This document summarizes key concepts from a psychology unit on memory, including:
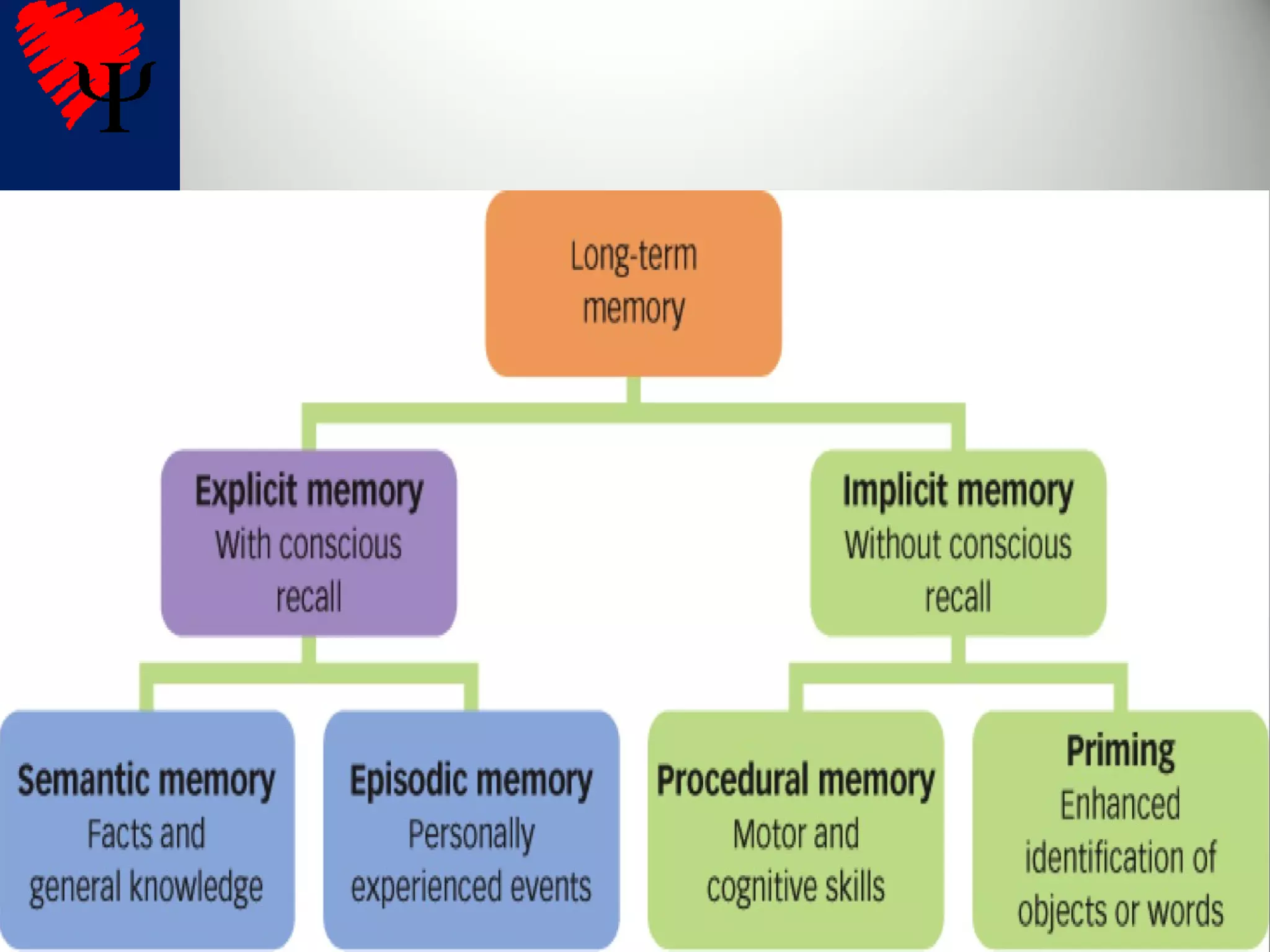
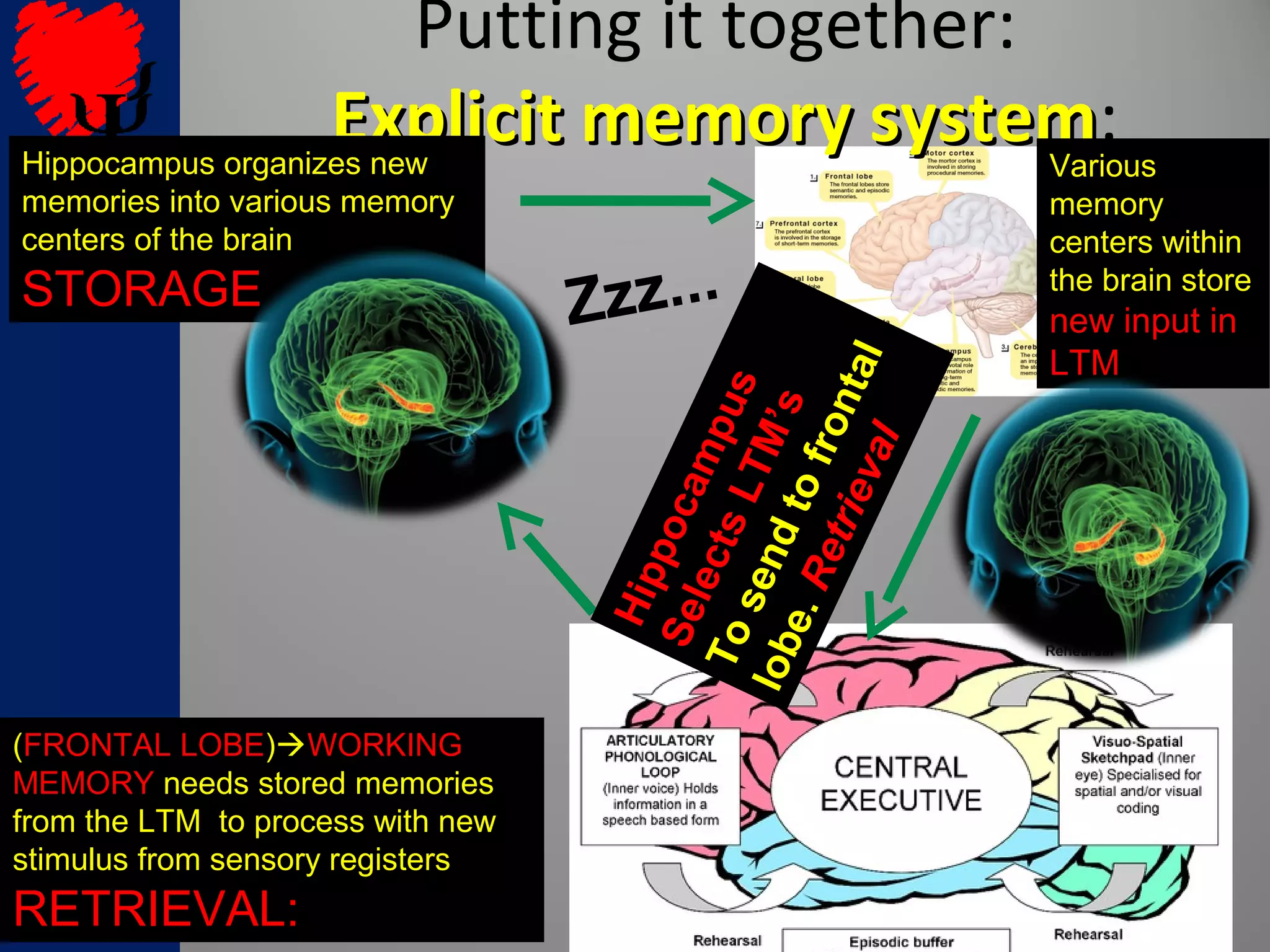
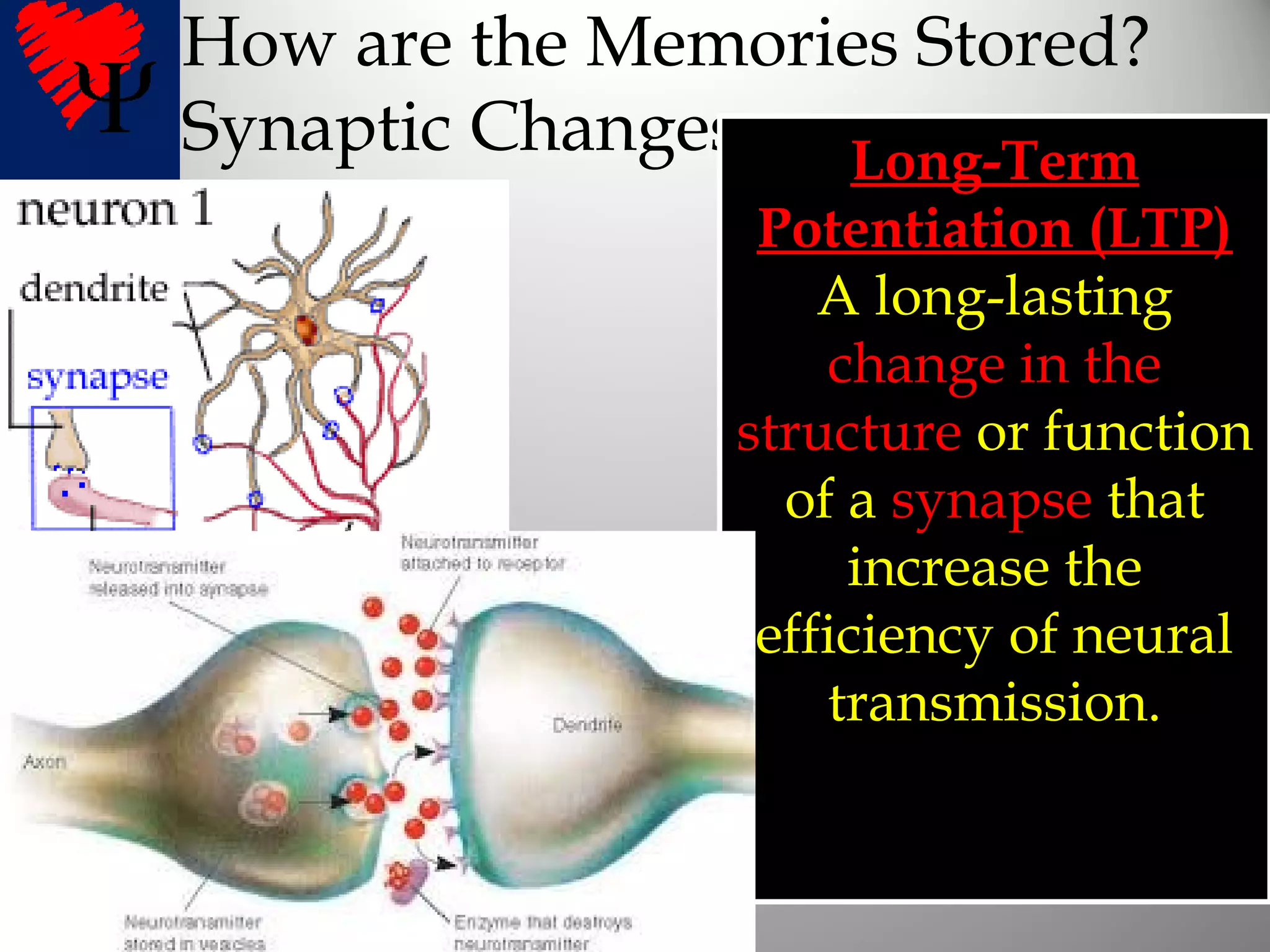
