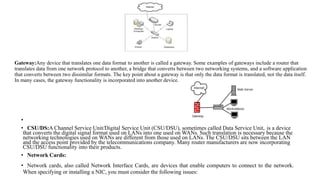
The document discusses various networking devices and their functions:
- Hubs broadcast messages to all connected devices, using more bandwidth than switches. Switches only send messages to the targeted device.
- Bridges divide larger networks and manage data flow between segments by examining MAC addresses.
- Routers route data between network segments by reading packet headers to determine destinations.
- Gateways translate between different data formats but not the data itself.
- Other devices discussed include wireless access points, modems, firewalls, network interface cards, and devices for specific media like fiber optics.