Embed presentation
Downloaded 24 times

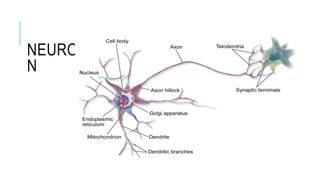
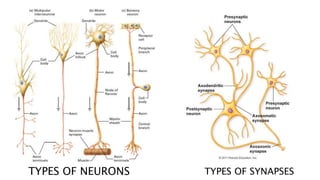
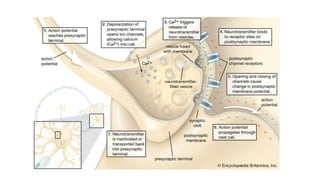
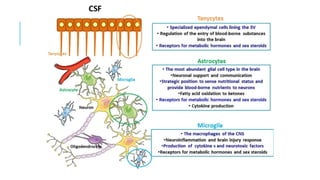
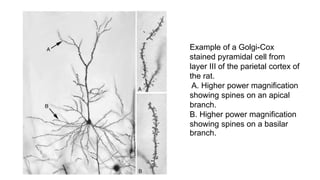





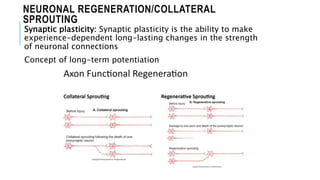

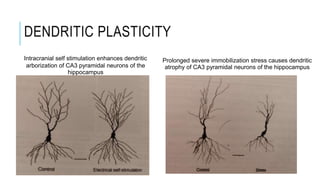
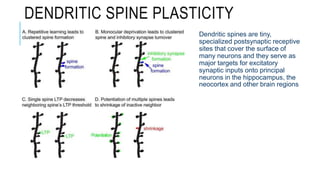





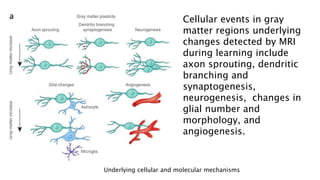
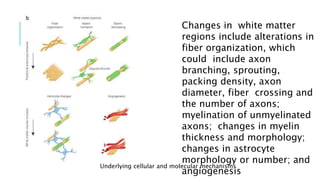



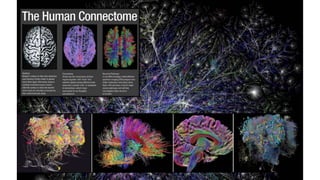
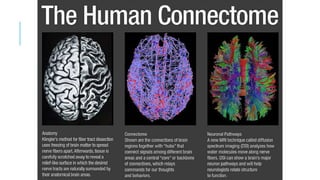



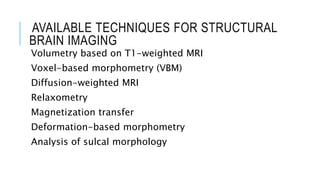
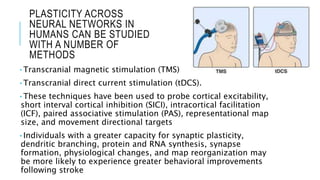










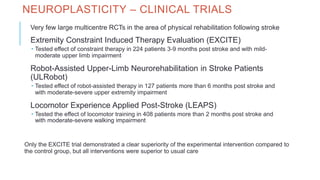




1. Neuroplasticity refers to the brain's ability to change and reorganize itself in response to experience or injury. It allows the brain to compensate for damage and to adjust its activity in response to new situations or information. 2. Several mechanisms underlie neuroplasticity including neuronal regeneration, synaptic plasticity, neurogenesis, gliogenesis, dendritic remodeling, and functional reorganization through processes like vicariation. 3. Neuroplasticity can be measured at the cellular level through changes in synapses and at the neural network level through reorganization of maps. Imaging techniques like MRI can also measure plastic changes in gray and white matter.














