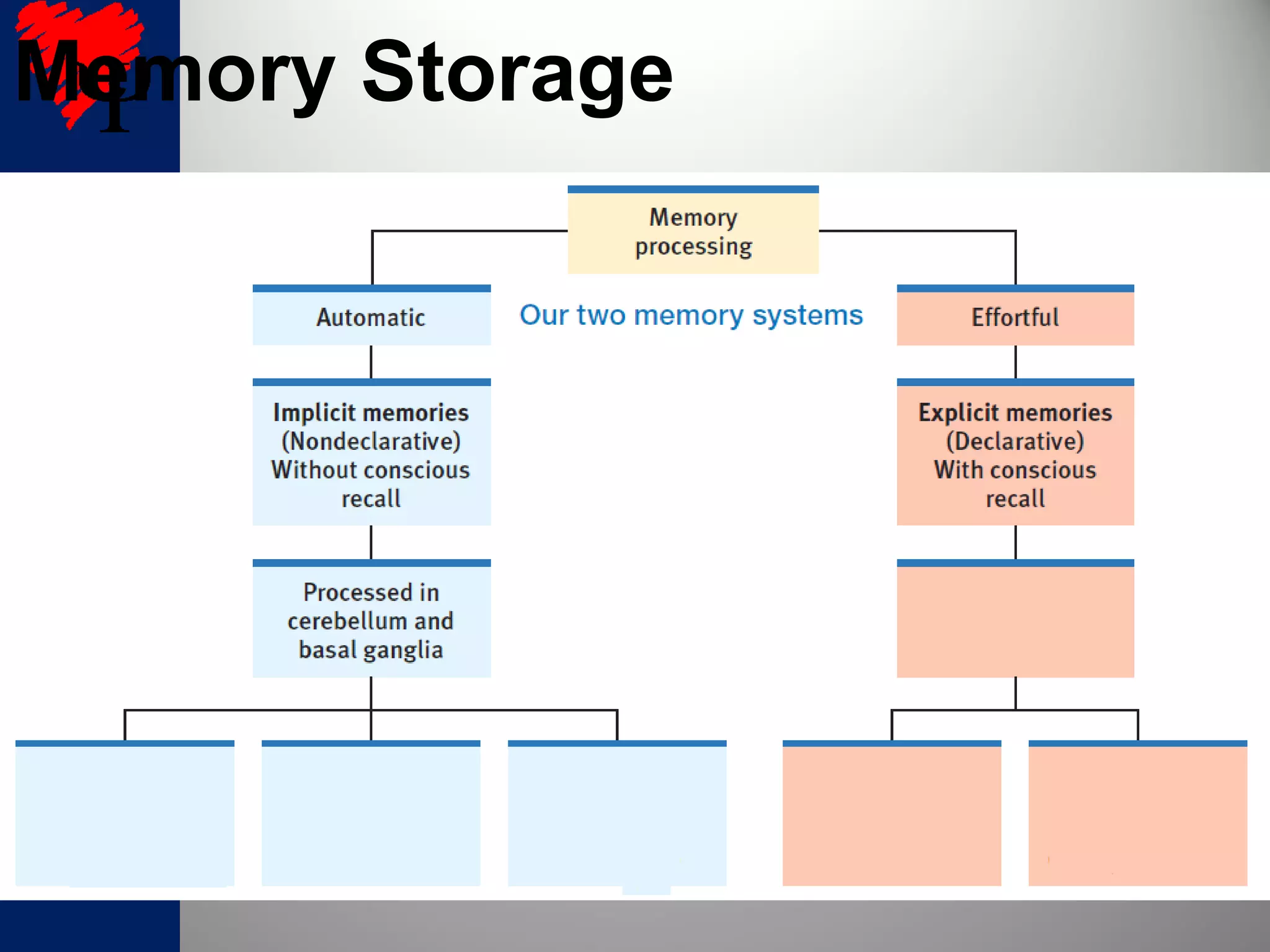
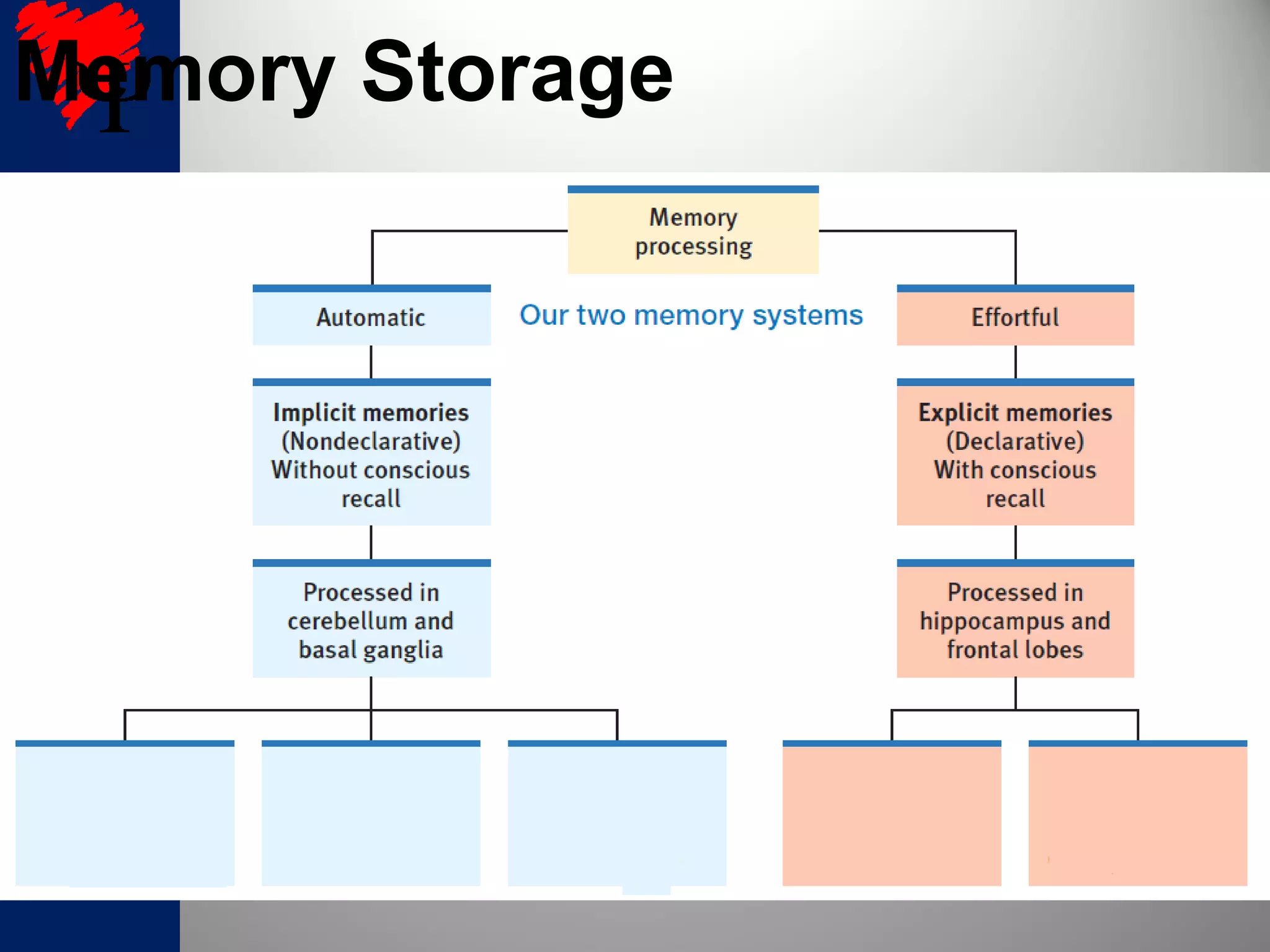
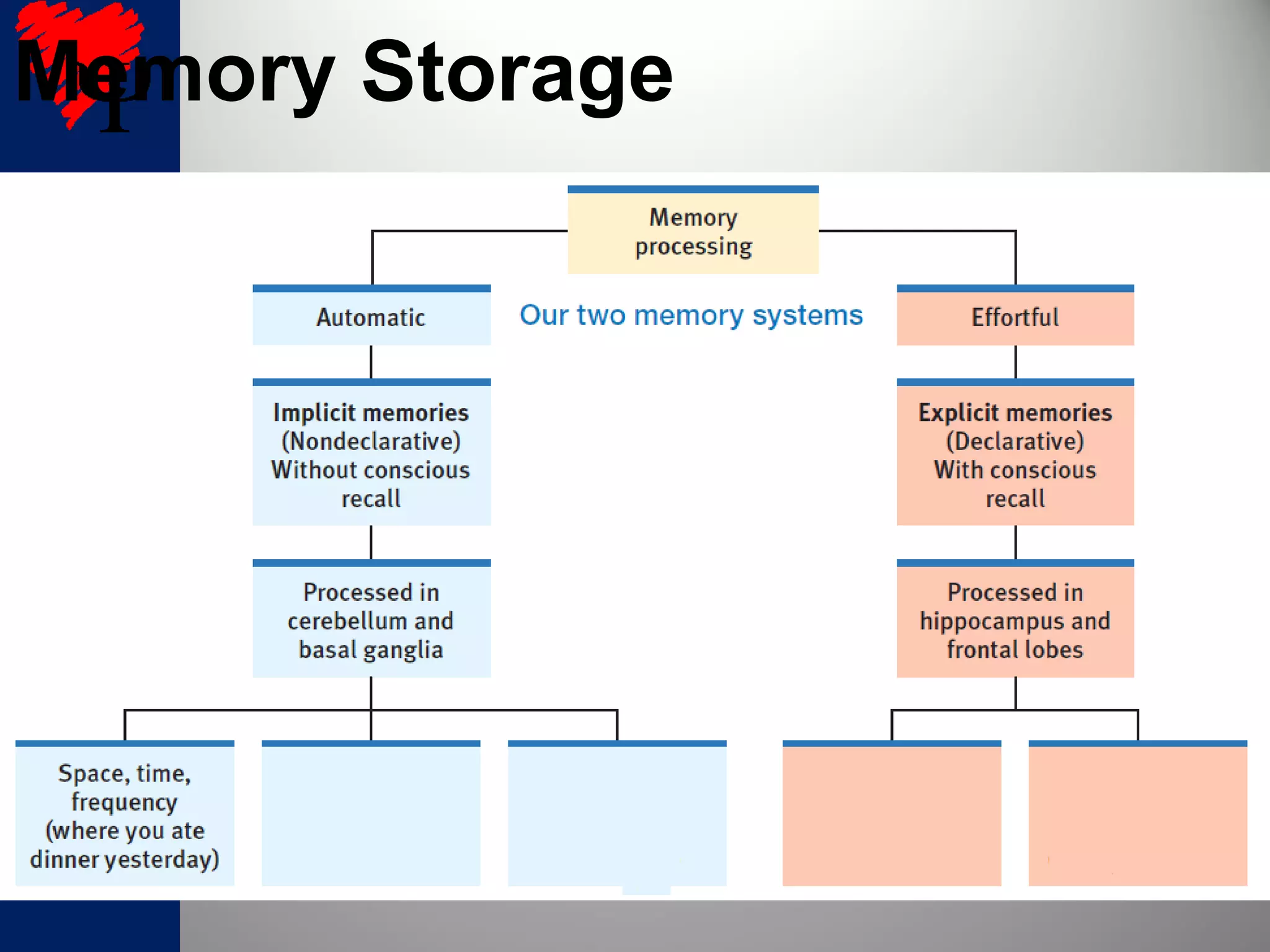
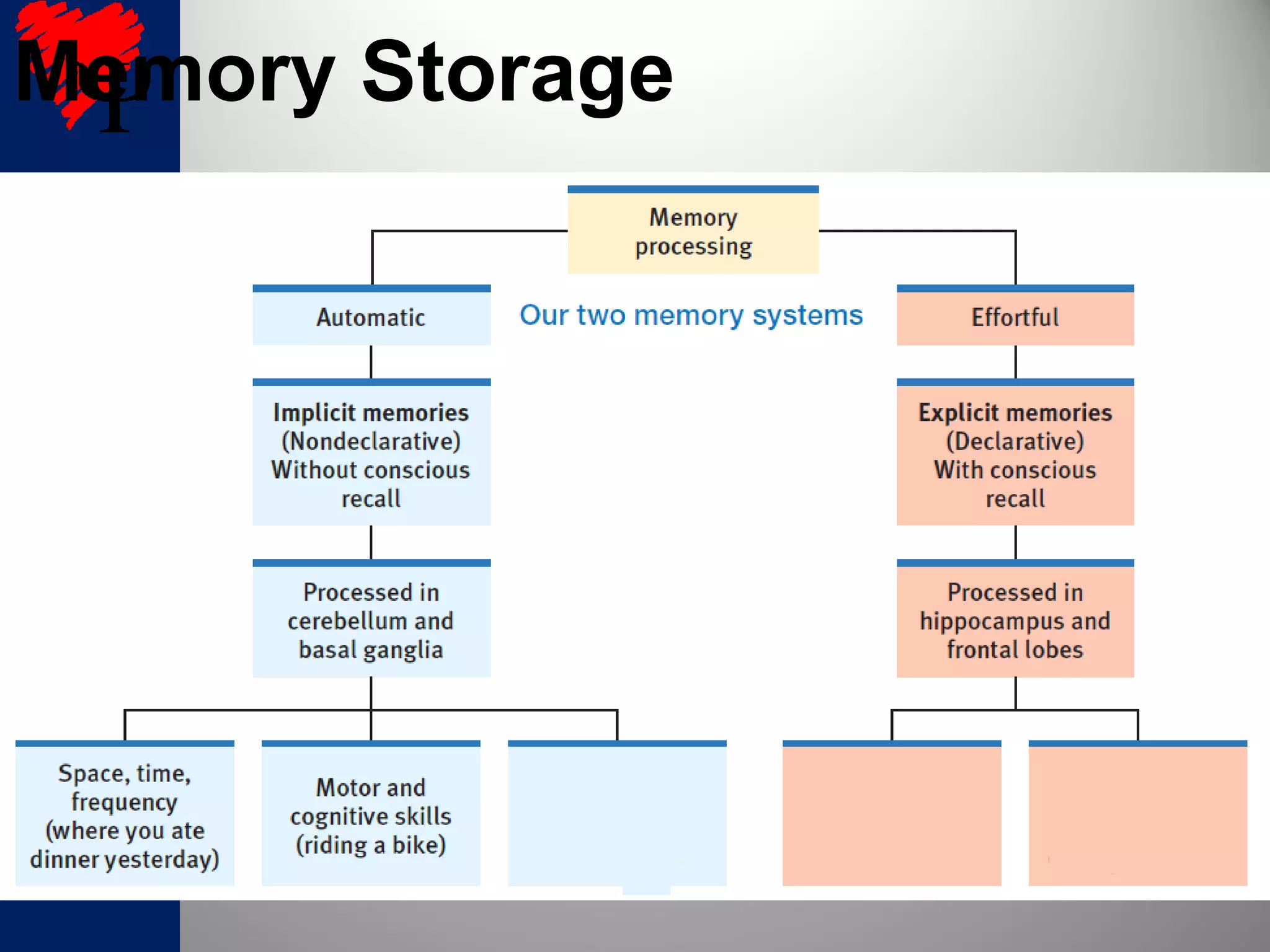
1. Long-term memories have an unlimited capacity and are stored across interconnected brain networks rather than single locations. The hippocampus organizes new memories and stores them in various brain centers.
