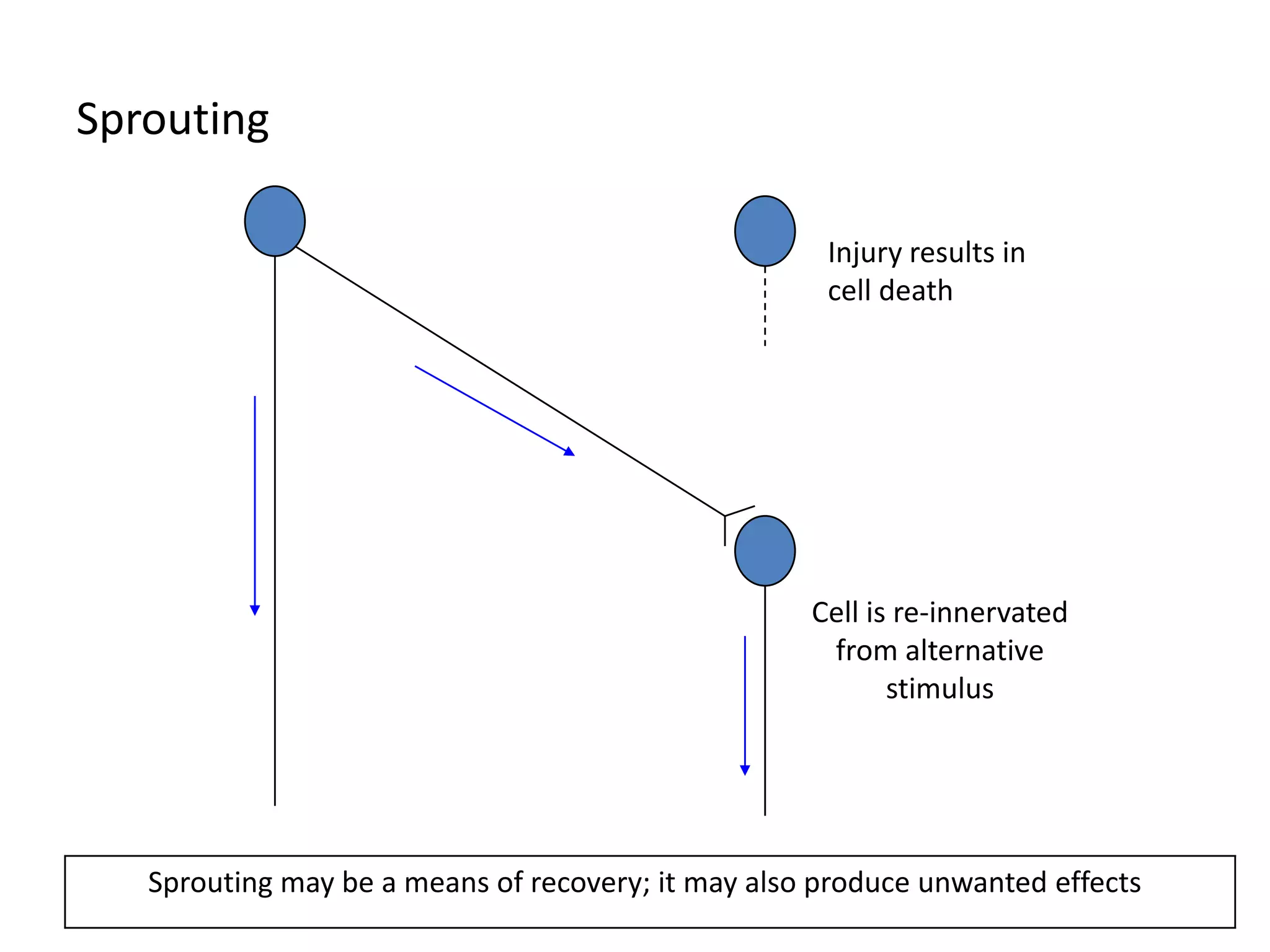
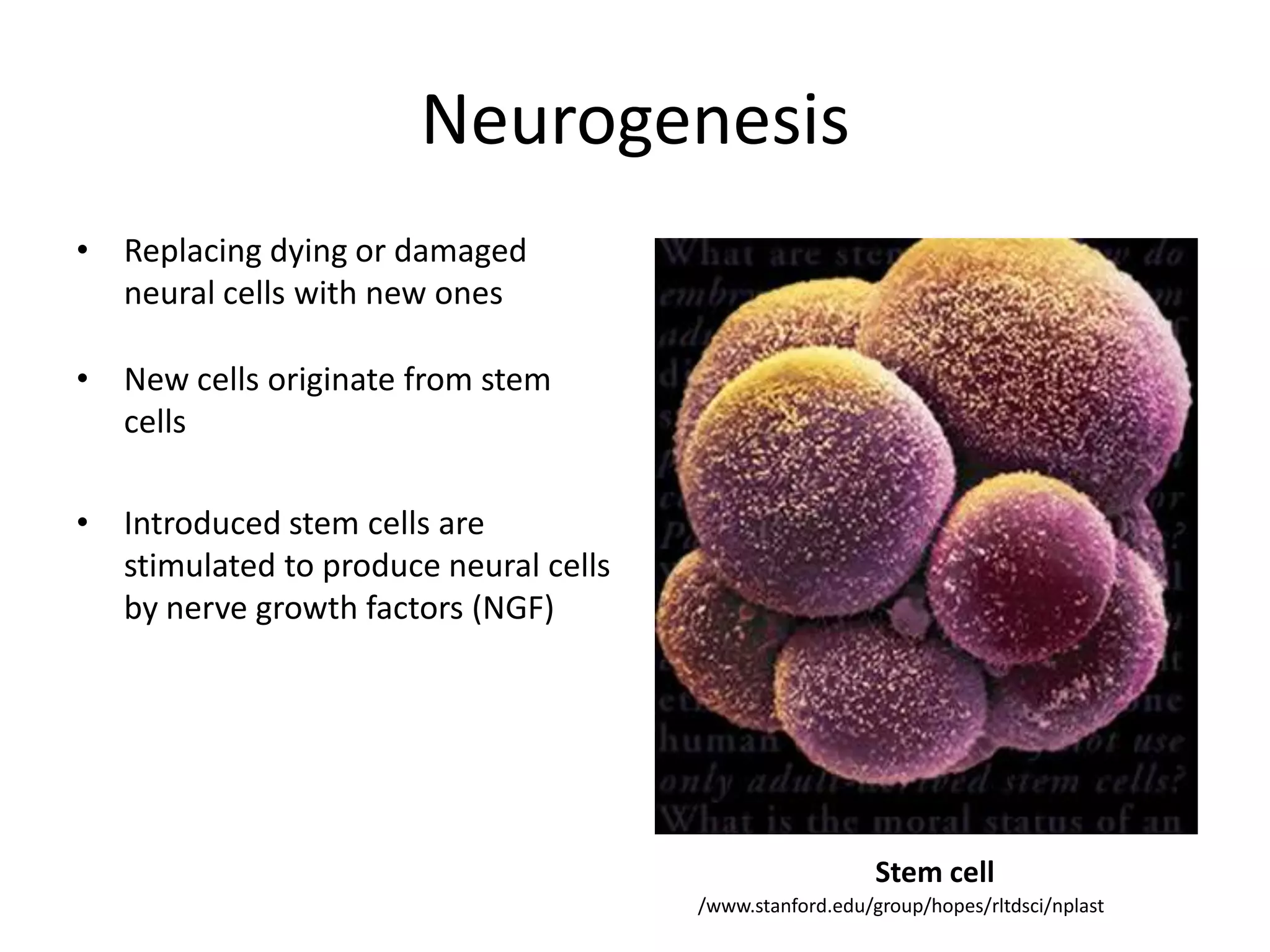
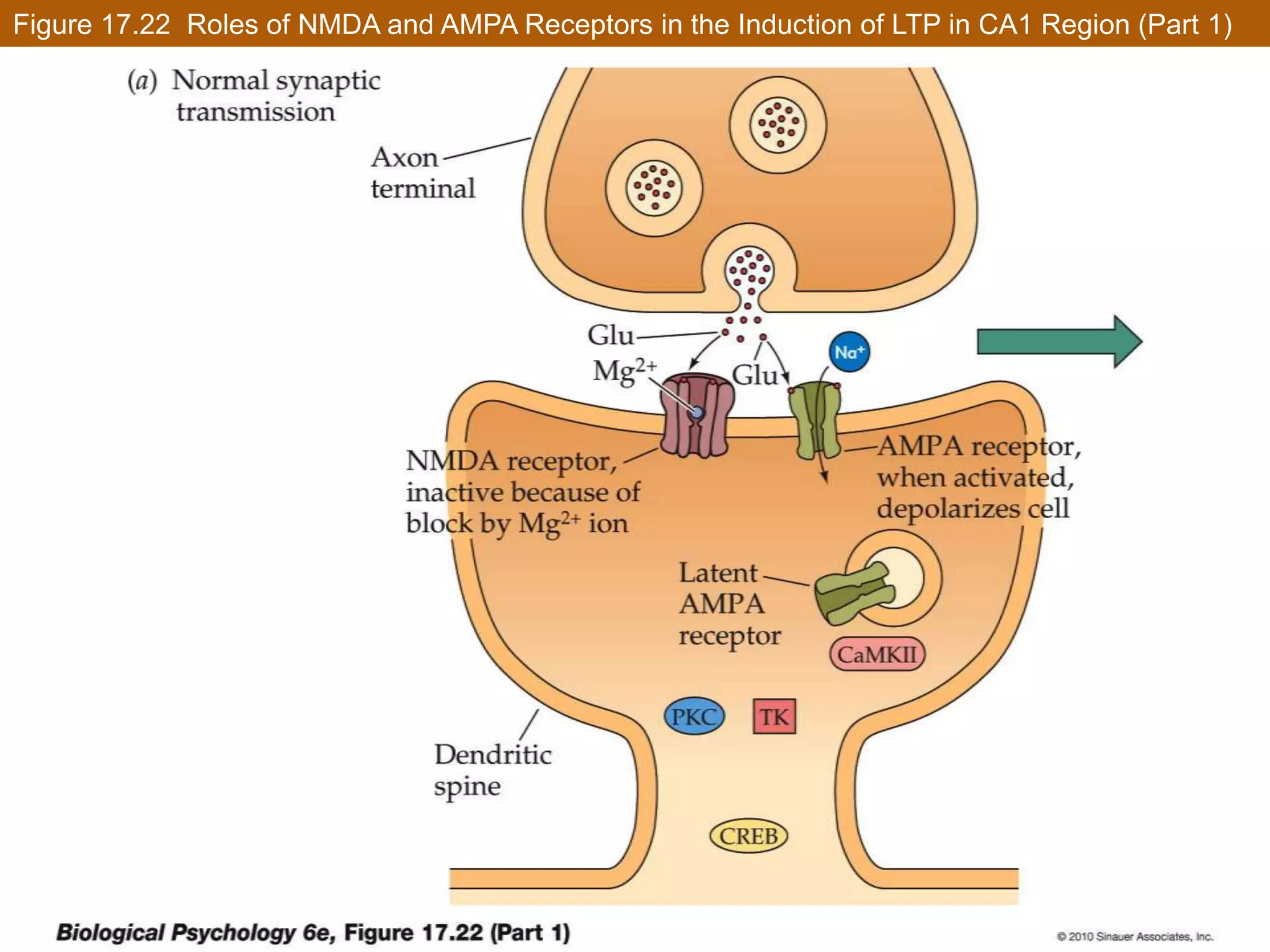
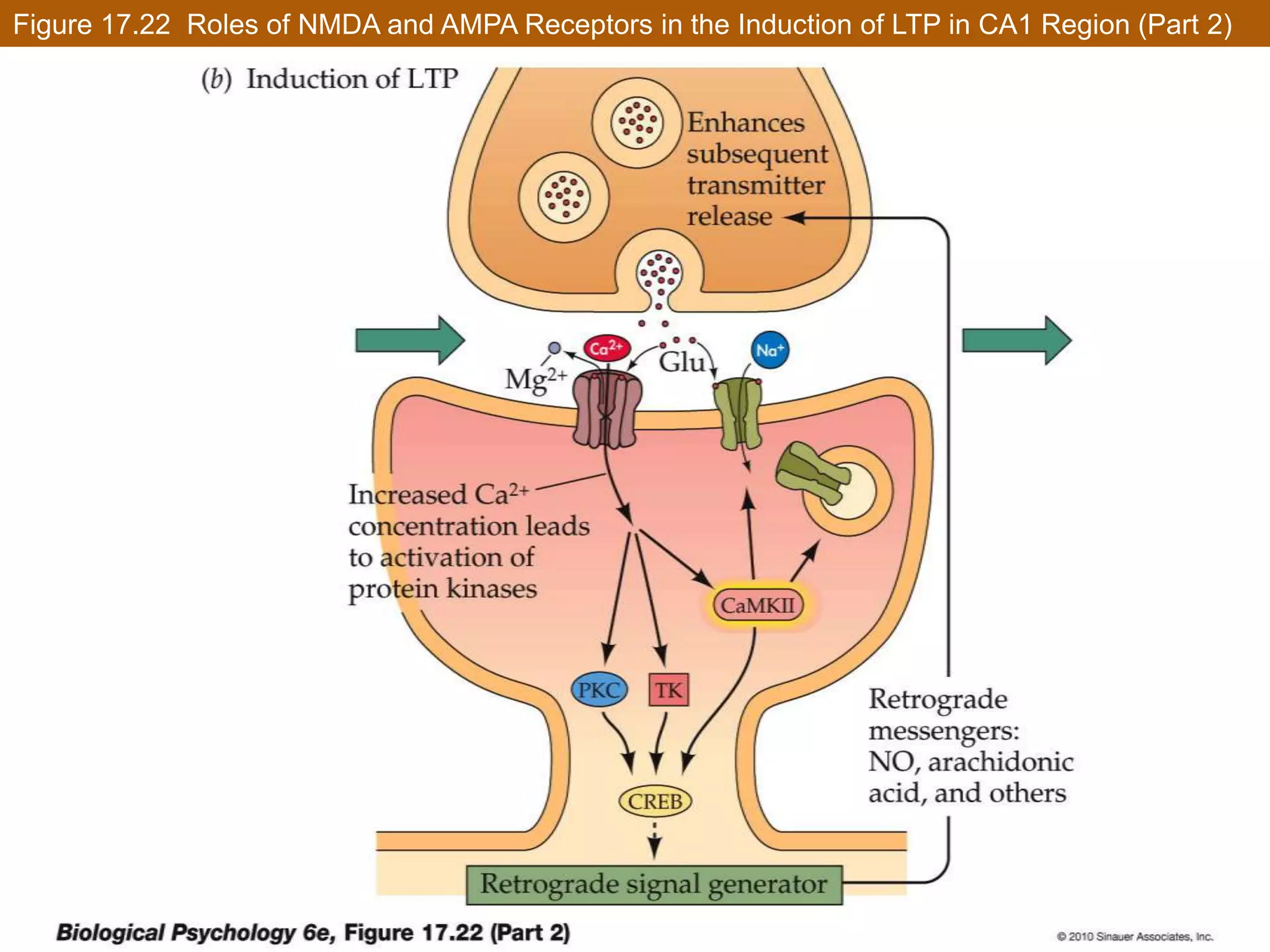
