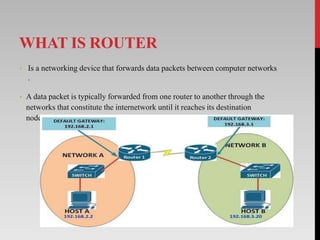
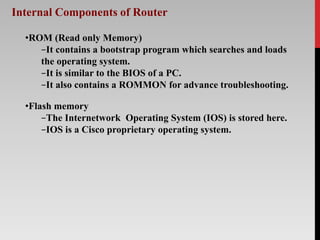
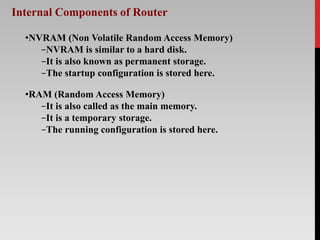
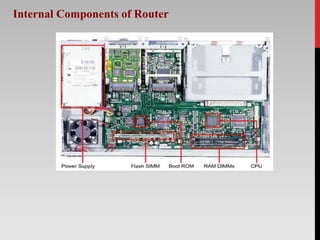
The document outlines the functions, types, and internal components of routers, emphasizing their role in forwarding data packets between networks. It categorizes routers into hardware and software types, as well as specific types like core, edge, and wireless routers, detailing their respective functions and purposes. Additionally, the document touches on Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) and mentions notable manufacturers such as Cisco and TP-Link.