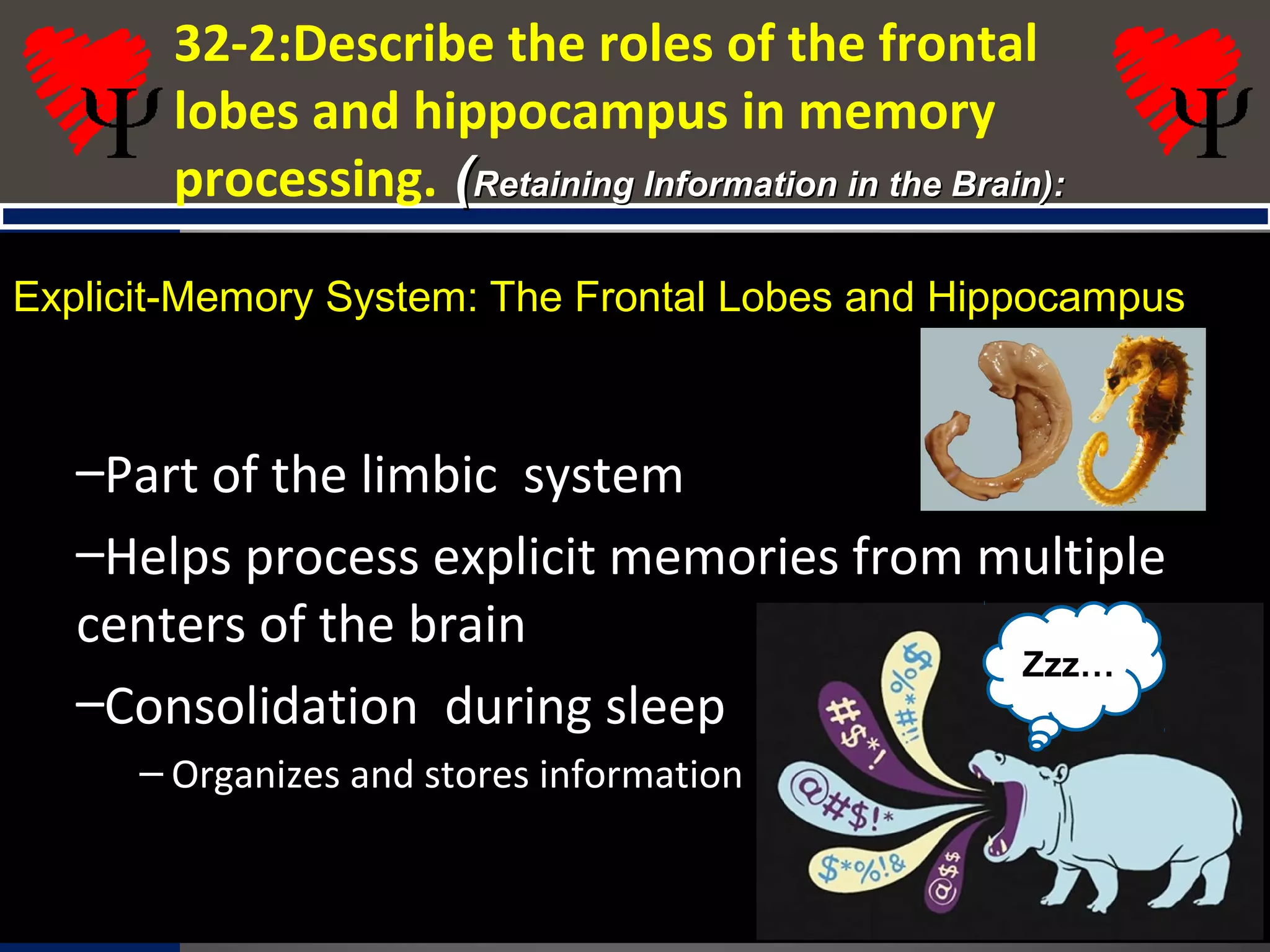
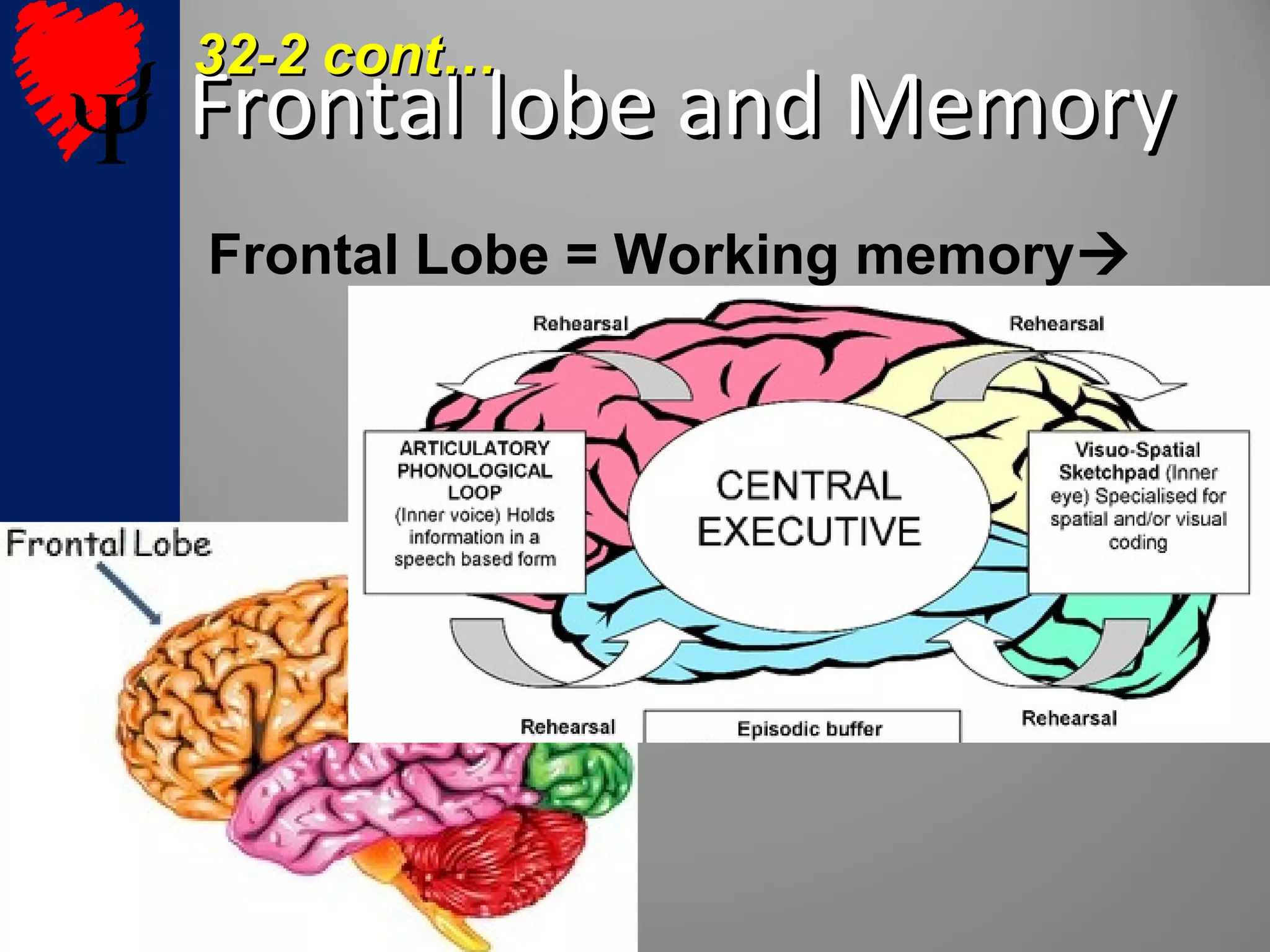
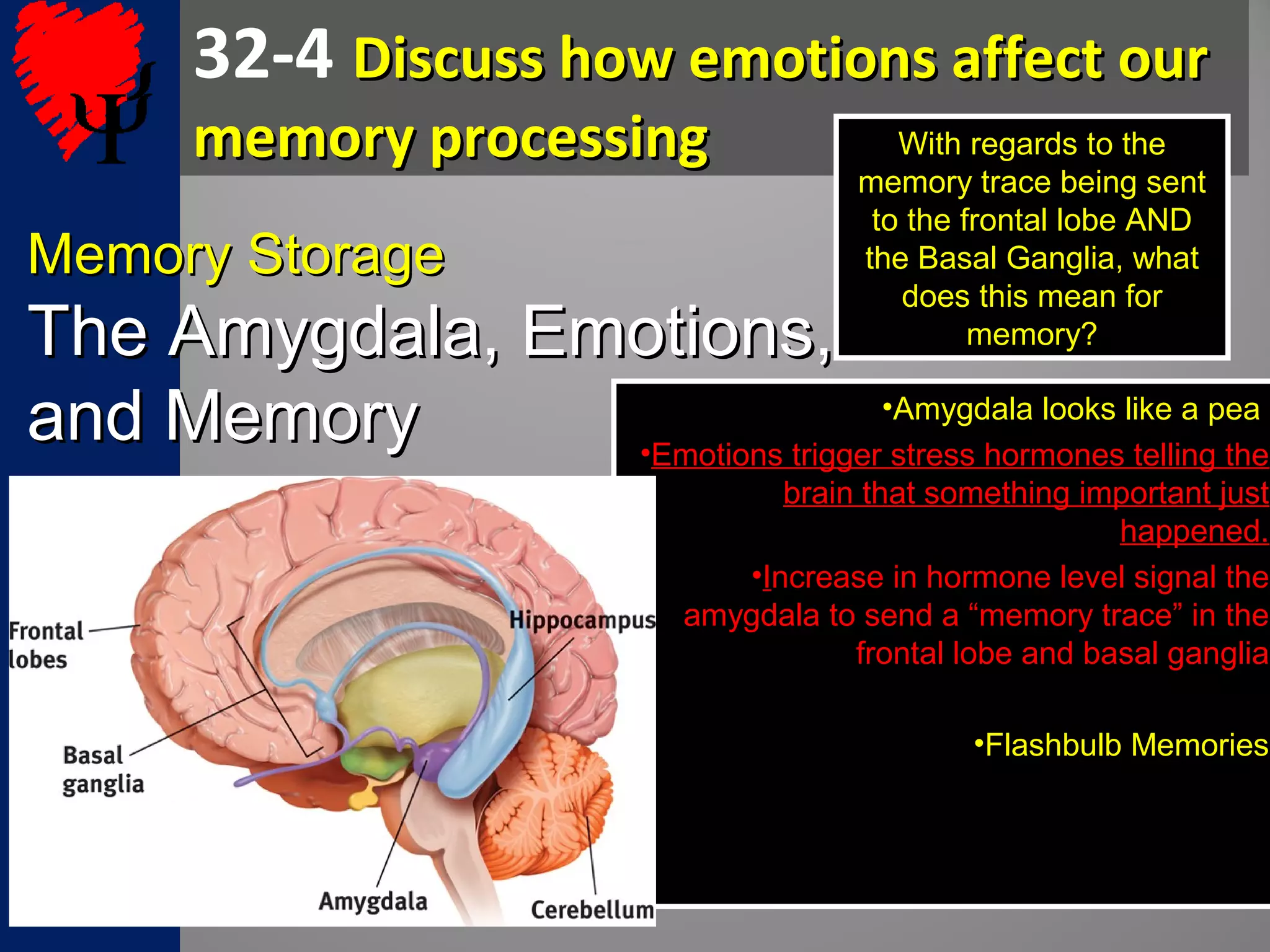
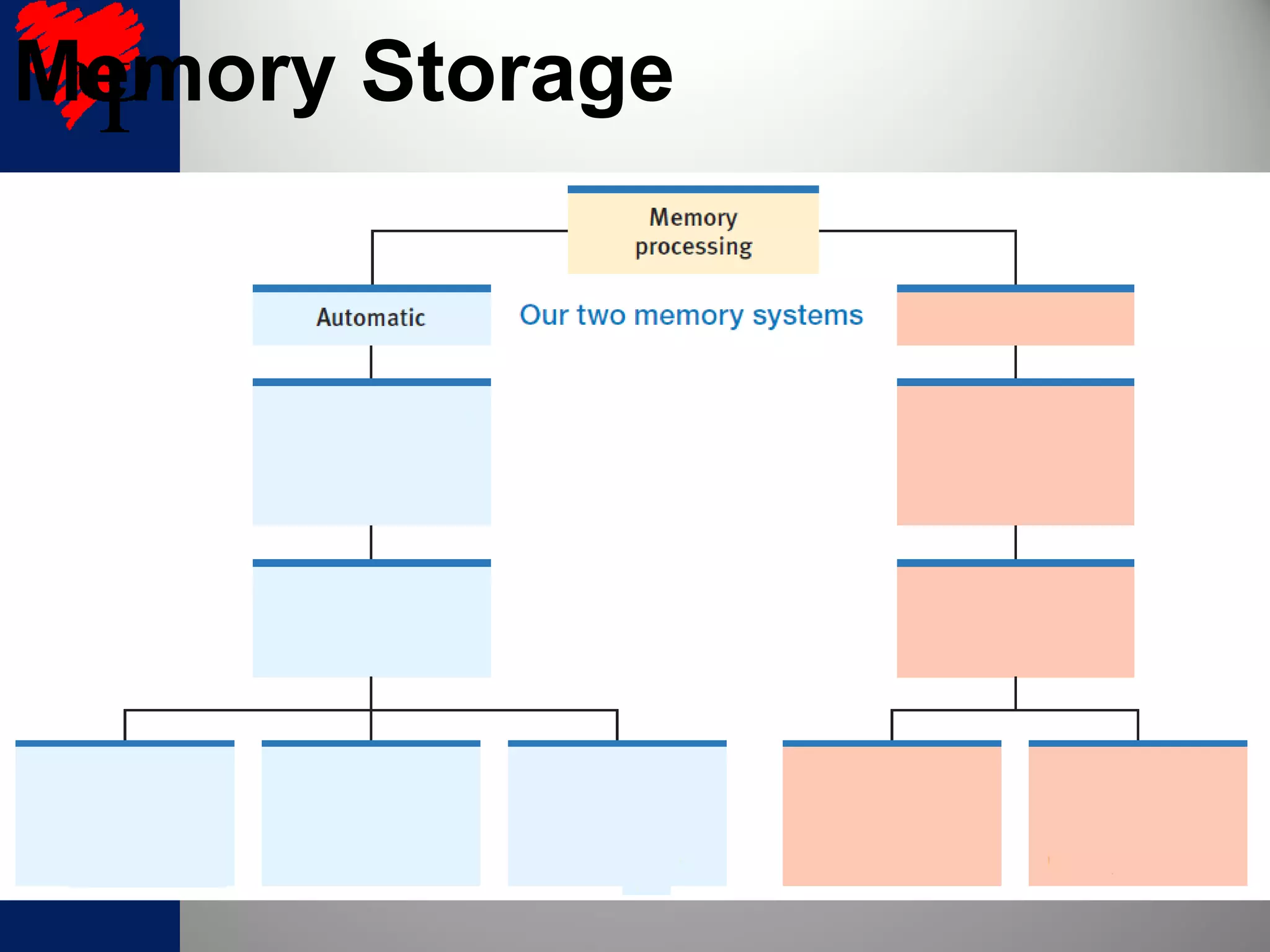
