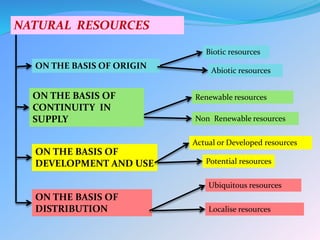
Resources can be classified as natural, human-made, or human. Natural resources come from nature and include biotic resources like plants and animals as well as abiotic resources like air and water. They can also be classified as renewable like solar energy or non-renewable like fossil fuels. Human-made resources are those created through human technology and skill while human resources refers to people. It is important to conserve resources through sustainable use and development to meet current needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs.