Embed presentation
Downloaded 15 times



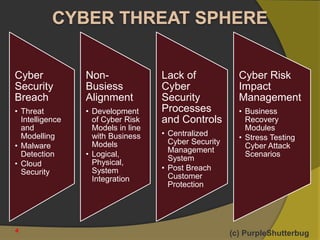

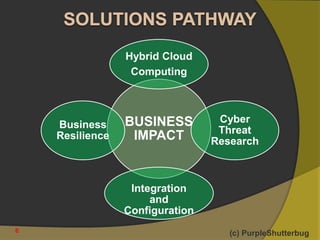

This document discusses various topics related to cyber security including: 1) SIEM, technical cyber security architecture, IT environment phasing, deep packet inspection tools, and disaster recovery and business continuity plans. 2) Implementing a cyber risk governance grid within an organization as a central breach management tool and compliance-centric cyber risk mitigation strategies. 3) Key areas related to cyber security breaches, threats, malware detection, cloud security, cyber risk impact management, and business recovery.





