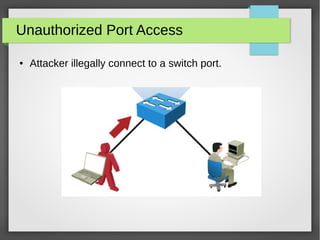
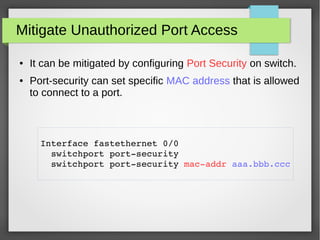
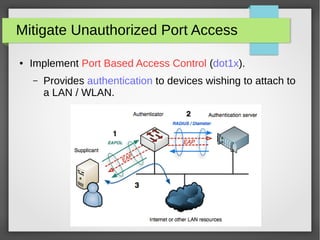
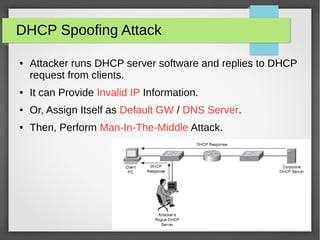
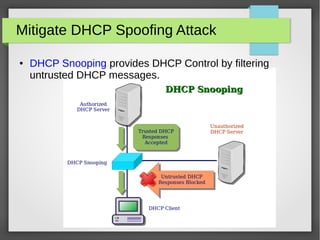
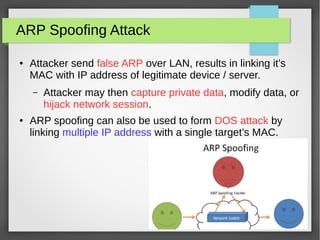
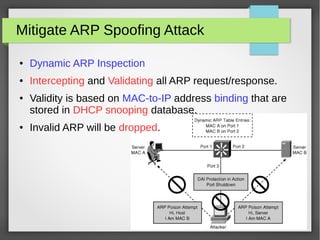
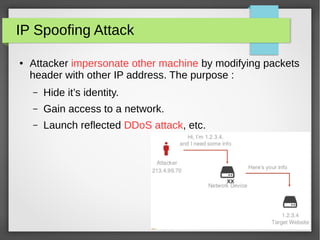
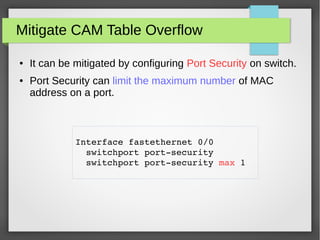
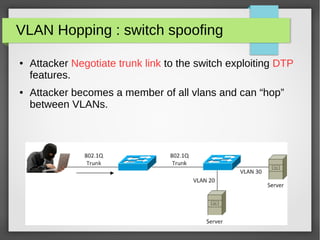
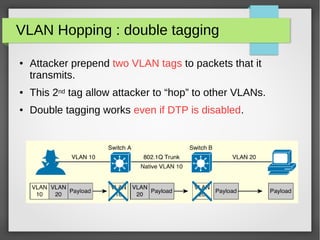
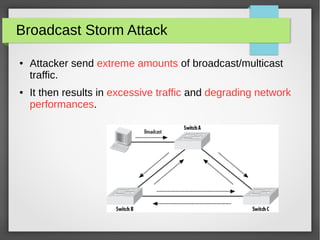
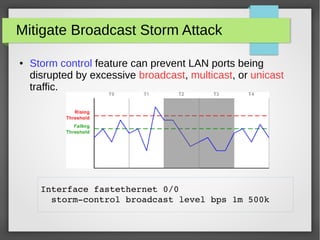
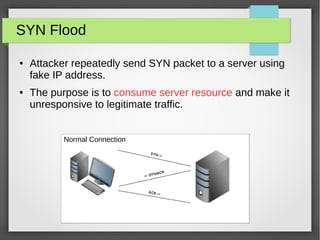
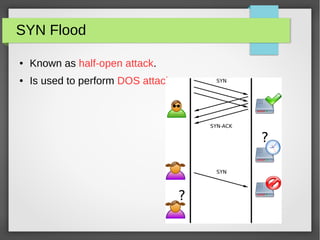
The document discusses various network attacks such as unauthorized port access, DHCP spoofing, DHCP starvation, ARP spoofing, IP spoofing, CAM table overflows, VLAN hopping, spanning tree attacks, broadcast storms, routing protocol attacks, and SYN floods. It also provides recommendations to mitigate each attack such as configuring port security, DHCP snooping, dynamic ARP inspection, IP source guard, storm control, BPDU guard, root guard, authentication for routing protocols, and firewalls/IDS systems.