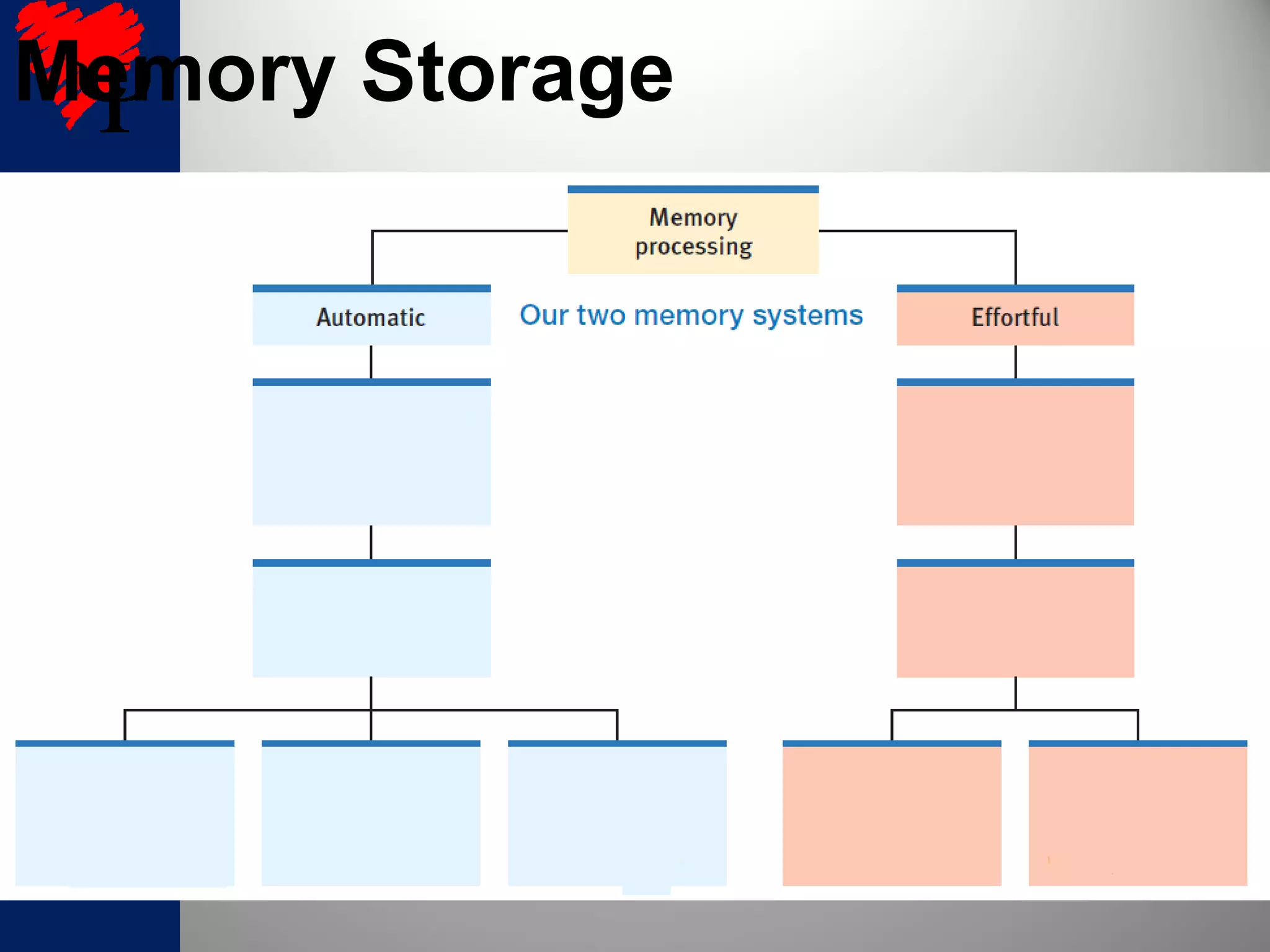
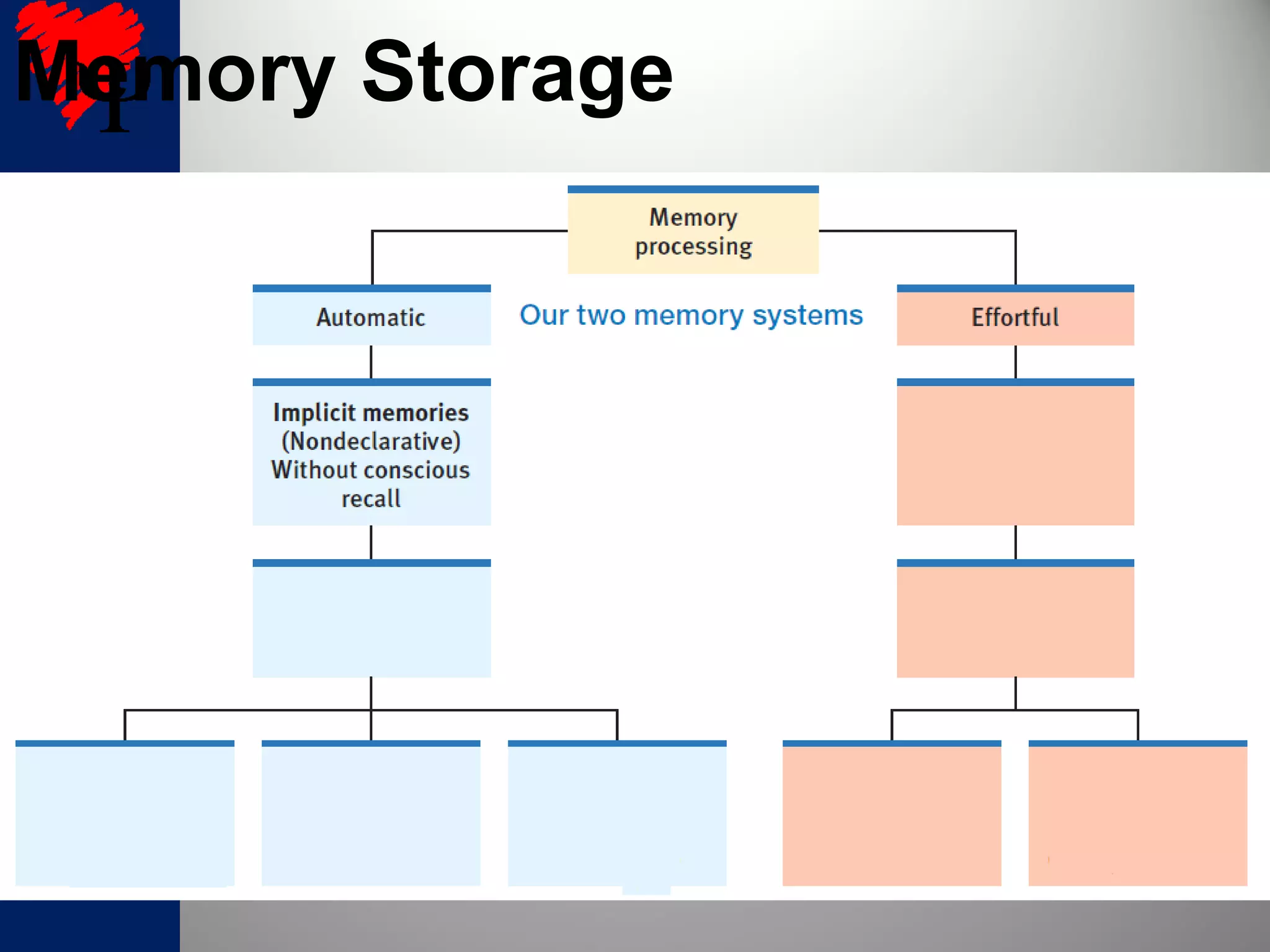
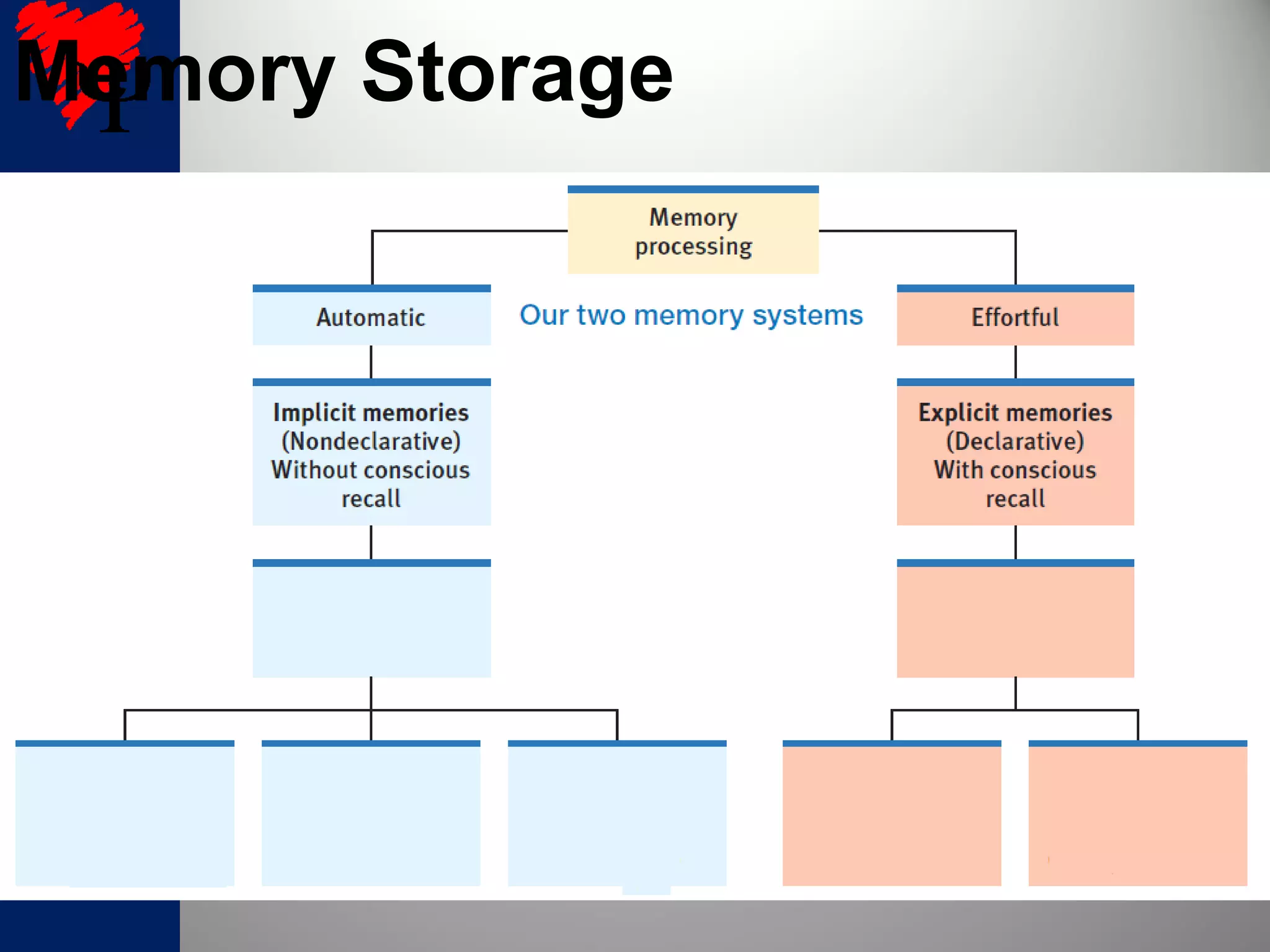
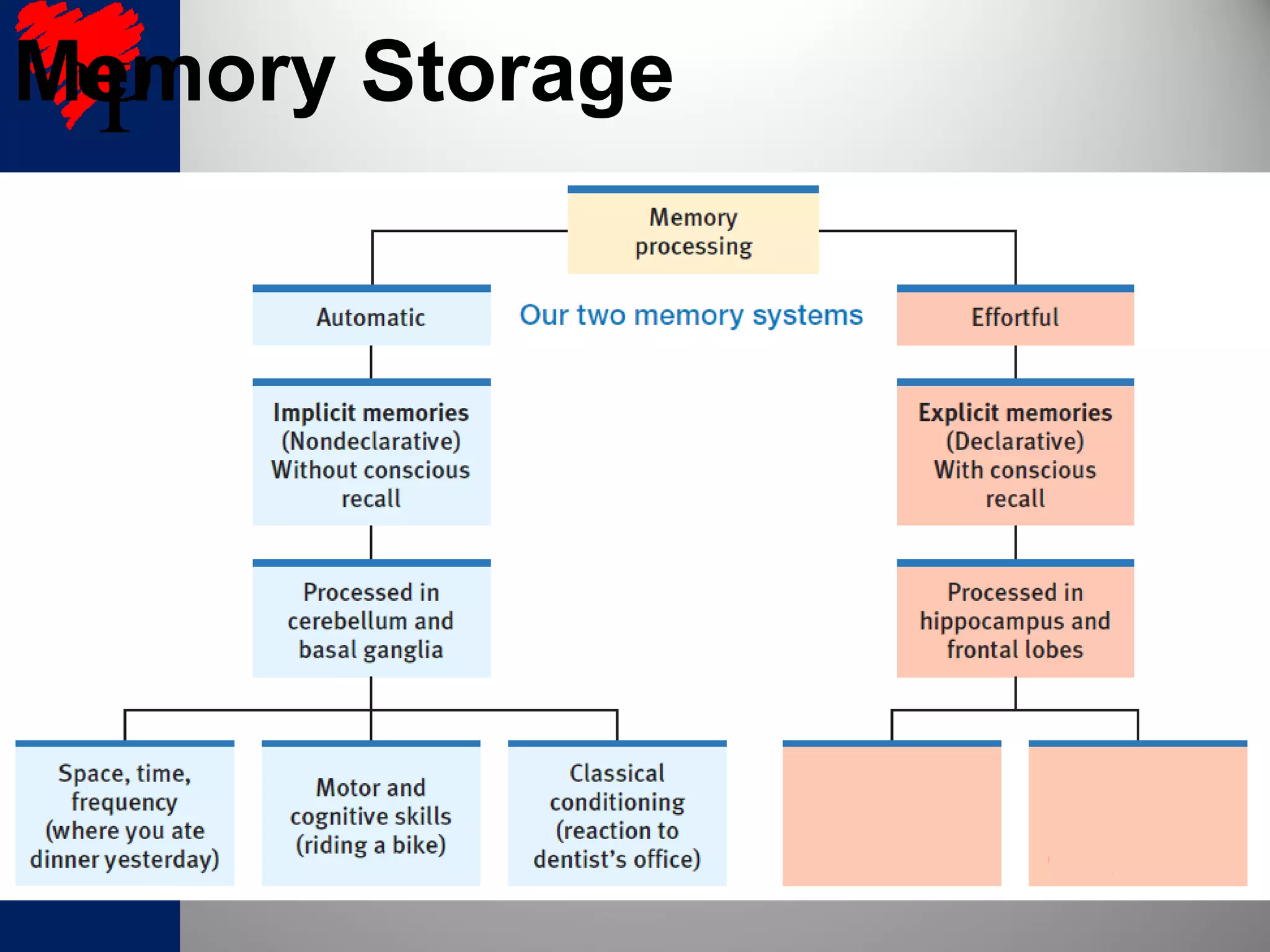
