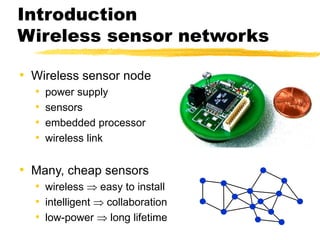
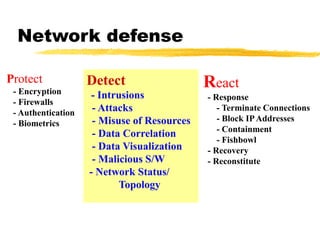
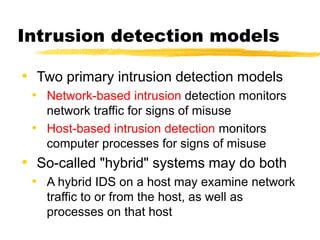
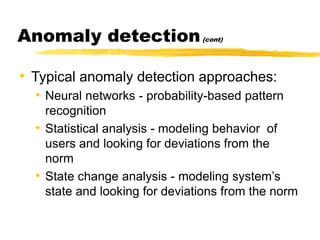
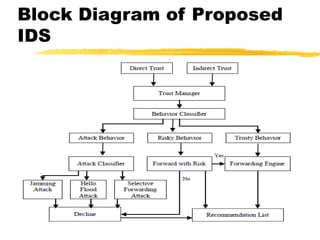
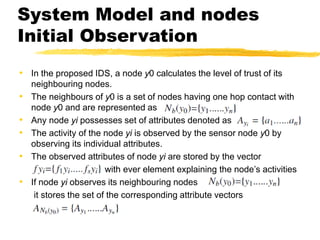
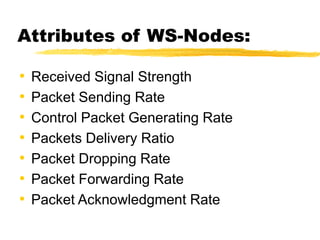
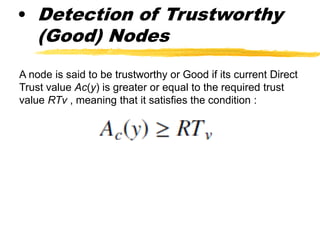
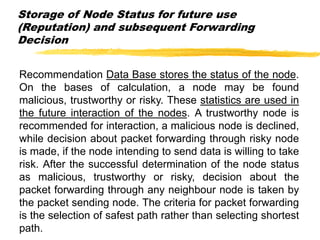
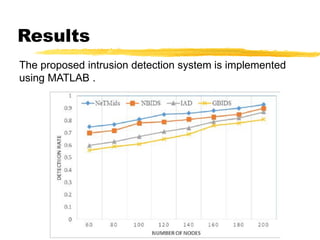
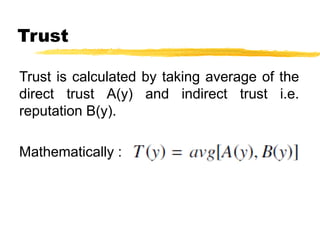The document presents a neighbor node trust-based intrusion detection system (IDS) for wireless sensor networks (WSNs) that utilizes trust calculations to classify neighboring nodes as trustworthy, risky, or malicious. It effectively detects attacks such as hello flood, jamming, and selective forwarding by analyzing network statistics and node behaviors. The proposed system includes a trust manager, behavior classifier, and a recommendation database to aid in secure packet forwarding decisions.