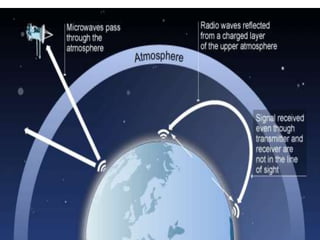
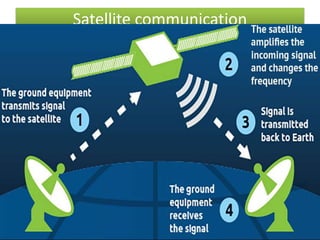
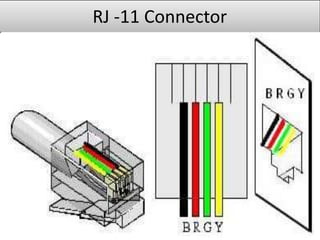
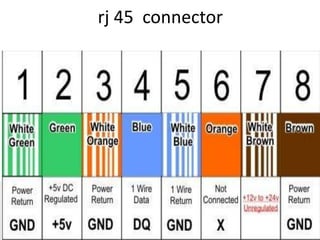
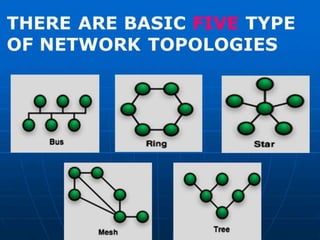
This document provides information on various topics related to wireless networking and networking devices. It discusses wireless networks and their advantages like mobility and easy installation. It also mentions applications of wireless networking like QR codes and microwave transmission. Concepts discussed include line of sight transmission, uni-directional communication, and how wireless networks rely on devices like routers, switches, and satellites to transmit data.