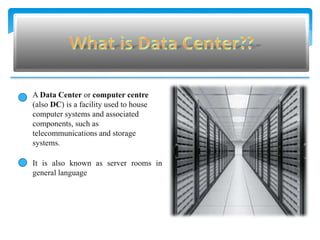
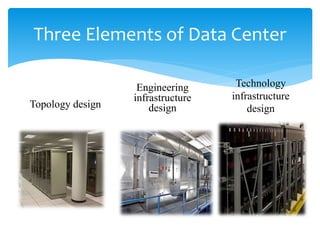
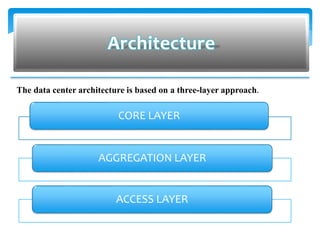
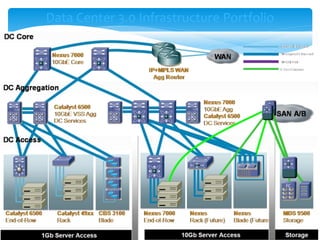
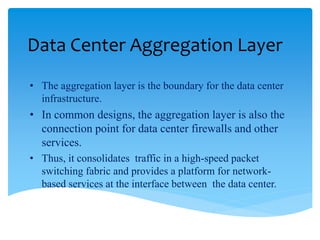
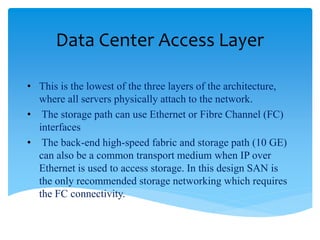
This document summarizes key aspects of data centers, including their history, components, requirements, physical infrastructure, and modular approaches. A data center houses computer systems and associated equipment to provide data storage and Internet connectivity solutions. It discusses the core, aggregation, and access layers that make up their physical network architecture. Modern data centers require careful facility design for layout, power, cooling, and security, as well as robust system and service management infrastructures. Modular and containerized approaches provide scalable and portable alternatives to traditional building-based data center facilities.