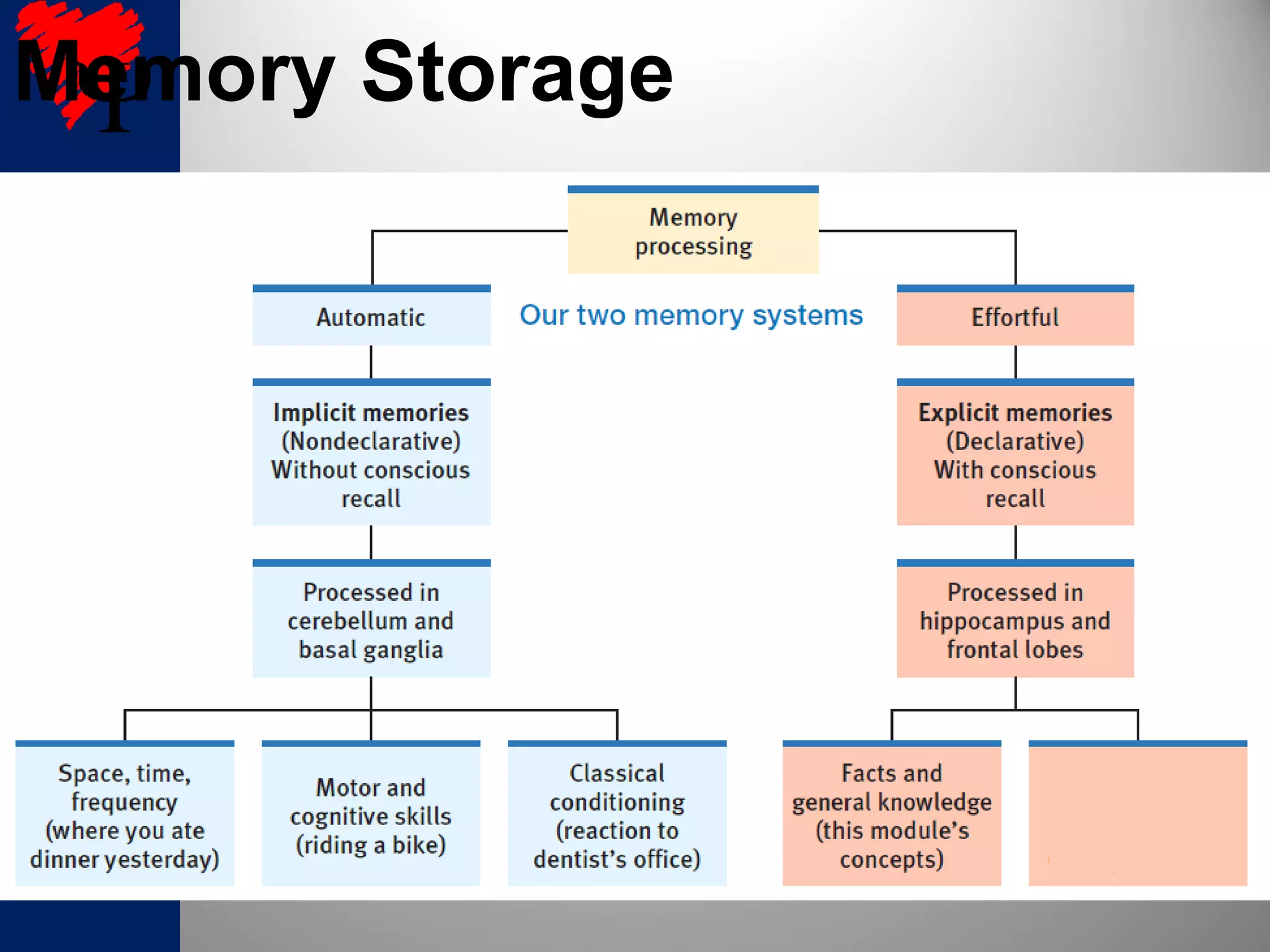
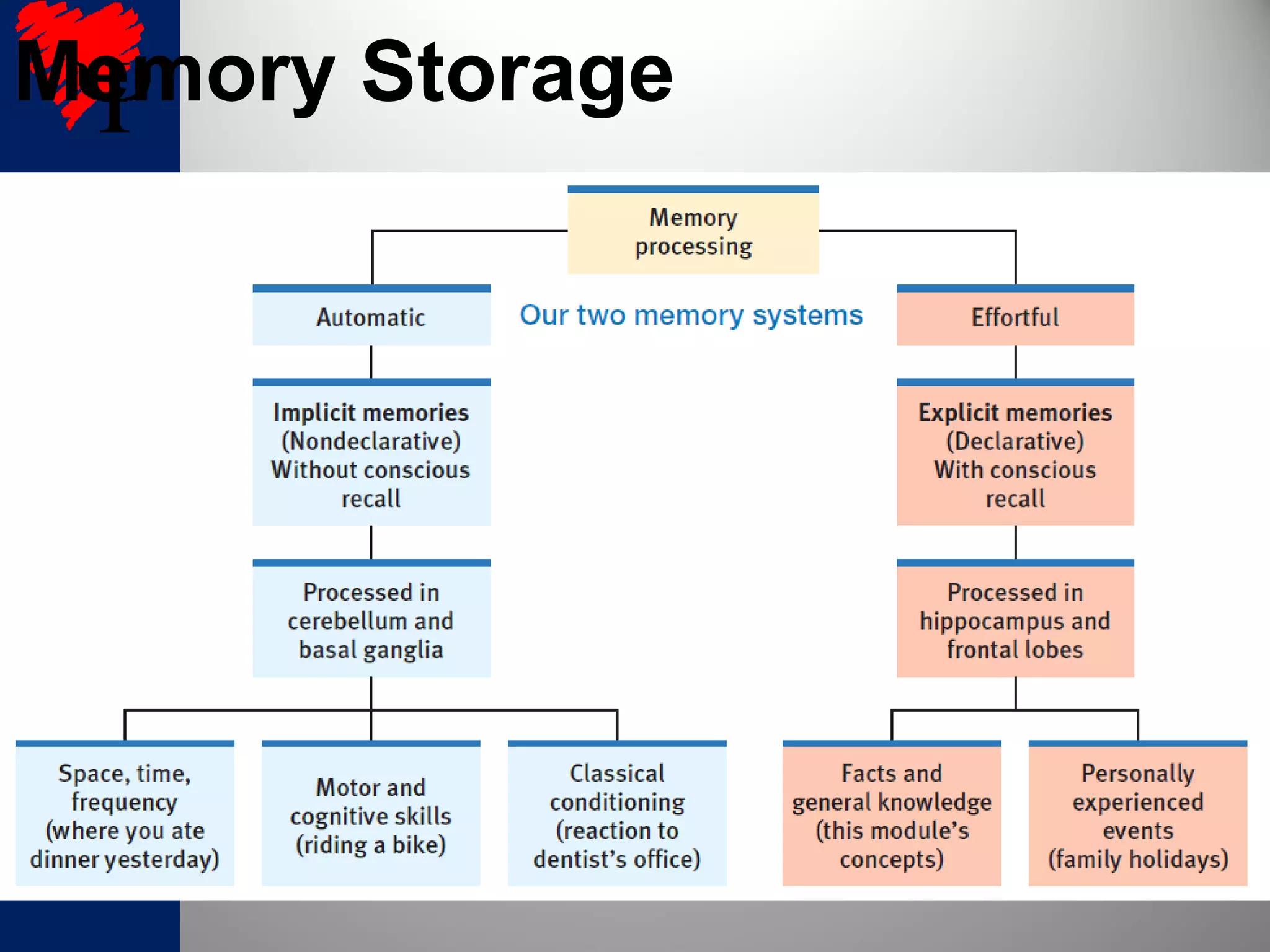
2. The frontal lobes support working memory while the hippocampus processes explicit memories by consolidating short-term memories into long-term storage during sleep. Damage to the hippocampus impairs new explicit memory formation.
