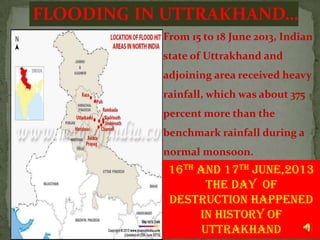
The document is a presentation about the natural disaster of flooding in Uttarakhand, India in 2013. It provides an overview of Uttarakhand, describes the heavy rainfall and flooding that occurred in June 2013 which caused widespread damage, and discusses the consequences including thousands of deaths and massive economic losses. It also outlines the large-scale rescue and relief operations conducted by the Indian military and disaster response teams and analyzes whether the disaster was due to natural or man-made causes such as construction projects and deforestation.