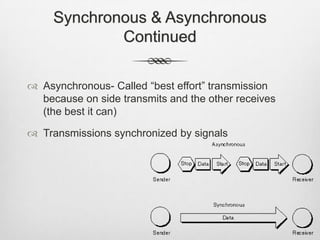
The document defines key networking concepts including clients, servers, hosts, mainframes, grid computing, Ethernet, peer-to-peer networks, LANs, WANs, VLANs, the internet, intranets, extranets, VPNs, routers, switches, hubs, optical fiber, cables, WiFi, WiMax, Bluetooth, network operating systems, storage area networks, RAID, network administration, access control, authentication, authorization, accountability, computer security, physical security, network policies, ethics, protocols, synchronous and asynchronous communication, remote access, bandwidth, broadband, and bit rates.