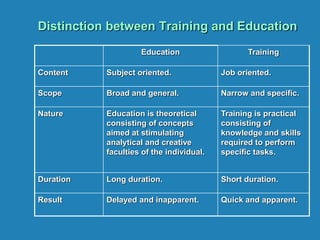
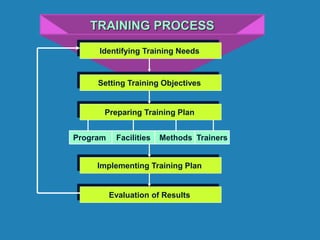
The document outlines the importance and distinctions between training and development in the workplace, emphasizing that training involves specific skill enhancement for current job performance, while development focuses on long-term personal and professional growth. It details various methods for identifying training needs and describes both on-the-job and off-the-job training techniques. Key components of effective training processes include thorough analysis of organizational needs, task requirements, and individual performance to design targeted training interventions.