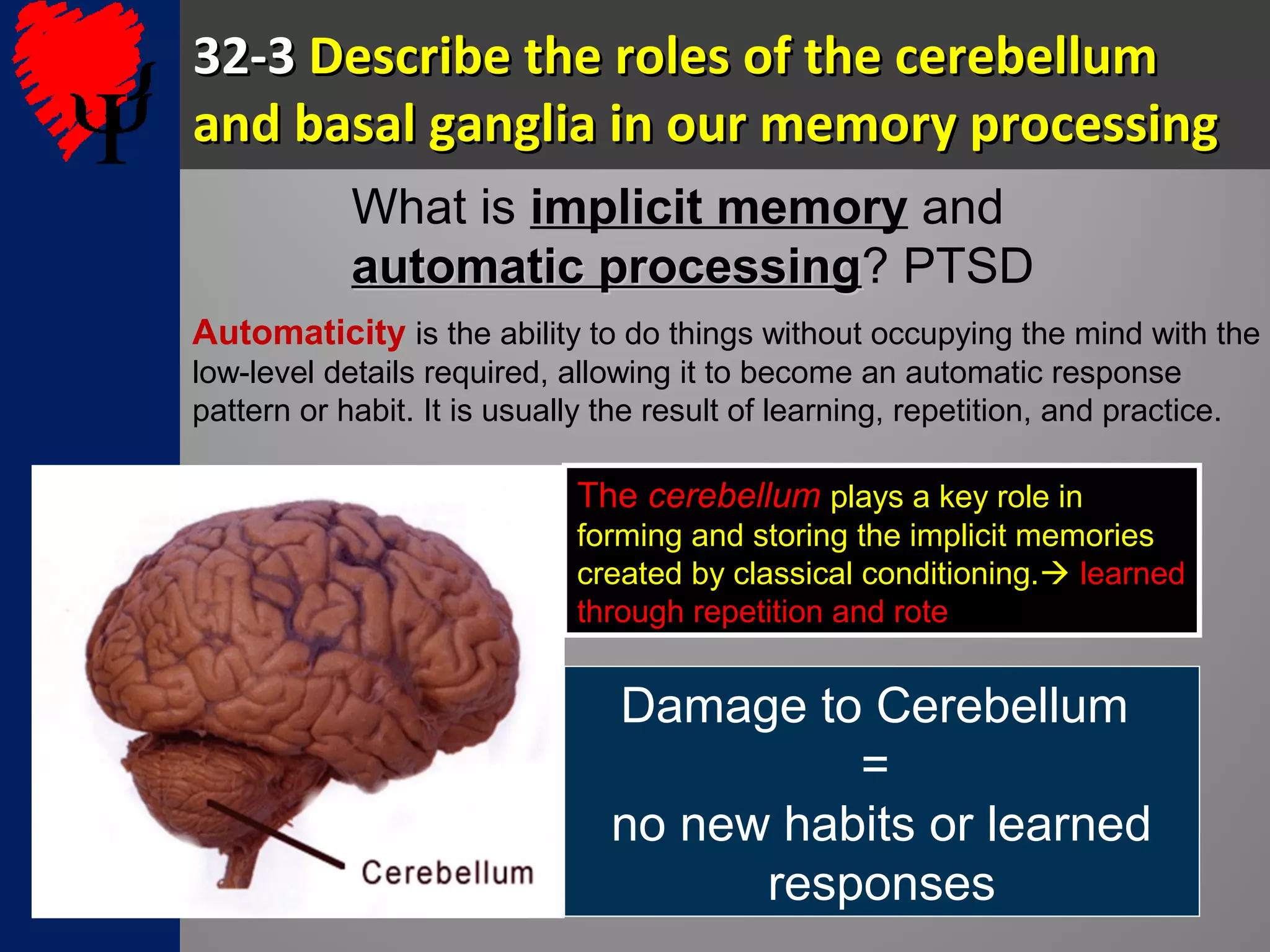
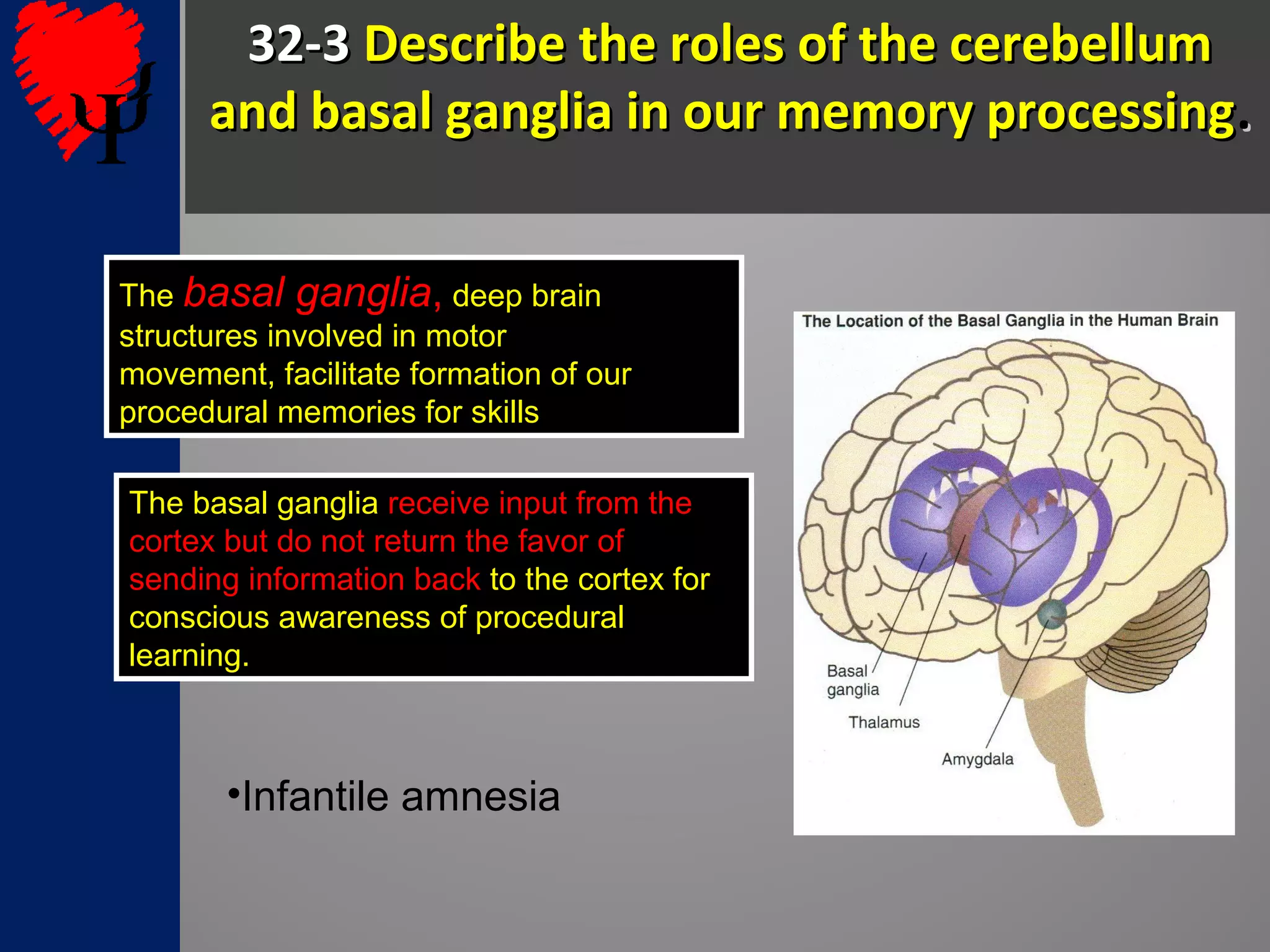
3. The cerebellum and basal ganglia support implicit memory and automatic processing through classical conditioning and procedural memory formation. Damage to the cerebellum inhibits new habit formation.