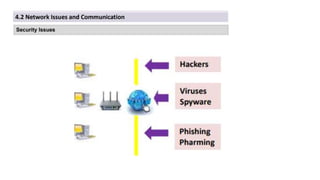
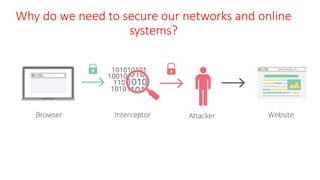
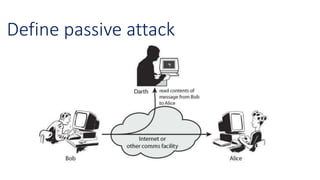
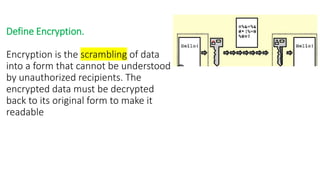
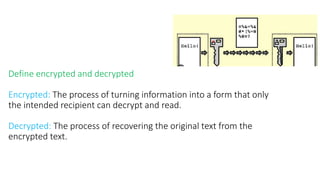
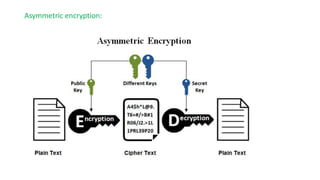
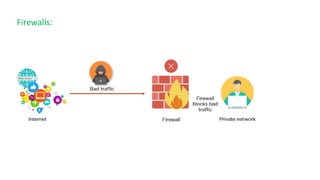
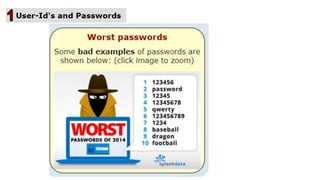
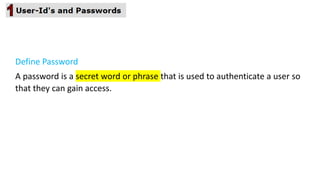
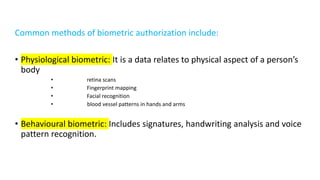
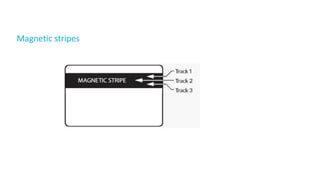
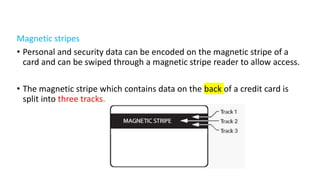
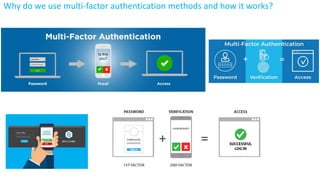
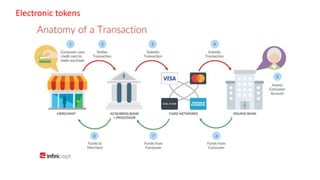
The document discusses the importance of securing computer networks against data interception and theft, highlighting concepts such as types of attacks, encryption methods, and password security. It details various network protection strategies including firewalls, multi-factor authentication, and biometric verification. Additionally, it covers the functionality of smart cards, electronic tokens, and the concept of zero login for enhanced security.