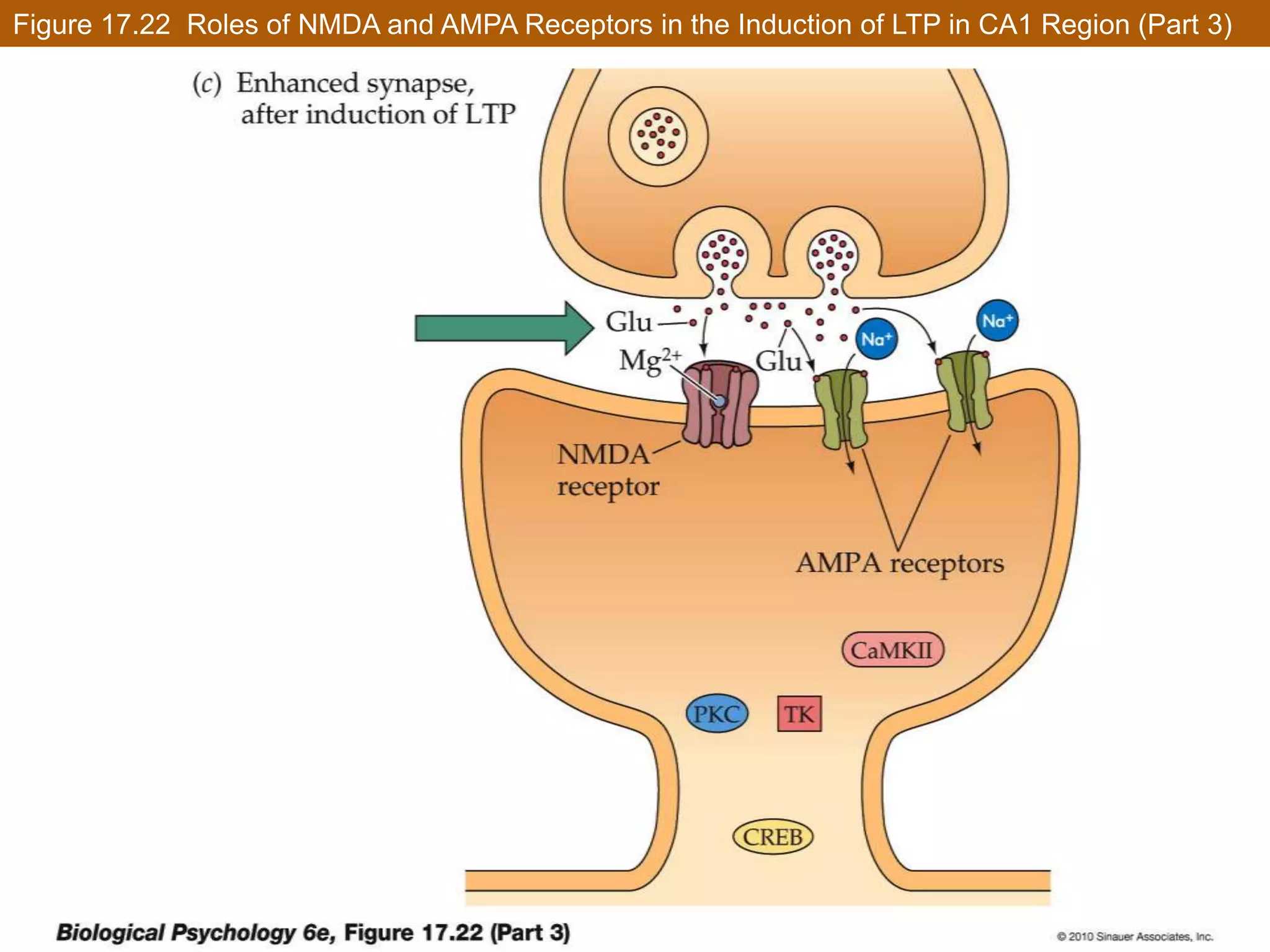
This document discusses neuronal plasticity, which refers to the brain's ability to change and adapt as a result of experience. It describes various types and mechanisms of neuroplasticity, including enhancement of existing connections through synapse development and strengthening, and formation of new connections through unmasking of silent synapses and axon sprouting. It also discusses cortical remapping in deaf individuals and long-term potentiation as the basis of neuronal plasticity. Synaptic plasticity can be measured in the hippocampus, where strong stimulation leads to calcium influx and activation of protein kinases that strengthen synapses.